
Draw the square ABCD of area 9 square centimeters.
Answer
624.9k+ views
Hint: As the formula for finding the area of square is (s x s), that is \[{{\left( s \right)}^{2}}\]
Therefore, the side of this square will be equal to 3 centimeters because, (3 x 3) or \[{{\left( 3 \right)}^{2}}=9\] .
For making a right angle, we must first draw a semicircle, then where the semicircle cuts the line, we make another cut on the semicircle by putting the compass at the cut. Now we make two cuts by placing the compass at both the prior two cuts and then make a line which passes through the intersection.
Complete step-by-step answer:
For the first step, we need to draw a line measuring 3 centimeter.

Now, secondly, draw another line forming a right angle at point B, measuring 3 centimeters.
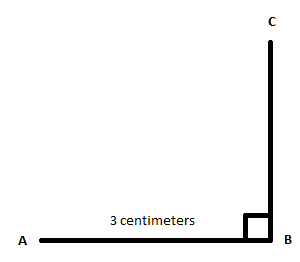
Thirdly, we need to draw one more line forming a right angle at point C, measuring 3 centimeters.
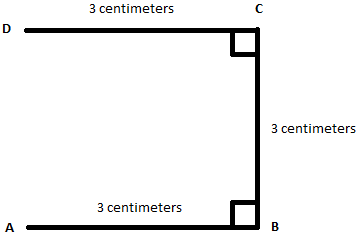
Lastly, we need to draw a line forming a right angle at point D, measuring 3 centimeters.
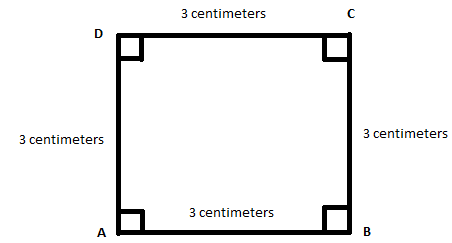
Now, let us calculate the area of this square ABCD,
Formula for the area of square = side x side
Area of the square ABCD = 3 x 3=9cm
Note:-
One must remember the formulas of the areas of some basic shapes such as rectangle, square, circle, triangle, rhombus, parallelogram, etc.
1. RECTANGLE: (l x b), i.e., (length x breadth), where length is the length of the rectangle and breadth is the breadth of the rectangle.
2. SQUARE: As mentioned above, (s x s) or \[{{\left( s \right)}^{2}}\], i.e., (side x side), where side refers to the length of one side of the square.
3. TRIANGLE - ( \[\dfrac{1}{2}base\times height\] ), where base refers to the length of the base of the triangle and height refers to the height of the triangle.
4. RHOMBUS - ( \[~\dfrac{1}{2}diagonal{{l}_{1}}\times diagonal{{l}_{2}}\] ), where diagonal1 refers to the length of a diagonal of the rhombus and diagonals 2 refers to the length of other diagonal of the rhombus.
5. PARALLELOGRAM: (b x h), i.e., (base x height), where base refers to the length of the base and height refers to the height of the rhombus.
6. CIRCLE- \[(~\pi {{r}^{2}})\]where \[{{\left( radius \right)}^{2}}\] refers to the square of the length of the radius of the square.
Therefore, the side of this square will be equal to 3 centimeters because, (3 x 3) or \[{{\left( 3 \right)}^{2}}=9\] .
For making a right angle, we must first draw a semicircle, then where the semicircle cuts the line, we make another cut on the semicircle by putting the compass at the cut. Now we make two cuts by placing the compass at both the prior two cuts and then make a line which passes through the intersection.
Complete step-by-step answer:
For the first step, we need to draw a line measuring 3 centimeter.

Now, secondly, draw another line forming a right angle at point B, measuring 3 centimeters.

Thirdly, we need to draw one more line forming a right angle at point C, measuring 3 centimeters.

Lastly, we need to draw a line forming a right angle at point D, measuring 3 centimeters.

Now, let us calculate the area of this square ABCD,
Formula for the area of square = side x side
Area of the square ABCD = 3 x 3=9cm
Note:-
One must remember the formulas of the areas of some basic shapes such as rectangle, square, circle, triangle, rhombus, parallelogram, etc.
1. RECTANGLE: (l x b), i.e., (length x breadth), where length is the length of the rectangle and breadth is the breadth of the rectangle.
2. SQUARE: As mentioned above, (s x s) or \[{{\left( s \right)}^{2}}\], i.e., (side x side), where side refers to the length of one side of the square.
3. TRIANGLE - ( \[\dfrac{1}{2}base\times height\] ), where base refers to the length of the base of the triangle and height refers to the height of the triangle.
4. RHOMBUS - ( \[~\dfrac{1}{2}diagonal{{l}_{1}}\times diagonal{{l}_{2}}\] ), where diagonal1 refers to the length of a diagonal of the rhombus and diagonals 2 refers to the length of other diagonal of the rhombus.
5. PARALLELOGRAM: (b x h), i.e., (base x height), where base refers to the length of the base and height refers to the height of the rhombus.
6. CIRCLE- \[(~\pi {{r}^{2}})\]where \[{{\left( radius \right)}^{2}}\] refers to the square of the length of the radius of the square.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

What is the color of ferrous sulphate crystals? How does this color change after heating? Name the products formed on strongly heating ferrous sulphate crystals. What type of chemical reaction occurs in this type of change.

What is the Full Form of ICSE / ISC ?

Find the mode and median of the data 13 16 12 14 1-class-9-maths-CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it




