
Draw the ray diagram to show the formation of an image for the object of height $1cm$ placed at $5cm$ distance in front of a convex mirror having the radius of curvature $R=5cm$.
Answer
557.1k+ views
Hint: Different types of images are formed from convex and concave mirrors respectively due to different properties of their respective reflecting surfaces. The distance of the object from the mirror also plays an important role in determining the type of image that is formed. A ray diagram indicates the rays of light emanating from the object source and shows how they reflect to form the image.
Complete answer:
Convex mirror:
The incident ray X is incident parallel to the principal axis on the reflecting surface of the mirror and it reflects back in a different direction. When we extend the reflected ray behind the mirror, we find that it meets at the principal focus of the mirror on the axis. Another ray Y is incident on the mirror at an angle and reflects back making the same angle in the opposite direction. Now, when this ray is extended behind the mirror, it meets the other reflected ray at a point. This is the point where the image is formed. It is formed between the principal axis and the point of intersection of the reflected rays.
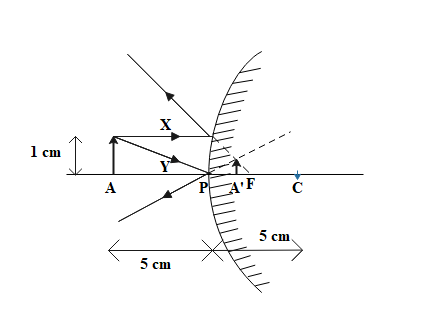
The image formed is virtual, erect and diminished in size.
Note: Convex mirrors form images that are diminished (smaller) in size. Since the image formed in a convex mirror is smaller, therefore one is able to see more of the area in the mirror. This is why these mirrors are used as rear-view mirrors and in parking lots at sharp turns so that the driver is able to see cars coming from other directions and avoid accidents.
Complete answer:
Convex mirror:
The incident ray X is incident parallel to the principal axis on the reflecting surface of the mirror and it reflects back in a different direction. When we extend the reflected ray behind the mirror, we find that it meets at the principal focus of the mirror on the axis. Another ray Y is incident on the mirror at an angle and reflects back making the same angle in the opposite direction. Now, when this ray is extended behind the mirror, it meets the other reflected ray at a point. This is the point where the image is formed. It is formed between the principal axis and the point of intersection of the reflected rays.

The image formed is virtual, erect and diminished in size.
Note: Convex mirrors form images that are diminished (smaller) in size. Since the image formed in a convex mirror is smaller, therefore one is able to see more of the area in the mirror. This is why these mirrors are used as rear-view mirrors and in parking lots at sharp turns so that the driver is able to see cars coming from other directions and avoid accidents.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




