
Draw the ray diagram of the geometric images for concave mirrors and also state the characteristics of images when the object is in between principal focus and centre of curvature.
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint:By using the two rules of reflection draw the ray diagram for concave mirrors where the object is in between principal focus and centre of curvature. From the diagram describe the image location, type, orientation and the size.
Complete step by step solution:
To draw the ray diagram of the geometric images for the concave mirrors, we have to follow two rules of reflection for concave mirrors that is
i)Any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis on the way to the mirror will pass through the focal point upon reflection.
ii)Any incident ray passing through the focal point on the way to the mirror will travel parallel to the principal axis upon reflection.
Consider the following ray diagram of the geometric images for concave mirrors
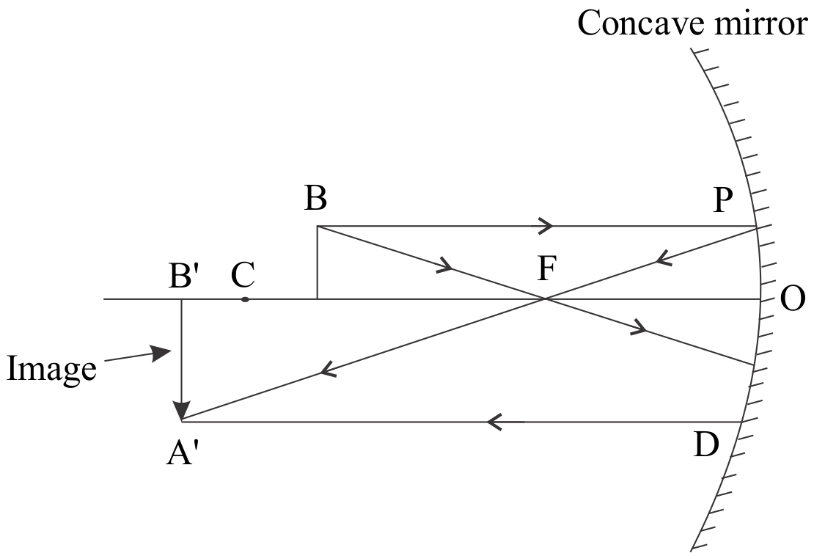 $C$
$C$
In the above diagram is the centre of curvature and $F$ is the focal point.The object is in between centre of the curvature and focal point.So the First ray is coming from the top of the object ($B$) and going in parallel to the principal axis so upon reflection it passes through the focal point according to rule of reflection.Second ray is going through the focal point and upon reflection it travel parallel to the principal axis and meet with first ray at point $A'$ and form the image.
Characteristics of the image:
i) Image location : ${d_i} > C$ Image will form beyond the centre of the curvature.
ii) Orientation: The orientation of the image will be inverted.
iii) Size: The size of the image will be larger than the original object.
iv) Type: Because the image forms in the same side mirror as the object so the image will be real.
Note:We will get the virtual image if the image is from behind the mirror and in case of concave it will be obtained when the object is in between the focus and the center of the mirror. Plane mirror always produces virtual images.
Complete step by step solution:
To draw the ray diagram of the geometric images for the concave mirrors, we have to follow two rules of reflection for concave mirrors that is
i)Any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis on the way to the mirror will pass through the focal point upon reflection.
ii)Any incident ray passing through the focal point on the way to the mirror will travel parallel to the principal axis upon reflection.
Consider the following ray diagram of the geometric images for concave mirrors

In the above diagram is the centre of curvature and $F$ is the focal point.The object is in between centre of the curvature and focal point.So the First ray is coming from the top of the object ($B$) and going in parallel to the principal axis so upon reflection it passes through the focal point according to rule of reflection.Second ray is going through the focal point and upon reflection it travel parallel to the principal axis and meet with first ray at point $A'$ and form the image.
Characteristics of the image:
i) Image location : ${d_i} > C$ Image will form beyond the centre of the curvature.
ii) Orientation: The orientation of the image will be inverted.
iii) Size: The size of the image will be larger than the original object.
iv) Type: Because the image forms in the same side mirror as the object so the image will be real.
Note:We will get the virtual image if the image is from behind the mirror and in case of concave it will be obtained when the object is in between the focus and the center of the mirror. Plane mirror always produces virtual images.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




