
Draw the molecular orbital energy level diagram of ${N_2}$ molecules .
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint:When two atomic orbitals combine they form two new molecular orbitals , one by the additive effect of the atomic orbitals which is called the bonding molecular orbital and the other is formed by the subtractive effect of the atomic orbitals which is called the antibonding molecular orbital .
Complete step by step answer:
The electronic configuration of nitrogen atom ( Z=7 ) is $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p_x}^12{p_y}^12{p_z}^1$
The total number of electrons present in ${N_2}$ molecule is 14, seven from each nitrogen atom . Keeping in view the various rules of filling of molecular orbitals the electronic configuration of $N_2$ molecule will be
${[\sigma (1s)]^2}{[\sigma *(1s)]^2}{[\sigma (2s)]^2}{[\sigma *(2s)]^2}{[\Pi (2{p_x})]^2}{[\Pi (2{p_y})]^2}{[\Pi (2{p_z})]^2}$
The energy level diagram of nitrogen molecule is as follows :
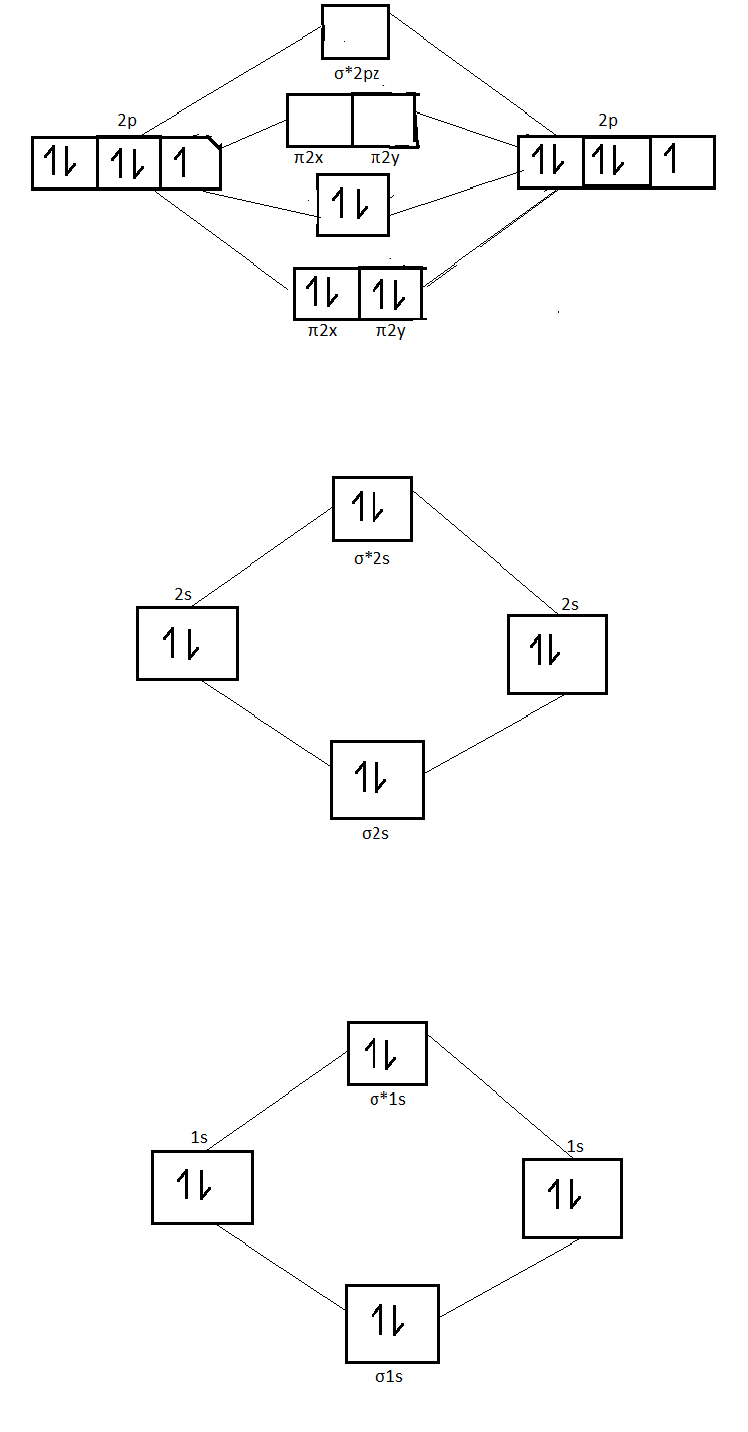
From the diagram it is clear that there are four fully filled bonding molecular orbitals and one completely filled antibonding molecular orbital .
The bond order is calculated by subtracting the number of electrons in antibonding molecular orbitals $({N_b})$ from the number of electrons in bonding molecular orbitals $({N_a})$ and dividing the difference by 2.
Bond order = $\dfrac{1}{2}({N_b} - {N_b})$
Hence , the bond order of nitrogen molecules is $\dfrac{1}{2}(8 - 2) = 3$ .
The bond order is 3 which means it has a triple bond and hence it has high bond strength . Also since there are no unpaired electrons present it is diamagnetic in nature .
Note:
The inner shell does not take part in bonding hence these orbitals are called non bonding orbitals and the electrons present in them are called non bonding electrons . So in the energy level diagram also this part is usually omitted . In the case of nitrogen molecules the inner shell is 1s.
Complete step by step answer:
The electronic configuration of nitrogen atom ( Z=7 ) is $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p_x}^12{p_y}^12{p_z}^1$
The total number of electrons present in ${N_2}$ molecule is 14, seven from each nitrogen atom . Keeping in view the various rules of filling of molecular orbitals the electronic configuration of $N_2$ molecule will be
${[\sigma (1s)]^2}{[\sigma *(1s)]^2}{[\sigma (2s)]^2}{[\sigma *(2s)]^2}{[\Pi (2{p_x})]^2}{[\Pi (2{p_y})]^2}{[\Pi (2{p_z})]^2}$
The energy level diagram of nitrogen molecule is as follows :

From the diagram it is clear that there are four fully filled bonding molecular orbitals and one completely filled antibonding molecular orbital .
The bond order is calculated by subtracting the number of electrons in antibonding molecular orbitals $({N_b})$ from the number of electrons in bonding molecular orbitals $({N_a})$ and dividing the difference by 2.
Bond order = $\dfrac{1}{2}({N_b} - {N_b})$
Hence , the bond order of nitrogen molecules is $\dfrac{1}{2}(8 - 2) = 3$ .
The bond order is 3 which means it has a triple bond and hence it has high bond strength . Also since there are no unpaired electrons present it is diamagnetic in nature .
Note:
The inner shell does not take part in bonding hence these orbitals are called non bonding orbitals and the electrons present in them are called non bonding electrons . So in the energy level diagram also this part is usually omitted . In the case of nitrogen molecules the inner shell is 1s.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




