
Draw the molecular orbital diagram of ${N_2}$ and calculate the bond order.
Answer
507k+ views
Hint: The molecular orbital theory is primarily used for explaining the type of bonding that exists in a molecule which cannot be explained by valence bond theory. The theory explains the geometry and bonding of the molecule which involve some form of resonance.
Complete answer: The basic rules of molecular orbital theory are as follows:
First principle: The number of molecular orbitals formed is always equal to the total number of atomic orbitals that have combined to form bonds.
Second principle: Bonding molecular orbitals always comprises lower energy as compared to antibonding molecular orbitals.
Third principle: Electrons of the molecule are always assigned to the orbitals in the increasing order of the orbital energy.
Fourth principle: atomic orbitals of similar energy combine to form most effective molecular orbitals.
The molecular orbital diagram of ${N_2}$ is shown as follows:
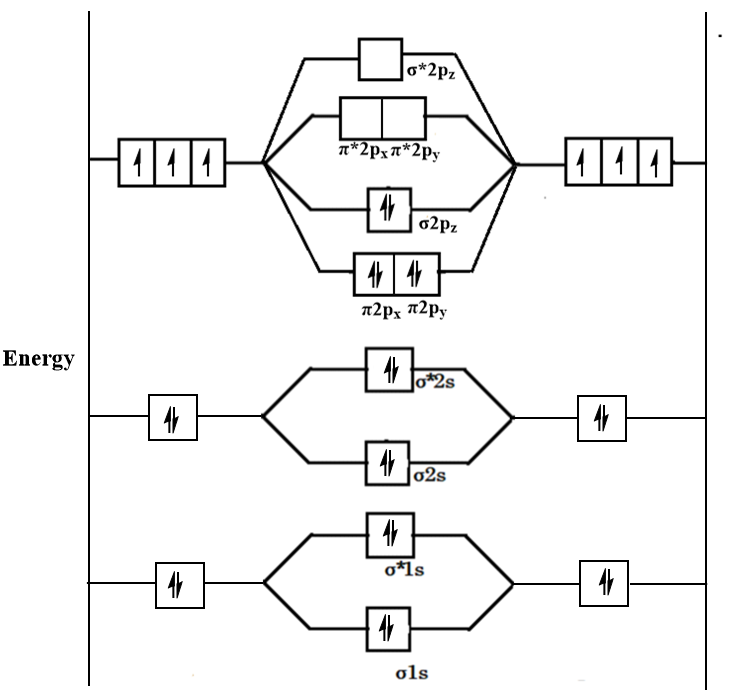
Now, the bond order of a molecule is determined by the formula which is as follows:
$BO = \dfrac{{BMO - ABMO}}{2}$
Where, BMO represents the number of electrons present in the bonding molecular orbital and ABMO represents the number of electrons in antibonding molecular orbital.
For the given molecular orbital diagram, the value of BMO is 10 and the value of ABMO is 4. Therefore, the bond order will be as follows:
$BO = \dfrac{{10 - 4}}{2} \Rightarrow 3$
Thus, we can conclude that the bond order of ${N_2}$ is 3.
Note:
It is important to note that all the elements in the second period before oxygen consist of small energy difference between 2s and 2p orbitals so that he s-p mixing can occur lowering the energy of $\sigma 2s$ and ${\sigma ^*}2s$ and increase the energy of $\sigma 2p$ and ${\sigma ^*}2p$. But on moving right in a period, the s-orbital becomes more stabilized than p-orbital and the difference in their energies increases due to which the s-p mixing of oxygen becomes smaller.
Complete answer: The basic rules of molecular orbital theory are as follows:
First principle: The number of molecular orbitals formed is always equal to the total number of atomic orbitals that have combined to form bonds.
Second principle: Bonding molecular orbitals always comprises lower energy as compared to antibonding molecular orbitals.
Third principle: Electrons of the molecule are always assigned to the orbitals in the increasing order of the orbital energy.
Fourth principle: atomic orbitals of similar energy combine to form most effective molecular orbitals.
The molecular orbital diagram of ${N_2}$ is shown as follows:

Now, the bond order of a molecule is determined by the formula which is as follows:
$BO = \dfrac{{BMO - ABMO}}{2}$
Where, BMO represents the number of electrons present in the bonding molecular orbital and ABMO represents the number of electrons in antibonding molecular orbital.
For the given molecular orbital diagram, the value of BMO is 10 and the value of ABMO is 4. Therefore, the bond order will be as follows:
$BO = \dfrac{{10 - 4}}{2} \Rightarrow 3$
Thus, we can conclude that the bond order of ${N_2}$ is 3.
Note:
It is important to note that all the elements in the second period before oxygen consist of small energy difference between 2s and 2p orbitals so that he s-p mixing can occur lowering the energy of $\sigma 2s$ and ${\sigma ^*}2s$ and increase the energy of $\sigma 2p$ and ${\sigma ^*}2p$. But on moving right in a period, the s-orbital becomes more stabilized than p-orbital and the difference in their energies increases due to which the s-p mixing of oxygen becomes smaller.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




