
Draw the graph of the function \[y = |x - 1| + |x + 1|\] and discuss the continuity and differentiability of the function.
Answer
558.3k+ views
Hint: Here we simply draw the graph of the given function. A function is said to be continues if the curve has no missing points or breaking points in a given interval or domain. Function F(x) is said to be differentiable at a point then the differentiation of that function at that point exists. We know the definition of modulus of x.
Complete step by step answer:
We know have, \[|x| = \left\{ \begin{gathered}
x{\text{ }}x \geqslant 0 \\
- x{\text{ }}x < 0 \\
\end{gathered} \right.\] this is the standard definition.
We have \[|x - 1| = \left\{ \begin{gathered}
x - 1{\text{ }}x > 1 \\
- (x - 1){\text{ }}x < 1 \\
\end{gathered} \right.\] and \[|x + 1| = \left\{ \begin{gathered}
x + 1{\text{ }}x > - 1 \\
- (x + 1){\text{ }}x < - {\text{1}} \\
\end{gathered} \right.\]. ----- (1)
We have \[y = |x - 1| + |x + 1|\] ---- (2)
At \[x > 1\], the value of y will be
See the above definition (1) then we have,
\[ \Rightarrow y = x - 1 + x + 1 = 2x\] Is differentiable.
At \[x < - 1\],
By the definition (1) we will have,
\[ \Rightarrow y = - (x - 1) + ( - x - 1)\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = - x + 1 - x - 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = - 2x\] Is differentiable.
At \[x > 1\] in \[|x - 1|\] and \[x > - 1\]in \[|x + 1|\], then the value of y will be,
\[y = - (x + 1) + x + 1 = 2\] . Is differentiable.
We can see that y is differentiable,
Let’s draw the graph and check the continuity and differentiability.
At \[x = 0\] in equation (2) we have \[y = 2\]
Similarly, at \[x = 1\]\[ \Rightarrow y = 2\]
At \[x = - 1\]\[ \Rightarrow y = 2\]
At \[x = 2\]\[ \Rightarrow y = 4\]
At \[x = - 2\]\[ \Rightarrow y = 4\] and so on.
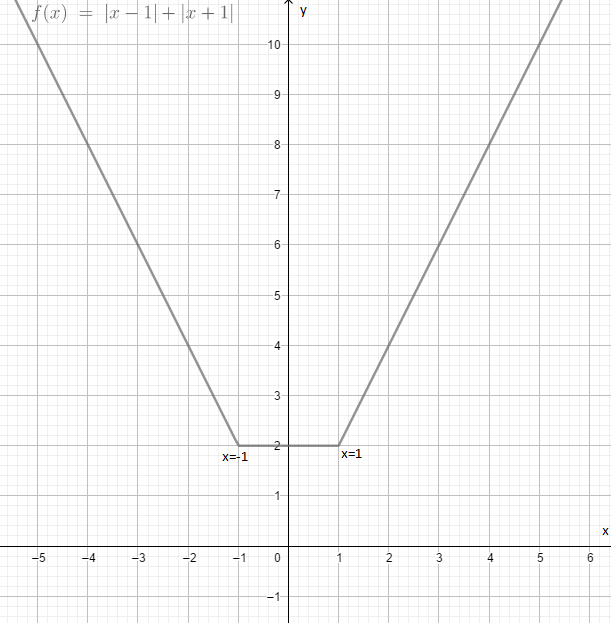
As we can see that the curve is continuous with no break points or missing points. That is \[y = |x - 1| + |x + 1|\] is continuous.
But while in differentiability, at point -1 and 1 the function \[y = |x - 1| + |x + 1|\] is not differentiable. Hence \[y = |x - 1| + |x + 1|\] is differentiable in \[R - \{ - 1,1\} \]. Or we can also say that it is differentiable at (-1, 1)
Note: We can directly plot the graph and by observation we can tell whether it is differentiable or continuous. The function is not differentiable at \[x = 1, - 1\] because the slopes at these points are different on the left and right hand side. In other wards Differentiability is defined as tangent to a curve.
Complete step by step answer:
We know have, \[|x| = \left\{ \begin{gathered}
x{\text{ }}x \geqslant 0 \\
- x{\text{ }}x < 0 \\
\end{gathered} \right.\] this is the standard definition.
We have \[|x - 1| = \left\{ \begin{gathered}
x - 1{\text{ }}x > 1 \\
- (x - 1){\text{ }}x < 1 \\
\end{gathered} \right.\] and \[|x + 1| = \left\{ \begin{gathered}
x + 1{\text{ }}x > - 1 \\
- (x + 1){\text{ }}x < - {\text{1}} \\
\end{gathered} \right.\]. ----- (1)
We have \[y = |x - 1| + |x + 1|\] ---- (2)
At \[x > 1\], the value of y will be
See the above definition (1) then we have,
\[ \Rightarrow y = x - 1 + x + 1 = 2x\] Is differentiable.
At \[x < - 1\],
By the definition (1) we will have,
\[ \Rightarrow y = - (x - 1) + ( - x - 1)\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = - x + 1 - x - 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = - 2x\] Is differentiable.
At \[x > 1\] in \[|x - 1|\] and \[x > - 1\]in \[|x + 1|\], then the value of y will be,
\[y = - (x + 1) + x + 1 = 2\] . Is differentiable.
We can see that y is differentiable,
Let’s draw the graph and check the continuity and differentiability.
At \[x = 0\] in equation (2) we have \[y = 2\]
Similarly, at \[x = 1\]\[ \Rightarrow y = 2\]
At \[x = - 1\]\[ \Rightarrow y = 2\]
At \[x = 2\]\[ \Rightarrow y = 4\]
At \[x = - 2\]\[ \Rightarrow y = 4\] and so on.

As we can see that the curve is continuous with no break points or missing points. That is \[y = |x - 1| + |x + 1|\] is continuous.
But while in differentiability, at point -1 and 1 the function \[y = |x - 1| + |x + 1|\] is not differentiable. Hence \[y = |x - 1| + |x + 1|\] is differentiable in \[R - \{ - 1,1\} \]. Or we can also say that it is differentiable at (-1, 1)
Note: We can directly plot the graph and by observation we can tell whether it is differentiable or continuous. The function is not differentiable at \[x = 1, - 1\] because the slopes at these points are different on the left and right hand side. In other wards Differentiability is defined as tangent to a curve.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




