
Draw the following diagram in your answer book and show the formation of the image of the object AB with the help of suitable rays.

Answer
539.1k+ views
Hint: A concave mirror is also known as a converging mirror. If we place our object at infinity, the rays converge at focus and form a sharp image there. Here, we have an object between the centre of curvature and focus.
Complete answer:
The point C in the diagram is called the centre of curvature and point F is the focus of the mirror. An object placed at focus forms an image at infinity. An object placed at the C forms an image at C itself. Any object placed in between the two should likewise form an image between infinity and C. The image formed by a concave mirror when the object is between C and F will be real and inverted.
The ray diagram is depicted below.
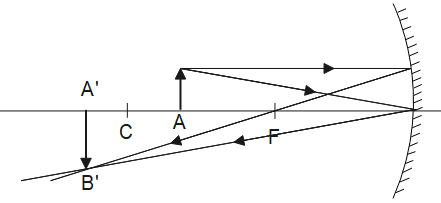
To draw this, follow two steps:
1. Pass a ray parallel to the axis, so that it reflects from the mirror and passes through the focus.
2. Next, pass a ray to the pole of the mirror so that it reflects making the same angle with the principal axis as the incident.
Thus, an image A’B’ is obtained at a point that is beyond C. This image formed is a real and inverted image.
Note:
There are basically three ways of making rays: (i) parallel to the principal axis or through the focus, (ii) towards the pole, (iii) through the centre of curvature (to the other side in convex). Any two of these three can form the required image. It is not like we cannot form any other rays. Sure, an object consists of infinite rays, we only pick the standard ones that generalize our result.
Complete answer:
The point C in the diagram is called the centre of curvature and point F is the focus of the mirror. An object placed at focus forms an image at infinity. An object placed at the C forms an image at C itself. Any object placed in between the two should likewise form an image between infinity and C. The image formed by a concave mirror when the object is between C and F will be real and inverted.
The ray diagram is depicted below.

To draw this, follow two steps:
1. Pass a ray parallel to the axis, so that it reflects from the mirror and passes through the focus.
2. Next, pass a ray to the pole of the mirror so that it reflects making the same angle with the principal axis as the incident.
Thus, an image A’B’ is obtained at a point that is beyond C. This image formed is a real and inverted image.
Note:
There are basically three ways of making rays: (i) parallel to the principal axis or through the focus, (ii) towards the pole, (iii) through the centre of curvature (to the other side in convex). Any two of these three can form the required image. It is not like we cannot form any other rays. Sure, an object consists of infinite rays, we only pick the standard ones that generalize our result.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




