
How can I draw the following amides: N-ethylbutanamide, N-propylpentanamide, N-3-dimethylhexanamide?
Answer
558.9k+ views
Hint: To solve this draw the base structures for each of the amides i.e. N-ethylbutanamide, N-propylpentanamide and N-3-dimethylhexanamide. The base name tells us the number of carbon atoms. The substituent on the nitrogen atom is indicated by the prefix N.
Complete answer:
We know that amides are organic compounds. Amides are a derivative of carboxylic acid in which the hydroxyl group i.e. $ - {\text{OH}}$ group of carboxylic acid is replaced by an amine group i.e. $ - {\text{N}}{{\text{R}}^,}{{\text{R}}^{,,}}$ group.
Let us draw the structures of given amides i.e. N-ethylbutanamide, N-propylpentanamide and N-3-dimethylhexanamide as follows:
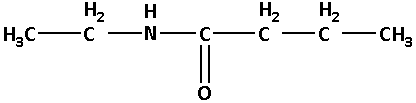
N-ethylbutanamide:
In N-ethylbutanamide, the base name is butanamide. Here, ‘butan’ suggests that there are four carbon atoms. N-ethyl suggests that there is an ethyl group attached to the nitrogen atom.
Thus, the structure of N-ethylbutanamide is as follows:
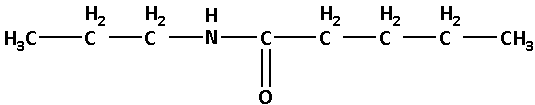
N-propylpentanamide:
In N-propylpentanamide, the base name is pentanamide. Here, ‘pentan’ suggests that there are five carbon atoms. N-propyl suggests that there is a propyl group attached to the nitrogen atom.
Thus, the structure of N-propylpentanamide is as follows:
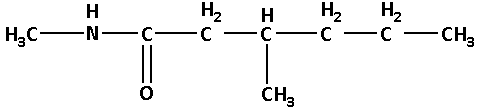
N-3-dimethylhexanamide:
In N-3-dimethylhexanamide, the base name is hexanamide. Here, ‘hexan’ suggests that there are six carbon atoms. N-3-dimethyl suggests that there are two methyl groups one of which is attached to the nitrogen atom and the other is attached to the carbon number 3.
Thus, the structure of N-3-dimethylhexanamide is as follows:
Note:Amides are organic compounds. Amides are a derivative of carboxylic acid in which the hydroxyl group i.e. $ - {\text{OH}}$ group of carboxylic acid is replaced by an amine group i.e. $ - {\text{N}}{{\text{R}}^,}{{\text{R}}^{,,}}$ group. Amides are classified as primary, secondary and tertiary amides depending on the position of nitrogen atom linked to the carbon atom.
Complete answer:
We know that amides are organic compounds. Amides are a derivative of carboxylic acid in which the hydroxyl group i.e. $ - {\text{OH}}$ group of carboxylic acid is replaced by an amine group i.e. $ - {\text{N}}{{\text{R}}^,}{{\text{R}}^{,,}}$ group.
Let us draw the structures of given amides i.e. N-ethylbutanamide, N-propylpentanamide and N-3-dimethylhexanamide as follows:
N-ethylbutanamide:
In N-ethylbutanamide, the base name is butanamide. Here, ‘butan’ suggests that there are four carbon atoms. N-ethyl suggests that there is an ethyl group attached to the nitrogen atom.
Thus, the structure of N-ethylbutanamide is as follows:

N-propylpentanamide:
In N-propylpentanamide, the base name is pentanamide. Here, ‘pentan’ suggests that there are five carbon atoms. N-propyl suggests that there is a propyl group attached to the nitrogen atom.
Thus, the structure of N-propylpentanamide is as follows:

N-3-dimethylhexanamide:
In N-3-dimethylhexanamide, the base name is hexanamide. Here, ‘hexan’ suggests that there are six carbon atoms. N-3-dimethyl suggests that there are two methyl groups one of which is attached to the nitrogen atom and the other is attached to the carbon number 3.
Thus, the structure of N-3-dimethylhexanamide is as follows:

Note:Amides are organic compounds. Amides are a derivative of carboxylic acid in which the hydroxyl group i.e. $ - {\text{OH}}$ group of carboxylic acid is replaced by an amine group i.e. $ - {\text{N}}{{\text{R}}^,}{{\text{R}}^{,,}}$ group. Amides are classified as primary, secondary and tertiary amides depending on the position of nitrogen atom linked to the carbon atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




