
Draw the diagram showing the structure of HIV.
Answer
594k+ views
Hint: The human immunodeficiency virus or in short HIV is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system in a person’s body. A person can be infected when they come in contact during unprotected sex or sharing drug needles with someone who has HIV. They are also infected by the virus when it contacts infected blood, semen, or vaginal fluids.
Complete answer:
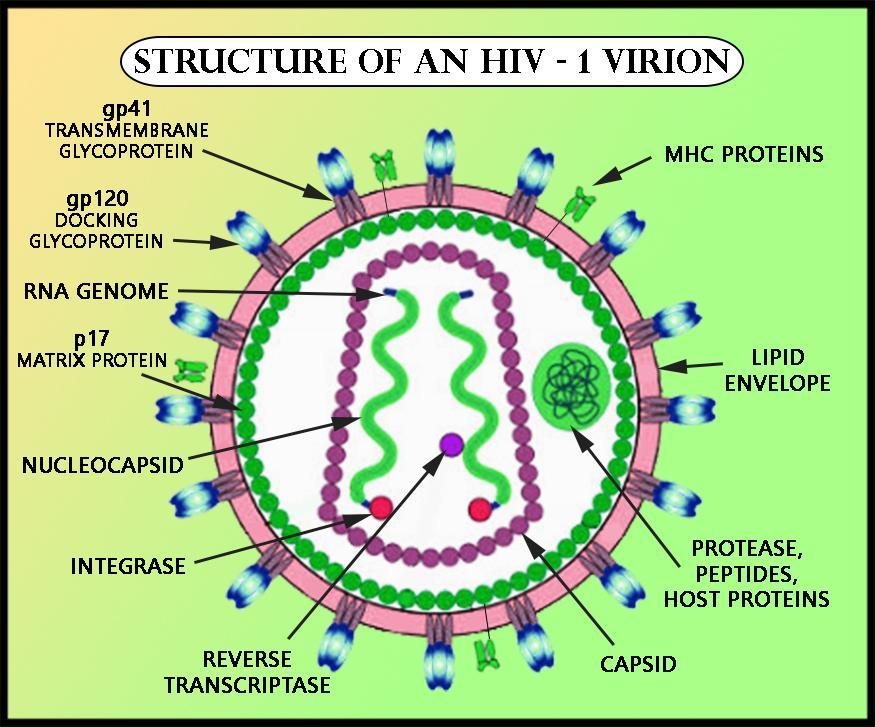
The structure of HIV is roughly spherical with about 120 nanometres in diameter. Red blood cells are nearly 60 times bigger than HIV. HIV has a lipid envelope and the surface glycoprotein gp120 is attached to the transmembrane glycoprotein gp41 are embedded in this envelope. These two viral proteins are encoded by the env gene and are helpful in an attachment to the host cell. Below is the matrix protein p17. The core proteins are p24 and p6. The nucleocapsid protein p7 which is bound to the RNA and the above mentioned are all encoded by the viral gag gene. The two copies of the positive viral RNA genome, protease, integrase, and reverse transcriptase enzymes lie inside the viral core and are encoded by the viral gene.
Note: HIV is said to be a lentivirus which means it is a slow virus. People who are infected with this virus die from secondary infections or cancer. AIDS or acquired immunodeficiency syndrome is a life-threatening condition caused by this virus. This virus once infected can never be cured as there are currently no medicines for it but they can be controlled by strict adherence to antiretroviral regimens (ARVs). This helps slow down the virus's progress.
Complete answer:

The structure of HIV is roughly spherical with about 120 nanometres in diameter. Red blood cells are nearly 60 times bigger than HIV. HIV has a lipid envelope and the surface glycoprotein gp120 is attached to the transmembrane glycoprotein gp41 are embedded in this envelope. These two viral proteins are encoded by the env gene and are helpful in an attachment to the host cell. Below is the matrix protein p17. The core proteins are p24 and p6. The nucleocapsid protein p7 which is bound to the RNA and the above mentioned are all encoded by the viral gag gene. The two copies of the positive viral RNA genome, protease, integrase, and reverse transcriptase enzymes lie inside the viral core and are encoded by the viral gene.
Note: HIV is said to be a lentivirus which means it is a slow virus. People who are infected with this virus die from secondary infections or cancer. AIDS or acquired immunodeficiency syndrome is a life-threatening condition caused by this virus. This virus once infected can never be cured as there are currently no medicines for it but they can be controlled by strict adherence to antiretroviral regimens (ARVs). This helps slow down the virus's progress.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




