
Draw the diagram of an electromagnetic wave.
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: Electromagnetic waves are also known as EM waves that are produced when an electric field comes in contact with the magnetic field. It can also be said that electromagnetic waves are the composition of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. Time varying magnetic fields give rise to electric fields and vice-versa. The behavior of time dependent electromagnetic waves is described by a set of equations known as Maxwell’s equations.
Complete step by step solution:
We have seen that in certain situations light $E$ may be described as a wave. The wave equation for light propagating in x-direction in vacuum may be written as
\[E = {E_o}\sin \omega \left( {t - \dfrac{x}{c}} \right)\]
Where, $E$ is the sinusoidally varying electric field at the position $x$ at time $t.$
The constant $c$ is the speed of light in vacuum. The electric field is in the Y-Z plane that is perpendicular to direction of propagation.
There is also the sinusoidally varying magnetic field associated with the electric field when light propagates. This magnetic field is perpendicular to direction of propagation as well as to the electric field $E.$ it is given by
$B = {B_o}\sin \omega \left( {t - \dfrac{x}{c}} \right)$
Such a combination of mutually perpendicular electric and magnetic fields is referred to as an electromagnetic wave in vacuum.
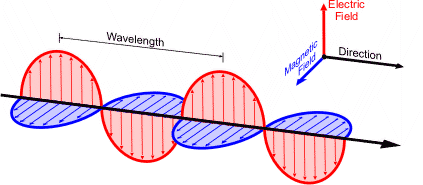
Electromagnetic waves are shown by a sinusoidal graph. It consists of time-varying electric and magnetic fields which are perpendicular to each other and are also perpendicular to the direction of propagation of waves. Electromagnetic waves are transverse in nature. The highest point of the wave is known as crest while the lowest point is known as a trough. In vacuum, the waves travel at a constant velocity of $3 \times {10^8}m{s^{ - 1}}.$
Note: Following are a few applications of electromagnetic waves:
1. Electromagnetic waves can transmit energy in vacuum or using no medium at all.
2. Electromagnetic waves play an important role in communication technology.
3. Electromagnetic waves are used in RADARS.
4. UV rays are used to detect forged bank notes. Real banknotes don’t turn fluorescent under the UV light.
5. Infrared radiation is used for night vision and is used in security cameras.
Complete step by step solution:
We have seen that in certain situations light $E$ may be described as a wave. The wave equation for light propagating in x-direction in vacuum may be written as
\[E = {E_o}\sin \omega \left( {t - \dfrac{x}{c}} \right)\]
Where, $E$ is the sinusoidally varying electric field at the position $x$ at time $t.$
The constant $c$ is the speed of light in vacuum. The electric field is in the Y-Z plane that is perpendicular to direction of propagation.
There is also the sinusoidally varying magnetic field associated with the electric field when light propagates. This magnetic field is perpendicular to direction of propagation as well as to the electric field $E.$ it is given by
$B = {B_o}\sin \omega \left( {t - \dfrac{x}{c}} \right)$
Such a combination of mutually perpendicular electric and magnetic fields is referred to as an electromagnetic wave in vacuum.

Electromagnetic waves are shown by a sinusoidal graph. It consists of time-varying electric and magnetic fields which are perpendicular to each other and are also perpendicular to the direction of propagation of waves. Electromagnetic waves are transverse in nature. The highest point of the wave is known as crest while the lowest point is known as a trough. In vacuum, the waves travel at a constant velocity of $3 \times {10^8}m{s^{ - 1}}.$
Note: Following are a few applications of electromagnetic waves:
1. Electromagnetic waves can transmit energy in vacuum or using no medium at all.
2. Electromagnetic waves play an important role in communication technology.
3. Electromagnetic waves are used in RADARS.
4. UV rays are used to detect forged bank notes. Real banknotes don’t turn fluorescent under the UV light.
5. Infrared radiation is used for night vision and is used in security cameras.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
How is the angle of emergence e related to the angle class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between lanthanoids and actinoids class 12 chemistry CBSE

Derive Lens Makers formula for a convex lens class 12 physics CBSE

a Draw Labelled diagram of Standard Hydrogen Electrode class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

State the principle of an ac generator and explain class 12 physics CBSE




