
Draw the circuit symbol of n-p-n transistor.
Answer
604.5k+ views
Hint: Circuit symbol is the pictorial representation of elements, so that we can identify them on the paper, n-p-n transistor is the combination of two n types of one p type semiconductor. We will discuss the n-p-n transistor in brief.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first define the n- type semiconductor and then p- type semiconductor
n- type semiconductor: When impurity of pentavalent ( such as phosphorus, arsenic) atom added to pure semiconductor of silicon or germanium. This increases the number of electrons in a semiconductor.
p- type semiconductor: When impurity of trivalent ( such as boron, aluminium) atom added to pure semiconductor of silicon or germanium. This decreases the number of electrons and increases the number of electrons in the semiconductor.
n-p-n transistor: In n-p-n transistor two segments of n-type semiconductor (emitter and collector) are separated by a segment of p- type semiconductor (base).
Emitter: Emitter is the segment on one side of the transistor. It is moderate in size and very heavily doped. It supplies a large number of majority carriers for the current flow through the transistor.
Base: This is the central segment between two n- type semiconductor. It is very thin and lightly doped.
Collector: This segment of transistor collects a major portion of the majority carriers supplied by the emitter. The collector side is moderately doped and larger in size as compared to an emitter.
Circuit Symbol of n-p-n transistor
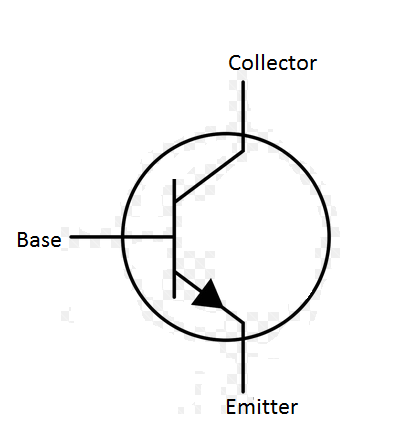
Emitter is connected in forward bias therefore the direction of current in the emitter is away from the base because the emitter has electrons as majority charge carriers.
Note: There is another type of transistor known as p-n-p transistor, that has two p-type semiconductor (emitter and collector) and one n type semiconductor (base).
Both n-p-n and p-n-p transistors are used to amplify the signal thus both are used as amplifiers. But we prefer n-p-n transistors over p-n-p transistors because the mobility of electrons is more than that of holes.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first define the n- type semiconductor and then p- type semiconductor
n- type semiconductor: When impurity of pentavalent ( such as phosphorus, arsenic) atom added to pure semiconductor of silicon or germanium. This increases the number of electrons in a semiconductor.
p- type semiconductor: When impurity of trivalent ( such as boron, aluminium) atom added to pure semiconductor of silicon or germanium. This decreases the number of electrons and increases the number of electrons in the semiconductor.
n-p-n transistor: In n-p-n transistor two segments of n-type semiconductor (emitter and collector) are separated by a segment of p- type semiconductor (base).
Emitter: Emitter is the segment on one side of the transistor. It is moderate in size and very heavily doped. It supplies a large number of majority carriers for the current flow through the transistor.
Base: This is the central segment between two n- type semiconductor. It is very thin and lightly doped.
Collector: This segment of transistor collects a major portion of the majority carriers supplied by the emitter. The collector side is moderately doped and larger in size as compared to an emitter.
Circuit Symbol of n-p-n transistor

Emitter is connected in forward bias therefore the direction of current in the emitter is away from the base because the emitter has electrons as majority charge carriers.
Note: There is another type of transistor known as p-n-p transistor, that has two p-type semiconductor (emitter and collector) and one n type semiconductor (base).
Both n-p-n and p-n-p transistors are used to amplify the signal thus both are used as amplifiers. But we prefer n-p-n transistors over p-n-p transistors because the mobility of electrons is more than that of holes.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




