
How to draw Lewis structure of $HCN$?
Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint: $HCN$ is known by the name hydrogen cyanide and sometimes by prussic acid. It is colorless, extremely poisonous and flammable liquid. It is a weak acid. Hydrogen cyanide is a linear molecule having a triple bond between carbon and nitrogen.
Complete answer:
Lewis structure basically tells us how the electrons are paired. In this every dot represents an electron and pair of dots between chemical symbols for atoms represents the bond. The main steps of draw a Lewis structure are as follows:
1. Calculate the valence electrons present in the molecule this can be calculated by adding the valency of individual atoms in the given molecule. In case of $HCN$ valence electrons are 10 as Hydrogen have valency 1, Carbon 4 and Nitrogen 5.
2. Now we have to find the octet electron for each atom and add them together so the octet electron for hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen are 2, 8 and 8 respectively so the total octet electrons are 18.
3. After that we have to find the bonding electrons which can be calculated by subtracting the octet electrons from valence electrons i.e. $18-10=8$
4. Now we have to find the number of bonds which can be calculated by dividing the bonding electrons by 2 = $\dfrac{8}{2}=4$ bonds.
5. The rest bonds are termed as non-bonding pairs which can be calculated by subtracting the bonding electrons from valence electrons i.e. $10-8=2$ which describes 1 lone pair.
By this we can draw the Lewis structure of $HCN$ which can be shown as follows:
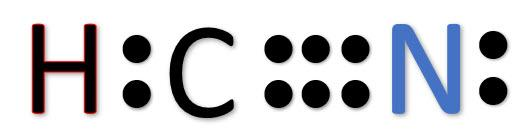
Note:
If we know the molecular formula of any compound we can easily draw its Lewis dot structure which is also known by the name electron dot structure. These diagrams generally describe the chemical bonding between atoms in a molecule and also display the total number of lone pairs present in each of the atoms.
Complete answer:
Lewis structure basically tells us how the electrons are paired. In this every dot represents an electron and pair of dots between chemical symbols for atoms represents the bond. The main steps of draw a Lewis structure are as follows:
1. Calculate the valence electrons present in the molecule this can be calculated by adding the valency of individual atoms in the given molecule. In case of $HCN$ valence electrons are 10 as Hydrogen have valency 1, Carbon 4 and Nitrogen 5.
2. Now we have to find the octet electron for each atom and add them together so the octet electron for hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen are 2, 8 and 8 respectively so the total octet electrons are 18.
3. After that we have to find the bonding electrons which can be calculated by subtracting the octet electrons from valence electrons i.e. $18-10=8$
4. Now we have to find the number of bonds which can be calculated by dividing the bonding electrons by 2 = $\dfrac{8}{2}=4$ bonds.
5. The rest bonds are termed as non-bonding pairs which can be calculated by subtracting the bonding electrons from valence electrons i.e. $10-8=2$ which describes 1 lone pair.
By this we can draw the Lewis structure of $HCN$ which can be shown as follows:

Note:
If we know the molecular formula of any compound we can easily draw its Lewis dot structure which is also known by the name electron dot structure. These diagrams generally describe the chemical bonding between atoms in a molecule and also display the total number of lone pairs present in each of the atoms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




