
How do you draw Fischer projections of carbohydrates?
Answer
541.2k+ views
Hint :Fischer projection is defined as the two dimensional representation of the three dimensional molecule of the organic compound with help of the projection. They help in representing the monosaccharides in biochemistry and organic chemistry. It helps in depicting the stereo formula in two dimensional form.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
So to know how the fischer projection of a compound is formed let us take the example of D- talose.
In making the Fischer projection we should firstly draw the chain vertically and place the aldehyde group at the top. The bonds present above and below any of the two adjacent carbon atoms are present behind the plane of paper. Whereas the horizontal bonds are coming out of the paper.
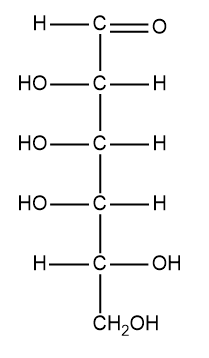
As we know that the geometry of carbon is tetrahedral that means the vertical groups 1 and 4 should be present behind the paper. When we have a longer vertical chain we look at any two of the adjacent atoms. These two atoms are present in the plane of the paper and the two atoms are present directly above and below them are present behind the plane of paper. We can keep the orientation as we move up and down the chain. The shape of the chain is arched as if we wrapped it around the cylindrical tube. When the structure is flattened on the surface of the cylinder we then get the Fischer projection. We can see the structure of D- talose. We must rotate the C- 3 and C-5 so they point up. The OH present at C-3 has become dashed whereas the other at C-5 has become wedged. So from the C-2 to the C-5 the orientation of the group of OH is dash dash dash wedge or we can say left left left right. The structure of the Fischer projection of the D- talose is the following:
Note :
A dextrorotatory compound is prefixed with (+) or d. whereas the levorotatory compound is prefixed with the (-) or l. These lowercase are considered to be different from those of the D and L prefixes which are used in differentiating the chiral configurations with the organic compounds. The carbohydrate is a biomolecule which comprises the carbon, hydrogen and the oxygen atoms.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
So to know how the fischer projection of a compound is formed let us take the example of D- talose.
In making the Fischer projection we should firstly draw the chain vertically and place the aldehyde group at the top. The bonds present above and below any of the two adjacent carbon atoms are present behind the plane of paper. Whereas the horizontal bonds are coming out of the paper.
As we know that the geometry of carbon is tetrahedral that means the vertical groups 1 and 4 should be present behind the paper. When we have a longer vertical chain we look at any two of the adjacent atoms. These two atoms are present in the plane of the paper and the two atoms are present directly above and below them are present behind the plane of paper. We can keep the orientation as we move up and down the chain. The shape of the chain is arched as if we wrapped it around the cylindrical tube. When the structure is flattened on the surface of the cylinder we then get the Fischer projection. We can see the structure of D- talose. We must rotate the C- 3 and C-5 so they point up. The OH present at C-3 has become dashed whereas the other at C-5 has become wedged. So from the C-2 to the C-5 the orientation of the group of OH is dash dash dash wedge or we can say left left left right. The structure of the Fischer projection of the D- talose is the following:

Note :
A dextrorotatory compound is prefixed with (+) or d. whereas the levorotatory compound is prefixed with the (-) or l. These lowercase are considered to be different from those of the D and L prefixes which are used in differentiating the chiral configurations with the organic compounds. The carbohydrate is a biomolecule which comprises the carbon, hydrogen and the oxygen atoms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




