
Draw a rough sketch of the region \[\{\left( x,y \right):{{y}^{2}}\le 3x,3{{x}^{2}}+3{{y}^{2}}\le 16\}\] and find the area enclosed by the region using integration.
Answer
577.2k+ views
Hint: Start by drawing the diagram of the situation given in the question. If you observe, you will see that the inequality ${{y}^{2}}\le 3x$ represents the region inside the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=3x$ and the inequality \[3{{x}^{2}}+3{{y}^{2}}\le 16\] represents the area inside the circle with the center as the origin. So, to find the area use the method of definite integration. For limits of integration, find the x-coordinate of intersection of the boundaries of two regions represented by the inequalities given in the question. To make the question easier, just find the area of the region enclosed above the x-axis and double it to get the total area.
Complete step-by-step solution -
We know that the equation ${{y}^{2}}=3x$ represents a parabola with vertex at origin. So, the inequality ${{y}^{2}}\le 3x$ represents the region inside the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=3x$ . Also, the equation \[3{{x}^{2}}+3{{y}^{2}}=16\] represents a circle with centre at the origin. So, the inequality \[3{{x}^{2}}+3{{y}^{2}}\le 16\] represents the area inside the circle with centre as the origin and radius $\sqrt{\dfrac{16}{3}}$ .
Let us draw the representative figure of the situation given the question.
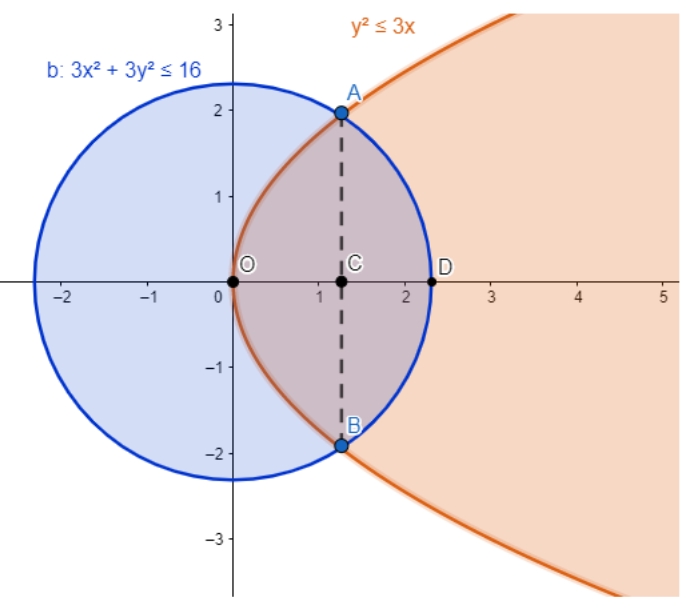
So, according to the question, we need to find the area of the region AOBD. We know that the given regions are symmetric about the x-axis, so to make the calculations easier, we will find the area above the x-axis, i.e., the area of the region AOD and double it to get the total area.
First, let us find the x-coordinates of the point A, which is the intersection of the curves ${{y}^{2}}=3x$ and \[3{{x}^{2}}+3{{y}^{2}}=16\] . so, let us substitute ${{y}^{2}}$ from equation of parabola in the equation of circle, on doing so, we get
\[3{{x}^{2}}+3{{y}^{2}}=16\]
\[\Rightarrow 3{{x}^{2}}+3\times 3x=16\]
\[\Rightarrow 3{{x}^{2}}+9x-16=0\]
As the above equation is a quadratic equation, we will use the quadratic formula, and as x is positive we will only consider the positive value of x.
$x=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}=\dfrac{-9\pm \sqrt{81+192}}{2\times 3}=\dfrac{-9\pm \sqrt{273}}{6}$
As the only positive value of x is to be considered, the x-coordinate of A is $\dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{6}$ .
Also, the x-coordinate of point D is equal to the radius of the circle, i.e., $\sqrt{\dfrac{16}{3}}$.
Now, to find the area of the region AOD, we need to use the method of definite integration. The equations are ${{y}^{2}}=3x\Rightarrow y=\sqrt{3x}$ and \[3{{x}^{2}}+3{{y}^{2}}=16\Rightarrow y=\sqrt{\dfrac{16-3{{x}^{2}}}{3}}\]. We know that the area bounded by any general curve y=f(x), in region x=a to x=b is given by $\int\limits_{a}^{b}{f(x)dx}$ .
$ar\left( AOD \right)=\int\limits_{0}^{\dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{6}}{\sqrt{3x}dx}+\int\limits_{\dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{6}}^{\sqrt{\dfrac{16}{3}}}{\sqrt{\dfrac{16-3{{x}^{2}}}{3}}dx}$
Now, we know that the integral of $\sqrt{x}$ is equal to $\dfrac{2\sqrt{{{x}^{3}}}}{3}$ .
\[ar\left( AOD \right)=\sqrt{3}\times \left. \dfrac{2\sqrt{{{x}^{3}}}}{3} \right|_{0}^{\dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{6}}+\int\limits_{\dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{6}}^{\sqrt{\dfrac{16}{3}}}{\sqrt{{{\left( \sqrt{\dfrac{16}{3}} \right)}^{2}}-{{x}^{2}}}dx}\]
Now we know that $\int{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}-{{x}^{2}}}dx=\dfrac{x}{2}\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}-{{x}^{2}}}}+\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}}{2}{{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{x}{a}+c$.
\[ar\left( AOD \right)=\sqrt{3}\times 2\times \dfrac{\sqrt{{{\left( \dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{6} \right)}^{3}}}}{3}\left. +\left( \dfrac{x}{2}\sqrt{\dfrac{16}{3}-{{x}^{2}}}+\dfrac{16}{6}{{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{\sqrt{3}x}{\sqrt{16}} \right) \right|_{\dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{6}}^{\sqrt{\dfrac{16}{3}}}\]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow ar\left( AOD \right)=\sqrt{3}\times 2\times \dfrac{\sqrt{{{\left( \dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{6} \right)}^{3}}}}{3}+\dfrac{16\times \pi }{6\times 2}- \\
& \left( \left( \dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{12} \right)\times \sqrt{\dfrac{16}{3}-{{\left( \dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{6} \right)}^{2}}}+\dfrac{16}{6}{{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{\sqrt{3}\times \left( -9+\sqrt{273} \right)}{6\times \sqrt{16}} \right) \\
\end{align}\]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow ar\left( AOD \right)=\sqrt{3}\times 2\times \dfrac{\sqrt{{{\left( \dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{6} \right)}^{3}}}}{3}+\dfrac{8\times \pi }{6}- \\
& \left( \left( \dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{12} \right)\times \sqrt{\dfrac{16}{3}-{{\left( \dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{6} \right)}^{2}}}+\dfrac{16}{6}{{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{\sqrt{3}\times \left( -9+\sqrt{273} \right)}{24} \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the area of the region AOBD is equal to twice the area of region AOD.
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow ar\left( AOBD \right)=4\times \sqrt{3}\times \dfrac{\sqrt{{{\left( \dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{6} \right)}^{3}}}}{3}+\dfrac{16\times \pi }{6}- \\
& 2\times \left( \left( \dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{12} \right)\times \sqrt{\dfrac{16}{3}-{{\left( \dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{6} \right)}^{2}}}+\dfrac{16}{6}{{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{\sqrt{3}\times \left( -9+\sqrt{273} \right)}{24} \right)\text{ uni}{{\text{t}}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Now if we put the approximate value of \[\dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{6}\] as 1.2, we get
\[ar\left( AOBD \right)=4\times \sqrt{3}\times \dfrac{\sqrt{{{1.2}^{3}}}}{3}+\dfrac{16\times \pi }{6}-2\times \left( \left( \dfrac{1.2}{2} \right)\times \sqrt{\dfrac{16}{3}-{{1.2}^{2}}}+\dfrac{16}{6}{{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{\sqrt{3}\times 1.2}{4} \right)\text{ uni}{{\text{t}}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow ar\left( AOBD \right)=\left( 3.04+8.37-2\times \left( 0.592+2.66{{\sin }^{-1}}(0.5) \right) \right)\text{ uni}{{\text{t}}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow ar\left( AOBD \right)=\left( 3.04+8.37-2\times \left( 0.592+2.66\times \dfrac{\pi }{6} \right) \right)\text{ uni}{{\text{t}}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow ar\left( AOBD \right)=\left( 3.04+8.97-2\times \left( 0.592+1.395 \right) \right)\text{ uni}{{\text{t}}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow ar\left( AOBD \right)=8.036uni{{t}^{2}}\]
Therefore, the approximate answer to the above question is 8.036 sq units.
Note: Learn the graphs of different standard functions, as in such questions, the most important part is the diagram and for drawing the diagram you need to know the curves. Also, be familiar with approximate values of roots of single-digit numbers, as they are used very often. Also, be careful about the calculation part, as the calculation part is very complex and approximation is required to reach an approximate value.
Complete step-by-step solution -
We know that the equation ${{y}^{2}}=3x$ represents a parabola with vertex at origin. So, the inequality ${{y}^{2}}\le 3x$ represents the region inside the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=3x$ . Also, the equation \[3{{x}^{2}}+3{{y}^{2}}=16\] represents a circle with centre at the origin. So, the inequality \[3{{x}^{2}}+3{{y}^{2}}\le 16\] represents the area inside the circle with centre as the origin and radius $\sqrt{\dfrac{16}{3}}$ .
Let us draw the representative figure of the situation given the question.

So, according to the question, we need to find the area of the region AOBD. We know that the given regions are symmetric about the x-axis, so to make the calculations easier, we will find the area above the x-axis, i.e., the area of the region AOD and double it to get the total area.
First, let us find the x-coordinates of the point A, which is the intersection of the curves ${{y}^{2}}=3x$ and \[3{{x}^{2}}+3{{y}^{2}}=16\] . so, let us substitute ${{y}^{2}}$ from equation of parabola in the equation of circle, on doing so, we get
\[3{{x}^{2}}+3{{y}^{2}}=16\]
\[\Rightarrow 3{{x}^{2}}+3\times 3x=16\]
\[\Rightarrow 3{{x}^{2}}+9x-16=0\]
As the above equation is a quadratic equation, we will use the quadratic formula, and as x is positive we will only consider the positive value of x.
$x=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}=\dfrac{-9\pm \sqrt{81+192}}{2\times 3}=\dfrac{-9\pm \sqrt{273}}{6}$
As the only positive value of x is to be considered, the x-coordinate of A is $\dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{6}$ .
Also, the x-coordinate of point D is equal to the radius of the circle, i.e., $\sqrt{\dfrac{16}{3}}$.
Now, to find the area of the region AOD, we need to use the method of definite integration. The equations are ${{y}^{2}}=3x\Rightarrow y=\sqrt{3x}$ and \[3{{x}^{2}}+3{{y}^{2}}=16\Rightarrow y=\sqrt{\dfrac{16-3{{x}^{2}}}{3}}\]. We know that the area bounded by any general curve y=f(x), in region x=a to x=b is given by $\int\limits_{a}^{b}{f(x)dx}$ .
$ar\left( AOD \right)=\int\limits_{0}^{\dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{6}}{\sqrt{3x}dx}+\int\limits_{\dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{6}}^{\sqrt{\dfrac{16}{3}}}{\sqrt{\dfrac{16-3{{x}^{2}}}{3}}dx}$
Now, we know that the integral of $\sqrt{x}$ is equal to $\dfrac{2\sqrt{{{x}^{3}}}}{3}$ .
\[ar\left( AOD \right)=\sqrt{3}\times \left. \dfrac{2\sqrt{{{x}^{3}}}}{3} \right|_{0}^{\dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{6}}+\int\limits_{\dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{6}}^{\sqrt{\dfrac{16}{3}}}{\sqrt{{{\left( \sqrt{\dfrac{16}{3}} \right)}^{2}}-{{x}^{2}}}dx}\]
Now we know that $\int{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}-{{x}^{2}}}dx=\dfrac{x}{2}\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}-{{x}^{2}}}}+\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}}{2}{{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{x}{a}+c$.
\[ar\left( AOD \right)=\sqrt{3}\times 2\times \dfrac{\sqrt{{{\left( \dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{6} \right)}^{3}}}}{3}\left. +\left( \dfrac{x}{2}\sqrt{\dfrac{16}{3}-{{x}^{2}}}+\dfrac{16}{6}{{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{\sqrt{3}x}{\sqrt{16}} \right) \right|_{\dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{6}}^{\sqrt{\dfrac{16}{3}}}\]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow ar\left( AOD \right)=\sqrt{3}\times 2\times \dfrac{\sqrt{{{\left( \dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{6} \right)}^{3}}}}{3}+\dfrac{16\times \pi }{6\times 2}- \\
& \left( \left( \dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{12} \right)\times \sqrt{\dfrac{16}{3}-{{\left( \dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{6} \right)}^{2}}}+\dfrac{16}{6}{{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{\sqrt{3}\times \left( -9+\sqrt{273} \right)}{6\times \sqrt{16}} \right) \\
\end{align}\]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow ar\left( AOD \right)=\sqrt{3}\times 2\times \dfrac{\sqrt{{{\left( \dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{6} \right)}^{3}}}}{3}+\dfrac{8\times \pi }{6}- \\
& \left( \left( \dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{12} \right)\times \sqrt{\dfrac{16}{3}-{{\left( \dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{6} \right)}^{2}}}+\dfrac{16}{6}{{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{\sqrt{3}\times \left( -9+\sqrt{273} \right)}{24} \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the area of the region AOBD is equal to twice the area of region AOD.
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow ar\left( AOBD \right)=4\times \sqrt{3}\times \dfrac{\sqrt{{{\left( \dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{6} \right)}^{3}}}}{3}+\dfrac{16\times \pi }{6}- \\
& 2\times \left( \left( \dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{12} \right)\times \sqrt{\dfrac{16}{3}-{{\left( \dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{6} \right)}^{2}}}+\dfrac{16}{6}{{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{\sqrt{3}\times \left( -9+\sqrt{273} \right)}{24} \right)\text{ uni}{{\text{t}}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Now if we put the approximate value of \[\dfrac{-9+\sqrt{273}}{6}\] as 1.2, we get
\[ar\left( AOBD \right)=4\times \sqrt{3}\times \dfrac{\sqrt{{{1.2}^{3}}}}{3}+\dfrac{16\times \pi }{6}-2\times \left( \left( \dfrac{1.2}{2} \right)\times \sqrt{\dfrac{16}{3}-{{1.2}^{2}}}+\dfrac{16}{6}{{\sin }^{-1}}\dfrac{\sqrt{3}\times 1.2}{4} \right)\text{ uni}{{\text{t}}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow ar\left( AOBD \right)=\left( 3.04+8.37-2\times \left( 0.592+2.66{{\sin }^{-1}}(0.5) \right) \right)\text{ uni}{{\text{t}}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow ar\left( AOBD \right)=\left( 3.04+8.37-2\times \left( 0.592+2.66\times \dfrac{\pi }{6} \right) \right)\text{ uni}{{\text{t}}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow ar\left( AOBD \right)=\left( 3.04+8.97-2\times \left( 0.592+1.395 \right) \right)\text{ uni}{{\text{t}}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow ar\left( AOBD \right)=8.036uni{{t}^{2}}\]
Therefore, the approximate answer to the above question is 8.036 sq units.
Note: Learn the graphs of different standard functions, as in such questions, the most important part is the diagram and for drawing the diagram you need to know the curves. Also, be familiar with approximate values of roots of single-digit numbers, as they are used very often. Also, be careful about the calculation part, as the calculation part is very complex and approximation is required to reach an approximate value.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




