
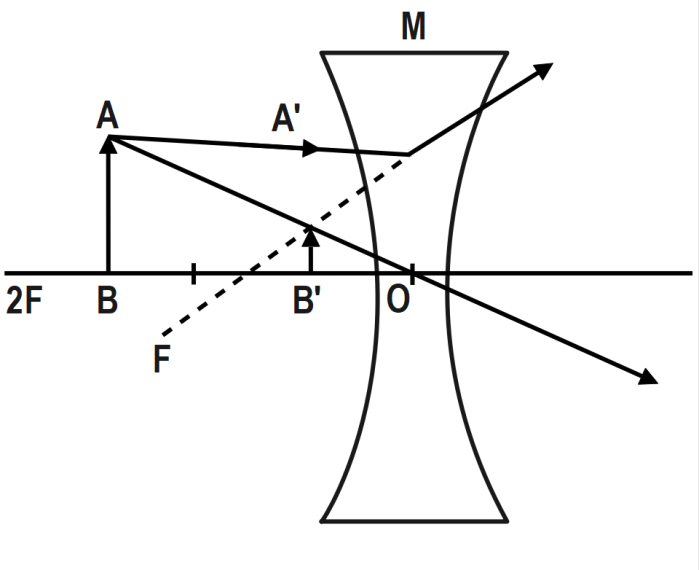
Draw a ray diagram to show the image formed by a concave lens for the object placed between $ f $ and $ 2f $ of the lens.
Answer
526.5k+ views
Hint: We know that we can use the way of tracking the rays of light in a lens. The light is coming from the object in the form of rays and the image is formed at the point where the rays intersect after passing through the lens. If the rays after passing through the lens are diverging then it means that a virtual image is formed. If the rays are converging after passing through the lens then the image formed is real.
Complete step by step answer:
An image is formed after passing through a lens because of the bending of light due to the lens refractive index. For convenience sake, the following rays are considered for tracking the rays. The ray that goes parallel to the principal axis, this ray bends and goes through the focal point after refracting. Let us consider this point as $ F $ .
The ray passing through the optic center (the center of the lens) this ray does not bend. Let us consider this center point as $ O $ . The ray that goes through the focal point and gets refracted parallel to the optical axis we trace these rays coming from the object and the point where these rays meet is where the image is formed. If the rays don’t meet and are diverging then the image is a virtual one.
Object between $ f $ and $ 2f $
Object $ \to $ between $ F~ $ and $ 2F. $
image $ \to $ between $ O $ and $ F. $
Size of image $ \to $ Diminished
Nature $ \to $ virtual and erect.
Note:
Remember that it might be noted from the above descriptions that there is a relationship between the object distance and object size and the image distance and image size. Starting from a large value, as the object distance decreases (i.e., the object is moved closer to the lens), the image distance increases, on the other hand, the image height increases.
Complete step by step answer:
An image is formed after passing through a lens because of the bending of light due to the lens refractive index. For convenience sake, the following rays are considered for tracking the rays. The ray that goes parallel to the principal axis, this ray bends and goes through the focal point after refracting. Let us consider this point as $ F $ .
The ray passing through the optic center (the center of the lens) this ray does not bend. Let us consider this center point as $ O $ . The ray that goes through the focal point and gets refracted parallel to the optical axis we trace these rays coming from the object and the point where these rays meet is where the image is formed. If the rays don’t meet and are diverging then the image is a virtual one.
Object between $ f $ and $ 2f $
Object $ \to $ between $ F~ $ and $ 2F. $
image $ \to $ between $ O $ and $ F. $
Size of image $ \to $ Diminished
Nature $ \to $ virtual and erect.

Note:
Remember that it might be noted from the above descriptions that there is a relationship between the object distance and object size and the image distance and image size. Starting from a large value, as the object distance decreases (i.e., the object is moved closer to the lens), the image distance increases, on the other hand, the image height increases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




