
Draw a ray diagram to illustrate the formation of the image obtained.
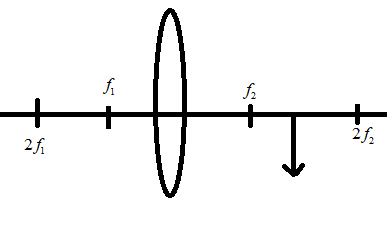

Answer
574.2k+ views
Hint: Since the given image is inverted and in between the $f_{2}$ and $2f_{2}$, then we can say that the object placed on the other side of the lens can be found using the ray diagram. We have around 5 possible situations where the image can possibly be.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the light has the ability to bend or bounce back when it interacts with a medium. This is given as the reflection and refraction of light. Here since the light rays travel from air to the lens and again to the air, we can say that they undergo refraction. Thus we can say that the object is placed on the other side of the lens. The possible positions of the object are
1. before $f_{1}$,
2. on $f_{1}$,
3. after $f_{1}$ and before $2f_{1}$,
4. on $2f_{1}$ or
5. after $2f_{1}$.
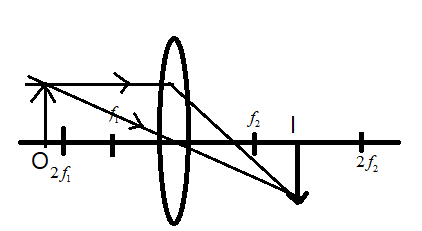
Since the given lens is convex and the image is inverted, we can clearly say that the object is placed outside the focus $f_{1}$ only. More specifically, the object is placed after $2f_{1}$, so that the image lies between the $f_{2}$ and $2f_{2}$, this can be obtained by tracing the rays from the image to the object as shown below.
Additional Information: Also, the lens makers formula as the name suggests is used in the making of the lens. Also clearly, more the refractive index of the lens or combination of lens and liquid, less the focal length. Whereas, the more the radius of curvature of the spherical lens, the more is the focal length of the lens.
The thickness of the lens is neglected. The formula can be used for any lens and when the object is placed is anywhere on the principal axis. Both the lens and the mirror formula can be used for both concave and convex mirrors. However, we must use the appropriate sign conventions.
Note: We know that the lens formula is the relationship between the distance of an object $u_{l}$, distance of Image $v_{l}$ and the focal length of the lens $f_{l}$. This law can be used for both concave and convex lenses with appropriate sign conventions. Given as $\dfrac{1}{v_{l}}- \dfrac{1}{u_{l}}=\dfrac{1}{f_{l}}$.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the light has the ability to bend or bounce back when it interacts with a medium. This is given as the reflection and refraction of light. Here since the light rays travel from air to the lens and again to the air, we can say that they undergo refraction. Thus we can say that the object is placed on the other side of the lens. The possible positions of the object are
1. before $f_{1}$,
2. on $f_{1}$,
3. after $f_{1}$ and before $2f_{1}$,
4. on $2f_{1}$ or
5. after $2f_{1}$.
Since the given lens is convex and the image is inverted, we can clearly say that the object is placed outside the focus $f_{1}$ only. More specifically, the object is placed after $2f_{1}$, so that the image lies between the $f_{2}$ and $2f_{2}$, this can be obtained by tracing the rays from the image to the object as shown below.

Additional Information: Also, the lens makers formula as the name suggests is used in the making of the lens. Also clearly, more the refractive index of the lens or combination of lens and liquid, less the focal length. Whereas, the more the radius of curvature of the spherical lens, the more is the focal length of the lens.
The thickness of the lens is neglected. The formula can be used for any lens and when the object is placed is anywhere on the principal axis. Both the lens and the mirror formula can be used for both concave and convex mirrors. However, we must use the appropriate sign conventions.
Note: We know that the lens formula is the relationship between the distance of an object $u_{l}$, distance of Image $v_{l}$ and the focal length of the lens $f_{l}$. This law can be used for both concave and convex lenses with appropriate sign conventions. Given as $\dfrac{1}{v_{l}}- \dfrac{1}{u_{l}}=\dfrac{1}{f_{l}}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




