
Draw a plot of \[{\text{lo}}{{\text{g}}_{{\text{10}}}}\left[ {\text{R}} \right]\] versus time 't' for a first order reaction. What is the slope of the line equal to?
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: The plot of \[{\text{lo}}{{\text{g}}_{{\text{10}}}}\left[ {\text{R}} \right]\] versus time 't' for a first order reaction is a straight line having negative slope. Write the integrated rate law for the first order reaction as \[{\text{lo}}{{\text{g}}_{{\text{10}}}}\left[ {\text{R}} \right]{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\left( { - \dfrac{k}{{2.303}}} \right)t{\text{ + lo}}{{\text{g}}_{{\text{10}}}}{\left[ {\text{R}} \right]_o}\]. Then compare it to the equation of the straight line \[Y = mX + C\] .Here, ‘m’ represents the slope.
Complete Step by step answer: Consider the following first order reaction:
\[{\text{R}} \to {\text{P}}\]
Here, R is the reactant and P is the product.
The rate of the first order reaction is given by the formula
\[ - \dfrac{{d\left[ {\text{R}} \right]}}{{dt}} = \dfrac{{d\left[ {\text{P}} \right]}}{{dt}} = k\left[ {\text{R}} \right]\]
Here, \[ - \dfrac{{d\left[ {\text{R}} \right]}}{{dt}}\] represents the rate at which the reactant R is consumed. It also represents the rate of the reaction. \[\dfrac{{d\left[ {\text{P}} \right]}}{{dt}}\] represents the rate of formation of the product P. k is the rate constant or the specific reaction rate. \[\left[ {\text{R}} \right]\] represents the concentration of the reactant R.
Write down the integrated rate law for the first order reaction.
\[{\text{lo}}{{\text{g}}_{{\text{10}}}}\left[ {\text{R}} \right]{\text{ }} = {\text{ lo}}{{\text{g}}_{{\text{10}}}}{\left[ {\text{R}} \right]_o} - \left( {\dfrac{k}{{2.303}}} \right)t\]
Rearrange the above rate law expression
\[{\text{lo}}{{\text{g}}_{{\text{10}}}}\left[ {\text{R}} \right]{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\left( { - \dfrac{k}{{2.303}}} \right)t{\text{ + lo}}{{\text{g}}_{{\text{10}}}}{\left[ {\text{R}} \right]_o}\]
Compare this to the equation of straight line of the type \[Y = mX + C\]
Here,
\[
Y = {\text{lo}}{{\text{g}}_{{\text{10}}}}\left[ {\text{R}} \right] \\
\Rightarrow m = - \dfrac{k}{{2.303}} \\
\Rightarrow X = t \\
\Rightarrow C = {\text{lo}}{{\text{g}}_{{\text{10}}}}{\left[ {\text{R}} \right]_o} \\
\]
Here, m is the slope and C is the Y-intercept.
When you draw a plot of logio[R] versus time 't' for a first order reaction, a straight line with negative slope is obtained.
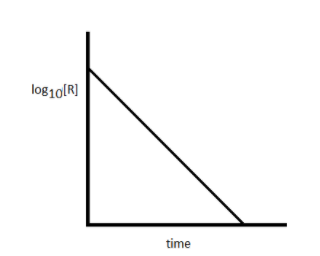
The slope of line equal to \[ - \dfrac{k}{{2.303}}\]
The Y-intercept is equal to \[{\text{lo}}{{\text{g}}_{{\text{10}}}}{\left[ {\text{R}} \right]_o}\]
Note: For the first order reaction, the rate of the reaction is directly proportional to the reactant concentration. If you plot \[{\text{lo}}{{\text{g}}_{{\text{10}}}}\left[ {\text{R}} \right]\] versus time 't' for the reaction and obtain a straight line with negative slope, then you can say that the reaction is of first order in nature.
Complete Step by step answer: Consider the following first order reaction:
\[{\text{R}} \to {\text{P}}\]
Here, R is the reactant and P is the product.
The rate of the first order reaction is given by the formula
\[ - \dfrac{{d\left[ {\text{R}} \right]}}{{dt}} = \dfrac{{d\left[ {\text{P}} \right]}}{{dt}} = k\left[ {\text{R}} \right]\]
Here, \[ - \dfrac{{d\left[ {\text{R}} \right]}}{{dt}}\] represents the rate at which the reactant R is consumed. It also represents the rate of the reaction. \[\dfrac{{d\left[ {\text{P}} \right]}}{{dt}}\] represents the rate of formation of the product P. k is the rate constant or the specific reaction rate. \[\left[ {\text{R}} \right]\] represents the concentration of the reactant R.
Write down the integrated rate law for the first order reaction.
\[{\text{lo}}{{\text{g}}_{{\text{10}}}}\left[ {\text{R}} \right]{\text{ }} = {\text{ lo}}{{\text{g}}_{{\text{10}}}}{\left[ {\text{R}} \right]_o} - \left( {\dfrac{k}{{2.303}}} \right)t\]
Rearrange the above rate law expression
\[{\text{lo}}{{\text{g}}_{{\text{10}}}}\left[ {\text{R}} \right]{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\left( { - \dfrac{k}{{2.303}}} \right)t{\text{ + lo}}{{\text{g}}_{{\text{10}}}}{\left[ {\text{R}} \right]_o}\]
Compare this to the equation of straight line of the type \[Y = mX + C\]
Here,
\[
Y = {\text{lo}}{{\text{g}}_{{\text{10}}}}\left[ {\text{R}} \right] \\
\Rightarrow m = - \dfrac{k}{{2.303}} \\
\Rightarrow X = t \\
\Rightarrow C = {\text{lo}}{{\text{g}}_{{\text{10}}}}{\left[ {\text{R}} \right]_o} \\
\]
Here, m is the slope and C is the Y-intercept.
When you draw a plot of logio[R] versus time 't' for a first order reaction, a straight line with negative slope is obtained.

The slope of line equal to \[ - \dfrac{k}{{2.303}}\]
The Y-intercept is equal to \[{\text{lo}}{{\text{g}}_{{\text{10}}}}{\left[ {\text{R}} \right]_o}\]
Note: For the first order reaction, the rate of the reaction is directly proportional to the reactant concentration. If you plot \[{\text{lo}}{{\text{g}}_{{\text{10}}}}\left[ {\text{R}} \right]\] versus time 't' for the reaction and obtain a straight line with negative slope, then you can say that the reaction is of first order in nature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




