
Draw a neat diagram of electrolytic cell used in the purification of copper and label the following:
(A) Cathode
(B) Anode
Answer
597.9k+ views
Hint: We should know that copper is purified by electrolysis. Electricity is passed through solutions containing copper compounds, such as copper (II) sulphate. The anode (positive electrode) is made from impure copper and the cathode (negative electrode) is made from pure copper.
Complete step by step solution:
> We should know that an electrolytic cell uses electrical energy to drive a non-spontaneous redox reaction. An electrolytic cell is a kind of electrochemical cell. It is often used to decompose chemical compounds, in a process called electrolysis. Important examples of electrolysis are the decomposition of water into hydrogen and oxygen, and bauxite into aluminium and other chemicals. Electrolysis is a technique that uses a direct electric current (DC). We should know that in an electrolytic cell there are three component parts: an electrolyte and two electrodes (a cathode and anode). The electrolyte is usually a solution of water or other solvents in which ions are dissolved.
> Cathode: When we talk about cathode in chemistry, it is said to be the electrode where reduction occurs. This is common in an electrochemical cell. Here, the cathode is negative as the electrical energy that is supplied to the cell results in the decomposition of chemical compounds. However, it can also be positive as in the case of a galvanic cell where a chemical reaction leads to the generation of electrical energy. In addition, a cathode is said to be either a hot cathode or a cold cathode. A cathode which is heated in the presence of a filament to emit electrons by thermionic emission is known as a hot cathode whereas cold cathodes are not heated by any filament. A cathode is usually flagged as “cold” if it emits more electrons compared to the ones generated by thermionic emission alone.
> Anode: In the most basic form, an anode in electrochemistry is the point where an oxidation reaction occurs. Generally, at an anode, negative ions or anions due to its electrical potential tend to react and give off electrons. These electrons then move up and into the driving circuit. If we take a galvanic cell, the anode is negative in nature and the electrons mostly move towards the external part of the circuit. In an electrolytic cell, it is again positive. Additionally, an anode can be a plate or wire having an excess positive charge.
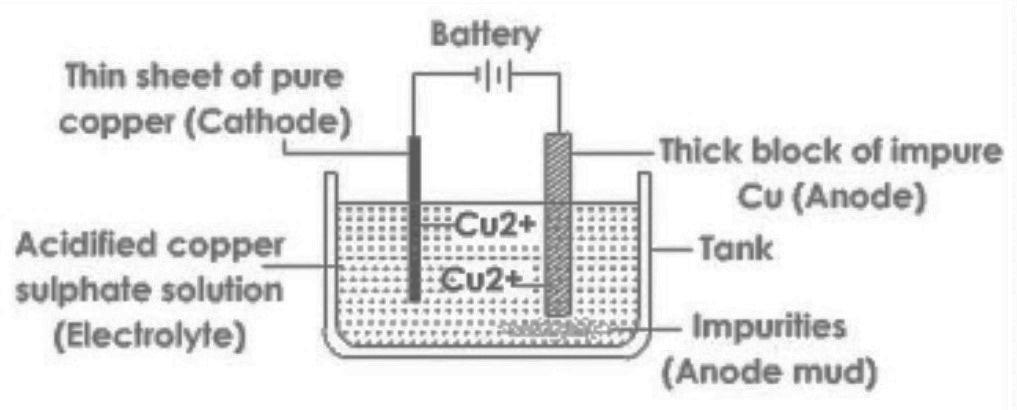
> The following diagram shows purification of copper by Electrolysis. We take impure copper from a smelter and we cast into a block to form the positive anode. The cathode is made of previously purified copper. These are dipped into an electrolyte of copper (II) sulphate solution. Then we pass D.C electrical current through the solution and electrolysis takes place. The copper anode dissolves forming blue copper (II) ions. These positive ions are attracted to the negative cathode and become copper atoms. The mass of copper dissolving at the anode exactly equals the mass of copper deposited on the cathode. The concentration of the copper (II) sulphate remains constant.
Any impurities present in the impure copper anode fall to the bottom of the electrolysis cell tank. This 'anode sludge' is not completely mineral waste; it can contain valuable metals such as silver.
Note: We should know some applications of copper and they are as follows:
Copper has properties that make it useful for electrical wiring and plumbing. Copper is a good conductor of electricity and heat, can be bent but is hard enough to be used to make pipes or tanks and does not react with water.
The alloy brass is a mixture of copper and zinc. It is a much more hard wearing metal than copper (too soft) and zinc (too brittle) but is more malleable than bronze for 'stamp
Complete step by step solution:
> We should know that an electrolytic cell uses electrical energy to drive a non-spontaneous redox reaction. An electrolytic cell is a kind of electrochemical cell. It is often used to decompose chemical compounds, in a process called electrolysis. Important examples of electrolysis are the decomposition of water into hydrogen and oxygen, and bauxite into aluminium and other chemicals. Electrolysis is a technique that uses a direct electric current (DC). We should know that in an electrolytic cell there are three component parts: an electrolyte and two electrodes (a cathode and anode). The electrolyte is usually a solution of water or other solvents in which ions are dissolved.
> Cathode: When we talk about cathode in chemistry, it is said to be the electrode where reduction occurs. This is common in an electrochemical cell. Here, the cathode is negative as the electrical energy that is supplied to the cell results in the decomposition of chemical compounds. However, it can also be positive as in the case of a galvanic cell where a chemical reaction leads to the generation of electrical energy. In addition, a cathode is said to be either a hot cathode or a cold cathode. A cathode which is heated in the presence of a filament to emit electrons by thermionic emission is known as a hot cathode whereas cold cathodes are not heated by any filament. A cathode is usually flagged as “cold” if it emits more electrons compared to the ones generated by thermionic emission alone.
> Anode: In the most basic form, an anode in electrochemistry is the point where an oxidation reaction occurs. Generally, at an anode, negative ions or anions due to its electrical potential tend to react and give off electrons. These electrons then move up and into the driving circuit. If we take a galvanic cell, the anode is negative in nature and the electrons mostly move towards the external part of the circuit. In an electrolytic cell, it is again positive. Additionally, an anode can be a plate or wire having an excess positive charge.
> The following diagram shows purification of copper by Electrolysis. We take impure copper from a smelter and we cast into a block to form the positive anode. The cathode is made of previously purified copper. These are dipped into an electrolyte of copper (II) sulphate solution. Then we pass D.C electrical current through the solution and electrolysis takes place. The copper anode dissolves forming blue copper (II) ions. These positive ions are attracted to the negative cathode and become copper atoms. The mass of copper dissolving at the anode exactly equals the mass of copper deposited on the cathode. The concentration of the copper (II) sulphate remains constant.
Any impurities present in the impure copper anode fall to the bottom of the electrolysis cell tank. This 'anode sludge' is not completely mineral waste; it can contain valuable metals such as silver.

Note: We should know some applications of copper and they are as follows:
Copper has properties that make it useful for electrical wiring and plumbing. Copper is a good conductor of electricity and heat, can be bent but is hard enough to be used to make pipes or tanks and does not react with water.
The alloy brass is a mixture of copper and zinc. It is a much more hard wearing metal than copper (too soft) and zinc (too brittle) but is more malleable than bronze for 'stamp
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




