
Draw a labelled diagram of an electric motor. Explain its principle and working. What is the function of a split ring in an electric motor?
Answer
603.3k+ views
Hint: An electric motor is a device which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. It works on the principle of electromagnetic induction. Example: electric motors are used to pump water to the overhead tanks.
Complete step-by-step solution -
An electric motor is a device which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. It works on the principle of electromagnetic induction, that is when a current carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field, it experiences a force, more specifically torque.
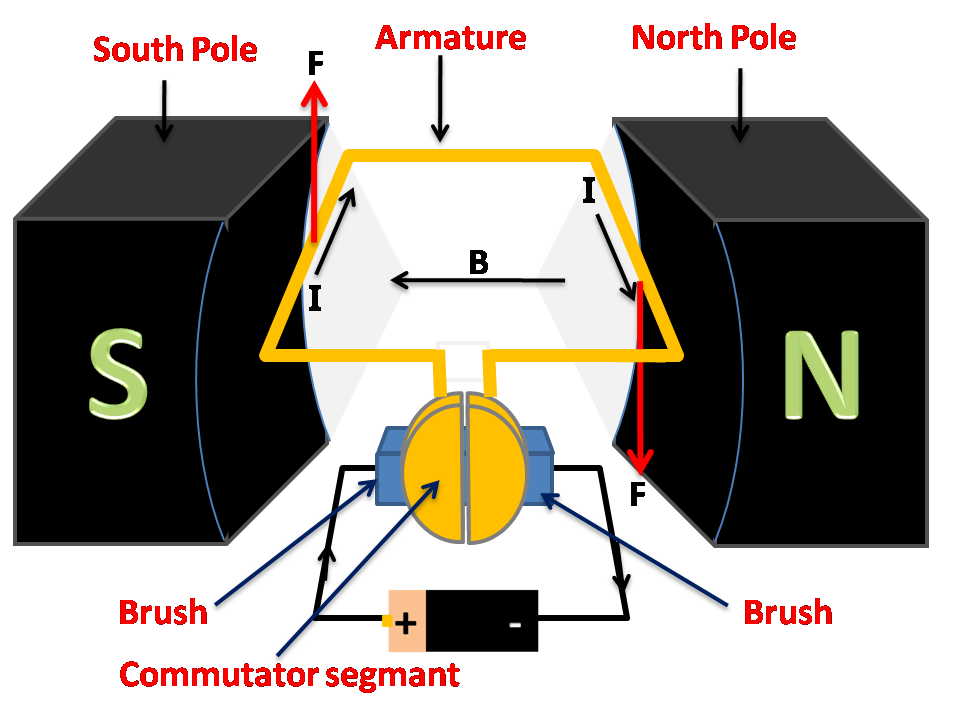
A electric motor, consists the following parts:
A dc power supply, a magnetic field which is either electromagnets or a permanent magnets, a current conducting coil, a rotor which rotates the coil, a commutator or split rings which reverse the direction of the current in the circuit and axle or brushes which are flexible and conducts electricity between the moving coil and the circuit.
When current flows through the coil which are placed in between the magnets. According to Fleming’s left hand rule, since the current is perpendicular to the magnetic field, the coil experiences a torque, due to which the coil starts to rotate. When the coil completes half the rotation, the DC current gets reversed, causing the torque in the opposite direction. This results in the coil to rotate in the completing the other half cycle in the same direction. This cycle continues.
Examples are: an electric motor is used to pump water to the overhead tanks.
A motor converts electrical energy to mechanical energy, whereas a generator converts mechanical energy to electrical energy.
Note: A motor converts electrical energy to mechanical energy, whereas a generator converts mechanical energy to electrical energy. The split rings reverse the direction of the current in the circuit, after every half cycle.
Complete step-by-step solution -
An electric motor is a device which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. It works on the principle of electromagnetic induction, that is when a current carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field, it experiences a force, more specifically torque.

A electric motor, consists the following parts:
A dc power supply, a magnetic field which is either electromagnets or a permanent magnets, a current conducting coil, a rotor which rotates the coil, a commutator or split rings which reverse the direction of the current in the circuit and axle or brushes which are flexible and conducts electricity between the moving coil and the circuit.
When current flows through the coil which are placed in between the magnets. According to Fleming’s left hand rule, since the current is perpendicular to the magnetic field, the coil experiences a torque, due to which the coil starts to rotate. When the coil completes half the rotation, the DC current gets reversed, causing the torque in the opposite direction. This results in the coil to rotate in the completing the other half cycle in the same direction. This cycle continues.
Examples are: an electric motor is used to pump water to the overhead tanks.
A motor converts electrical energy to mechanical energy, whereas a generator converts mechanical energy to electrical energy.
Note: A motor converts electrical energy to mechanical energy, whereas a generator converts mechanical energy to electrical energy. The split rings reverse the direction of the current in the circuit, after every half cycle.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

How is the angle of emergence e related to the angle class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between lanthanoids and actinoids class 12 chemistry CBSE

Derive Lens Makers formula for a convex lens class 12 physics CBSE

a Draw Labelled diagram of Standard Hydrogen Electrode class 12 chemistry CBSE




