
Draw a labeled ray diagram for the formation of an image by a convex lens of focal length $15cm$ when the object is placed at a distance $25cm$ from the lens. Determine the size of the image formed, if the size of the object is $4cm$.
Answer
575.1k+ views
Hint Convex lenses are thicker at the center. Rays of light that have the lens are brought nearer along (they converge). A convex lens may be a converging lens. When parallel rays of light have a convex lens, the refracted rays converge at the focus. The image fashioned is (in most cases, however, there are exceptions) real, inverted, and enlarged - we'll use this lens as a scientific instrument, or a simple lens by itself. It’s conjointly referred to as a “positive” lens.
Formula used
Lens formula,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$
Where,
$v$ is the image distance from the center.
$u$ Is the object distance from the center.
And $f$ will be the focal length of the lens.
Complete Step by Step Solution
Since it is a convex lens, and we have some know values given as-
$f = + 15cm$, $u = - 25cm$, ${h_1} = 4cm$
As we know the formula for the lens, so by using it
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$
From here we will calculate the value for the focal length
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{{ - 25}} = \dfrac{1}{{25}}$
Now, putting the value of focal length to get the image distance
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{{25}} = \dfrac{1}{{15}}$
On further solving more, we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{{15}} - \dfrac{1}{{25}}$
After simplifying the above equation,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{5 - 3}}{{75}} = \dfrac{2}{{75}}$
$ \Rightarrow v = \dfrac{{75}}{2} = 37.5cm$
Now the ratio of the height of an image to the height of an object can be written as,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{h_2}}}{{{h_1}}} = \dfrac{v}{u}$
On substituting the values of object and image distance, we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{h_2}}}{4} = \dfrac{{75}}{{2 \times \left( { - 75} \right)}}$
$ \Rightarrow {h_2} = \dfrac{{ - 75}}{{2 \times 25}} \times 4 = - 6cm$
So from the above, we have got the real and inverted image that is formed $37.5cm$away from the lens on the other side of an object. Now the diagram for the above values will be like this:
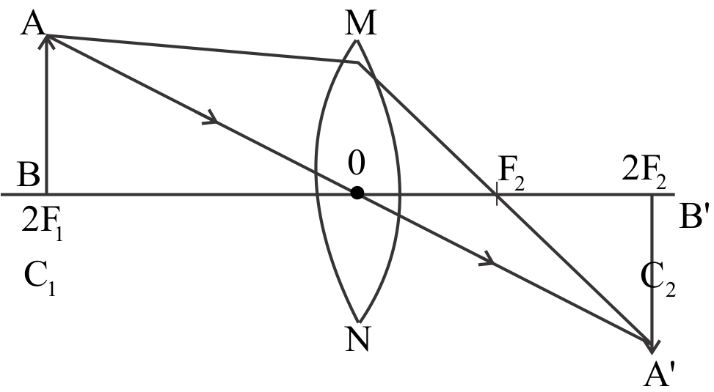
Note Concave lenses are thinner at the center. Rays of light that experience the lens are detached (they diverge). A concave lens could be a diverging lens. When parallel rays of light experience a concave lens the refracted rays diverge so they seem to come back from one purpose known as the principal focus. The image fashioned is virtual, upright, and diminished. It’s additionally known as the “negative” lens. This lens can’t be wont to kind a picture by itself, however, in combination(s) with positive (converging) lenses, it's wont to shorten the focal distance.
Formula used
Lens formula,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$
Where,
$v$ is the image distance from the center.
$u$ Is the object distance from the center.
And $f$ will be the focal length of the lens.
Complete Step by Step Solution
Since it is a convex lens, and we have some know values given as-
$f = + 15cm$, $u = - 25cm$, ${h_1} = 4cm$
As we know the formula for the lens, so by using it
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$
From here we will calculate the value for the focal length
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{{ - 25}} = \dfrac{1}{{25}}$
Now, putting the value of focal length to get the image distance
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{{25}} = \dfrac{1}{{15}}$
On further solving more, we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{{15}} - \dfrac{1}{{25}}$
After simplifying the above equation,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{5 - 3}}{{75}} = \dfrac{2}{{75}}$
$ \Rightarrow v = \dfrac{{75}}{2} = 37.5cm$
Now the ratio of the height of an image to the height of an object can be written as,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{h_2}}}{{{h_1}}} = \dfrac{v}{u}$
On substituting the values of object and image distance, we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{h_2}}}{4} = \dfrac{{75}}{{2 \times \left( { - 75} \right)}}$
$ \Rightarrow {h_2} = \dfrac{{ - 75}}{{2 \times 25}} \times 4 = - 6cm$
So from the above, we have got the real and inverted image that is formed $37.5cm$away from the lens on the other side of an object. Now the diagram for the above values will be like this:

Note Concave lenses are thinner at the center. Rays of light that experience the lens are detached (they diverge). A concave lens could be a diverging lens. When parallel rays of light experience a concave lens the refracted rays diverge so they seem to come back from one purpose known as the principal focus. The image fashioned is virtual, upright, and diminished. It’s additionally known as the “negative” lens. This lens can’t be wont to kind a picture by itself, however, in combination(s) with positive (converging) lenses, it's wont to shorten the focal distance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




