
Draw a duplicated chromosome and label its parts.
Answer
581.4k+ views
Hint: Chromosomes are the thread-like structures found in the nucleus that carry genetic information from generation to generation. They play a vital role in the process of cell division, heredity, variability, mutation, repair and regeneration.
Complete answer: Structure of chromosome: Each cell has a pair of each type of chromosome, called homologous chromosomes. Chromosomes are made up of chromatin, which contains a single DNA molecule and related proteins. Each chromosome contains hundreds and thousands of genes that can precisely encode several proteins in a cell. The chromosome structure is best seen during cell division.
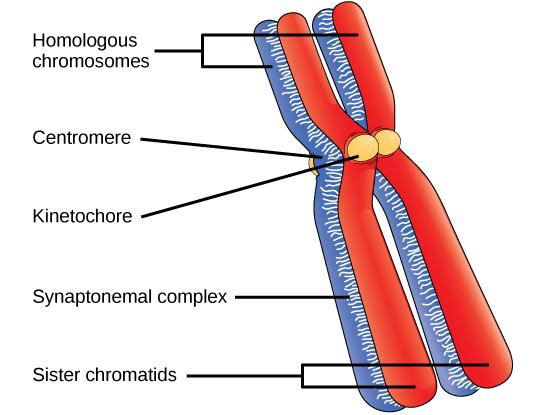
i. Centromere and kinetochore: Sister chromatids are linked by a centromere. Spindle fibres attach to the centromere during cell division. The number and position of the centromere vary in different chromosomes. The centromere is called the primary stenosis. It splits the chromosome into two parts, the shorter arm is known as the "p" arm and the longer arm is known as the "q" arm. A centromere contains a disk-shaped kinetochore that has a specific DNA sequence with special proteins associated with them. The kinetochore is the centre of tubulin protein polymerization and microtubule formation
ii. Chromatids: Each chromosome has two symmetrical structures called chromatids or sister chromatids that are visible in the mitotic metaphase. Each chromatid contains a single DNA molecule in mitotic cell division anaphase, sister chromatids separate and migrates to opposite poles
iii. The synaptonemal complex: It is a protein structure that is developed between homologous chromosomes during meiosis and is believed to mediate synapse and recombination during meiosis I in eukaryotes
Note: Chromosomes determine the sex: male gametes or sperm in humans and other mammals contain one of two types of sex chromosomes: X or Y. Female gametes or eggs, however, contain only X chromosomes, so if a sperm cell contains an X chromosome fertilizes the egg, the resulting zygote will be XX or female. Alternatively, if the sperm contains a Y chromosome, then the resulting zygote will be XY or male.
Complete answer: Structure of chromosome: Each cell has a pair of each type of chromosome, called homologous chromosomes. Chromosomes are made up of chromatin, which contains a single DNA molecule and related proteins. Each chromosome contains hundreds and thousands of genes that can precisely encode several proteins in a cell. The chromosome structure is best seen during cell division.

i. Centromere and kinetochore: Sister chromatids are linked by a centromere. Spindle fibres attach to the centromere during cell division. The number and position of the centromere vary in different chromosomes. The centromere is called the primary stenosis. It splits the chromosome into two parts, the shorter arm is known as the "p" arm and the longer arm is known as the "q" arm. A centromere contains a disk-shaped kinetochore that has a specific DNA sequence with special proteins associated with them. The kinetochore is the centre of tubulin protein polymerization and microtubule formation
ii. Chromatids: Each chromosome has two symmetrical structures called chromatids or sister chromatids that are visible in the mitotic metaphase. Each chromatid contains a single DNA molecule in mitotic cell division anaphase, sister chromatids separate and migrates to opposite poles
iii. The synaptonemal complex: It is a protein structure that is developed between homologous chromosomes during meiosis and is believed to mediate synapse and recombination during meiosis I in eukaryotes
Note: Chromosomes determine the sex: male gametes or sperm in humans and other mammals contain one of two types of sex chromosomes: X or Y. Female gametes or eggs, however, contain only X chromosomes, so if a sperm cell contains an X chromosome fertilizes the egg, the resulting zygote will be XX or female. Alternatively, if the sperm contains a Y chromosome, then the resulting zygote will be XY or male.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE




