
Draw a diagram of the microscopic structure of human sperm. Label the following parts in it and write their functions: (a) Acrosome (b) Nucleus (c) Middle piece.
Answer
540.9k+ views
Hint: Sperm is a tadpole-like structure with the presence of a single flagella known as the tail of sperm and it is covered with plasma membrane all around its surface. A sperm is divided into four parts: head, neck, middle piece and tail, where the head part consists of a nucleus with chromosomal material.
Complete answer:
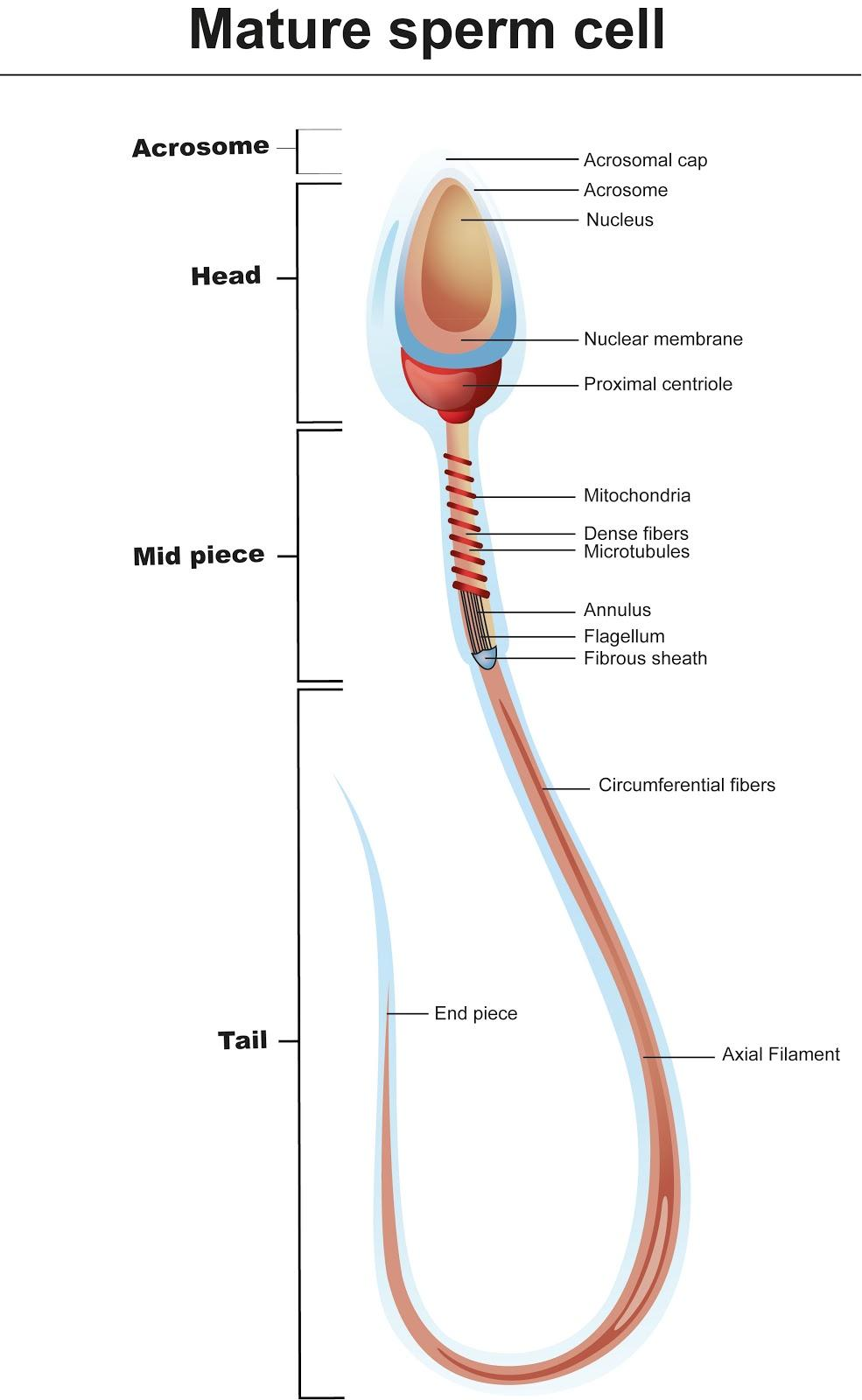
A sperm is a tadpole-like uniflagellate, which is covered with plasma membrane all around its surface. A sperm has mainly four parts like head, neck, middle piece and tail.
-Acrosome is present anterior to the head part of sperm which covers around two-third part of the head surface. It is also called a cap-like acrosome. It consists of enzymes like hyaluronidase, corona penetrating enzyme, acrosin and zona lysin and these enzymes are collectively known as sperm lysin. Enzyme acrosin helps in gamete fusion and zona pellucida penetration which enable the entry of sperm inside the ovum by breaking the thick zona pellucida membrane and fusion of both plasma membranes which results in fertilisation.
-Nucleus is present inside the headpiece of sperm with less dense surface known as nuclear vacuoles. It is haploid with 23 chromosomes which after fertilization with ovum form diploid zygote.
- The middle piece of sperm is a long cylindrical structure which is 5-7 micrometre in length and about 1 micrometre in diameter. It consists of axial filaments of microtubules which are covered by a mitochondrial spiral sheath. This mitochondrial sheath helps in providing energy for sperm swimming toward the ovum. It also resists the death of sperm cells.
Note:
The function of acrosome is similar to lysosome as both consist of lysosomal enzyme hyaluronidase and acrosin. The acrosome is derived from the Golgi complex of spermatid whereas lysosome is derived from the Golgi complex of a normal cell.
In teleost fish acrosomes are absent and fertilisation takes place by the entry of sperm through the micropylar region of the egg.
Complete answer:

A sperm is a tadpole-like uniflagellate, which is covered with plasma membrane all around its surface. A sperm has mainly four parts like head, neck, middle piece and tail.
-Acrosome is present anterior to the head part of sperm which covers around two-third part of the head surface. It is also called a cap-like acrosome. It consists of enzymes like hyaluronidase, corona penetrating enzyme, acrosin and zona lysin and these enzymes are collectively known as sperm lysin. Enzyme acrosin helps in gamete fusion and zona pellucida penetration which enable the entry of sperm inside the ovum by breaking the thick zona pellucida membrane and fusion of both plasma membranes which results in fertilisation.
-Nucleus is present inside the headpiece of sperm with less dense surface known as nuclear vacuoles. It is haploid with 23 chromosomes which after fertilization with ovum form diploid zygote.
- The middle piece of sperm is a long cylindrical structure which is 5-7 micrometre in length and about 1 micrometre in diameter. It consists of axial filaments of microtubules which are covered by a mitochondrial spiral sheath. This mitochondrial sheath helps in providing energy for sperm swimming toward the ovum. It also resists the death of sperm cells.
Note:
The function of acrosome is similar to lysosome as both consist of lysosomal enzyme hyaluronidase and acrosin. The acrosome is derived from the Golgi complex of spermatid whereas lysosome is derived from the Golgi complex of a normal cell.
In teleost fish acrosomes are absent and fertilisation takes place by the entry of sperm through the micropylar region of the egg.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




