
What is the domain and range of $y = \dfrac{1}{{x - 3}}$ ?
Answer
513.6k+ views
Hint:The domain of a graph refers to the set of potential input values. The domain of a function includes all of the input values of x displayed on the x-axis. The range of the function is the set of all the values that the function can assume. Range is the set of possible values of y for every value of x in the domain. For finding the domain of a rational function, we must ensure that the denominator is not equal to zero. Also, for finding the range of a function, we find x in the terms of y and find out the permissible values of y for x belonging to the domain.
Complete step by step answer:
So, we have, $y = \dfrac{1}{{x - 3}}$. We know that the denominator cannot be equal to zero.So, we set the denominator of the function not equal to zero and find the permissible values of $x$. This is because we cannot divide by zero, which means the denominator can't be zero.So, we get, $\left( {x - 3} \right) \ne 0$
\[ \Rightarrow x \ne 3\]
Thus, $x$ assumes all the real values of x except the number $3$. So, the domain of the function is $\left( { - \inf , - 3} \right) \cup \left( {3,\inf } \right)$. So, as we can see, $x$ does not equals three as the domain excludes the number. So, there is a discontinuity in the graph for $x = 3$. Now, for the range of the function, we find $x$ in terms of $y$.
So, we have, $y = \dfrac{1}{{x - 3}}$
$ \Rightarrow x - 3 = \dfrac{1}{y}$
Isolating x in left side of the equation, we get,
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{1}{y} + 3$
Taking LCM of the denominators, we get,
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{1 + 3y}}{y}$
Now, we know that the denominator of a rational function cannot be zero.
Hence, we get, $y \ne 0$.
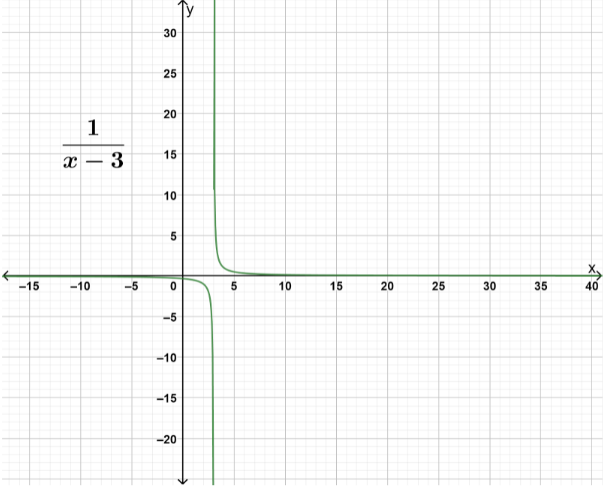
Hence, the range of the function $y = \dfrac{1}{{x - 3}}$ is all real values except zero.
Note:We must have basic knowledge about the terms domain and range. There are various methods to find the domain and range of different types of functions. In a rational function, the denominator must not be equal to zero. Also, we must know about transposition and rules of simplification in order to tackle these types of problems.
Complete step by step answer:
So, we have, $y = \dfrac{1}{{x - 3}}$. We know that the denominator cannot be equal to zero.So, we set the denominator of the function not equal to zero and find the permissible values of $x$. This is because we cannot divide by zero, which means the denominator can't be zero.So, we get, $\left( {x - 3} \right) \ne 0$
\[ \Rightarrow x \ne 3\]
Thus, $x$ assumes all the real values of x except the number $3$. So, the domain of the function is $\left( { - \inf , - 3} \right) \cup \left( {3,\inf } \right)$. So, as we can see, $x$ does not equals three as the domain excludes the number. So, there is a discontinuity in the graph for $x = 3$. Now, for the range of the function, we find $x$ in terms of $y$.
So, we have, $y = \dfrac{1}{{x - 3}}$
$ \Rightarrow x - 3 = \dfrac{1}{y}$
Isolating x in left side of the equation, we get,
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{1}{y} + 3$
Taking LCM of the denominators, we get,
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{1 + 3y}}{y}$
Now, we know that the denominator of a rational function cannot be zero.
Hence, we get, $y \ne 0$.

Hence, the range of the function $y = \dfrac{1}{{x - 3}}$ is all real values except zero.
Note:We must have basic knowledge about the terms domain and range. There are various methods to find the domain and range of different types of functions. In a rational function, the denominator must not be equal to zero. Also, we must know about transposition and rules of simplification in order to tackle these types of problems.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




