
Does VSEPR theory predict that $Xe{F_2}$ is linear?
Answer
495.9k+ views
Hint: The valence shell electron pair repulsion theory i.e., VSEPR theory is generally used to predict the molecular geometry of a compound. The basic feature of this theory is that repulsions among the pair of electrons on the central atom, be it a bonding or nonbonding electron pair, will control the overall geometry of the molecule.
Complete answer:
According to VSEPR theory, to decide the geometry of a molecule following steps must be followed:
1. The least electronegative atom is always considered as the central atom since this atom has the highest tendency to share its electrons with other atoms bonded to it.
2. The total number of valence electrons for the central atom must be counted.
3. Add one electron for each bonding atom i.e., count the number of bonds formed by the central atom.
4. Add or subtract the electrons for the charge (if any) for the molecule.
5. Divide the total of above values by 2 to find the total number of electron pairs which is also known as VESP number.
Now, as per above steps the geometry of $Xe{F_2}$ will be as follows:
In the $Xe{F_2}$ molecule, there are three lone pairs which occupy the equatorial positions and fluorine atoms occupy axial positions in order to minimize repulsion between lone pair of electrons. The structure of $Xe{F_2}$ can be represented as follows:
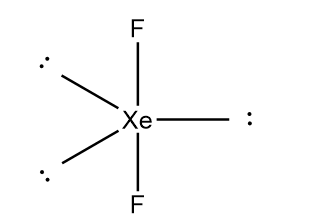
Thus, we can conclude that VSEPR theory accurately predicts that $Xe{F_2}$ is linear.
Note:
It is important to note that nonbonding orbitals exert more repulsions as compared to bonding orbitals because a nonbonding orbital has no nucleus at its far end so as to attract electron cloud towards it and thus, the charge in that orbital is concentrated on the central atom and due to which the repulsions are maximized.
Complete answer:
According to VSEPR theory, to decide the geometry of a molecule following steps must be followed:
1. The least electronegative atom is always considered as the central atom since this atom has the highest tendency to share its electrons with other atoms bonded to it.
2. The total number of valence electrons for the central atom must be counted.
3. Add one electron for each bonding atom i.e., count the number of bonds formed by the central atom.
4. Add or subtract the electrons for the charge (if any) for the molecule.
5. Divide the total of above values by 2 to find the total number of electron pairs which is also known as VESP number.
Now, as per above steps the geometry of $Xe{F_2}$ will be as follows:
| Central atom | $Xe$ |
| Valence electrons on central atom | $8$ |
| Contributing 1 electron for each fluorine atom | $2$ |
| Total | $10$ |
| Dividing by 2 to get VESP number | $5$ |
| Hybridization | $s{p^3}d$ |
| Number of lone pairs on central atom | $3$ |
| Geometry corresponding to VESP number | Linear |
In the $Xe{F_2}$ molecule, there are three lone pairs which occupy the equatorial positions and fluorine atoms occupy axial positions in order to minimize repulsion between lone pair of electrons. The structure of $Xe{F_2}$ can be represented as follows:

Thus, we can conclude that VSEPR theory accurately predicts that $Xe{F_2}$ is linear.
Note:
It is important to note that nonbonding orbitals exert more repulsions as compared to bonding orbitals because a nonbonding orbital has no nucleus at its far end so as to attract electron cloud towards it and thus, the charge in that orbital is concentrated on the central atom and due to which the repulsions are maximized.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




