
Why does the solution of chloroform and acetone show negative deviation from Raoult’s law?
Illustrate the deviation with the help of diagrams.
Answer
529.4k+ views
Hint: Negative deviations of non-ideal solution from Raoult's law arise when the new intermolecular interactions formed by mixing the component A and B (A-B) are stronger than the intermolecular interactions of pure components (A-A and A-B ). Example, phenol and aniline.
Complete step by step answer:
-Raoult’s law states that a solvent’s partial vapour pressure in a mixture or solution is identical to the vapour pressure of the pure solvent multiplied by its mole fraction. Solutions which obey this law are ideal solutions and which do not obey are non-ideal solutions.
-Non-ideal solutions are of two types. Solutions showing positive deviation from Raaoult’s law and solutions showing negative deviation from Raoult’s law.
-For solutions showing negative deviation from Raoult’s law, solvent-solute type of force is stronger than their pure ones. Also, the vapour pressure is lower than predicted by the law. This occurs due to the existence of strong hydrogen bonding between the two molecules when combined. This molecular force of attraction lowers the vapour pressure as it is hard to break the hydrogen bond.
-Their \[\Delta {H_{mixing}} < 0\] and \[\Delta {V_{mixing}} < 0\], each component is retained in the liquid phase due to attractive forces which are stronger than that in the pure liquid as its vapour pressure is low.
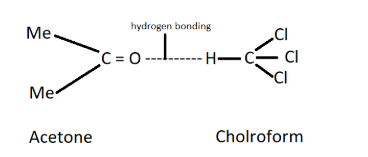
For example, chloroform and acetone show negative deviation from Raoult’s law. This is because there is an attractive interaction between these two that results in the formation of a hydrogen bonding as shown below.
Note:
The solutions which do not obey Raoult’s law, can be volatile or non-volatile. They can either dissociate or associate in a solution. Because the solutions that obey the law have these limitations that the solution should contain non-volatile solutes only and must not associate or dissociate in solution.
Complete step by step answer:
-Raoult’s law states that a solvent’s partial vapour pressure in a mixture or solution is identical to the vapour pressure of the pure solvent multiplied by its mole fraction. Solutions which obey this law are ideal solutions and which do not obey are non-ideal solutions.
-Non-ideal solutions are of two types. Solutions showing positive deviation from Raaoult’s law and solutions showing negative deviation from Raoult’s law.
-For solutions showing negative deviation from Raoult’s law, solvent-solute type of force is stronger than their pure ones. Also, the vapour pressure is lower than predicted by the law. This occurs due to the existence of strong hydrogen bonding between the two molecules when combined. This molecular force of attraction lowers the vapour pressure as it is hard to break the hydrogen bond.
-Their \[\Delta {H_{mixing}} < 0\] and \[\Delta {V_{mixing}} < 0\], each component is retained in the liquid phase due to attractive forces which are stronger than that in the pure liquid as its vapour pressure is low.
For example, chloroform and acetone show negative deviation from Raoult’s law. This is because there is an attractive interaction between these two that results in the formation of a hydrogen bonding as shown below.

Note:
The solutions which do not obey Raoult’s law, can be volatile or non-volatile. They can either dissociate or associate in a solution. Because the solutions that obey the law have these limitations that the solution should contain non-volatile solutes only and must not associate or dissociate in solution.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




