
What does the law of dominance state?
Answer
534.9k+ views
Hint: Gregor Mendel, after performing his experiments on pea plants, discovered the fundamental laws of inheritance. He proposed three laws of inheritance which we are studying to date. One law explains the power of one trait over the other.
Complete answer
According to Mendel's law of dominance “when parents with pure contrasting traits are crossed together, only one form of trait appears in the next generation. Only the dominant phenotypic trait will be exhibited even in the hybrid offspring. “
The first law of inheritance is also called the Law of Dominance. It is explained in this law that all of the traits, or the characters are controlled by the unit called the factors. These factors are found to be in pairs and are called alleles. If they occur in the same pair they are called homozygous, they can be either dominant or recessive and if the alleles occur in a different pair then it is called heterozygous, It will always be dominant.
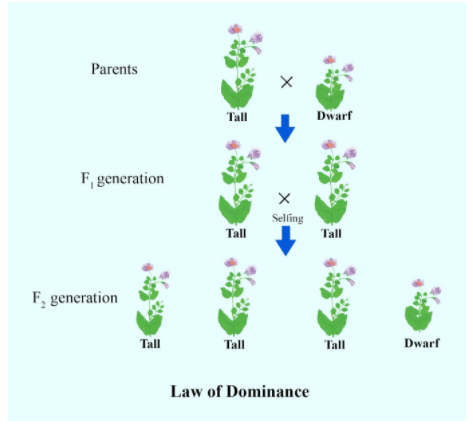
The Mendel’s law of dominance is well explained with the help of the monohybrid cross in between the parents having tallness (TT) and dwarfness (tt) as a single trait. In the first filial generation, the ratio obtained after the selfing of the two parents is 3:1, which means that all 4 are tall but 3 are homozygous while the 1 is heterozygous. There will be no dwarf plant because of the presence of ‘T’ (tallness) as a dominant trait while ‘t’ (dwarfness) is the recessive trait.
The hybrid formed after the selfing of these parents will have only one dominant trait and one recessive trait which does not show up.
Note: In 1865 and 1866 Gregor Johann Mendel originally proposed the Mendelian inheritance. In 1900, William Bateson rediscovered the Mendelian inheritance and made it infamous. The crossing of two parents is the basis of Mendel’s law which results in the formation of the offspring. The phenotypic ratio differs in the both the first and the second filial generation.
Complete answer
According to Mendel's law of dominance “when parents with pure contrasting traits are crossed together, only one form of trait appears in the next generation. Only the dominant phenotypic trait will be exhibited even in the hybrid offspring. “
The first law of inheritance is also called the Law of Dominance. It is explained in this law that all of the traits, or the characters are controlled by the unit called the factors. These factors are found to be in pairs and are called alleles. If they occur in the same pair they are called homozygous, they can be either dominant or recessive and if the alleles occur in a different pair then it is called heterozygous, It will always be dominant.
The Mendel’s law of dominance is well explained with the help of the monohybrid cross in between the parents having tallness (TT) and dwarfness (tt) as a single trait. In the first filial generation, the ratio obtained after the selfing of the two parents is 3:1, which means that all 4 are tall but 3 are homozygous while the 1 is heterozygous. There will be no dwarf plant because of the presence of ‘T’ (tallness) as a dominant trait while ‘t’ (dwarfness) is the recessive trait.
The hybrid formed after the selfing of these parents will have only one dominant trait and one recessive trait which does not show up.

Note: In 1865 and 1866 Gregor Johann Mendel originally proposed the Mendelian inheritance. In 1900, William Bateson rediscovered the Mendelian inheritance and made it infamous. The crossing of two parents is the basis of Mendel’s law which results in the formation of the offspring. The phenotypic ratio differs in the both the first and the second filial generation.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




