
How does the embryo get nourishment inside the mother’s body?
Answer
597.9k+ views
Hint: The embryonic membranes, allantois, and chorion of the fetus develop a connection between the umbilical cord and the mother's uterine cavity. It helps in the exchange of all nutrients, gases, and waste products.
Complete answer:
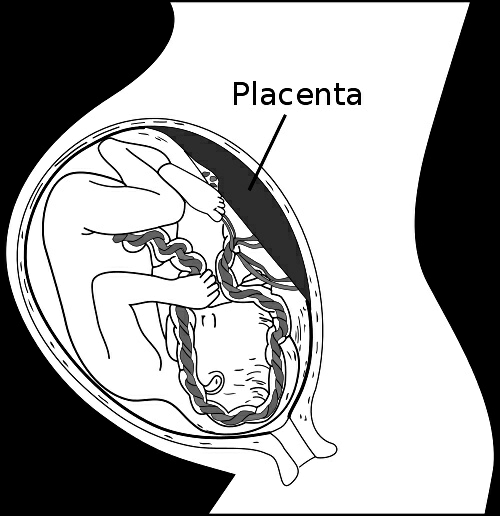
The embryo grows inside the mother’s womb and gets nourishment from the mother’s blood through the tissue called the placenta. The placenta is a temporary organ that connects the developing fetus to the uterine cavity of the mother via the umbilical. It facilitates the uptake of nutrients and the exchange of gases and waste products from the fetus to the mother. It also helps in regulating the body temperature of the fetus.
Additional Information:
Humans have a chorioallantoic placenta that forms from the chorion and allantois. In humans, the placenta is approximately 22 cm in length and weighs approximately 500 grams. It has a dark reddish-blue or crimson color. It connects to the fetus by an umbilical cord of approximately 55–60 cm in length, which contains two umbilical arteries and one umbilical vein.
Note: Numerous pathologies can affect the placenta like-
1. Placenta accreta- It is caused by the deep plantation of the placenta into the wall of the uterus.
2. Placenta praevia- It is caused by the placement of the placenta in such a way that either it is too close to the cervix or blocks the cervix.
3. Placental abruption- The premature detachment of the placenta is known as placental abruption.
Complete answer:
The embryo grows inside the mother’s womb and gets nourishment from the mother’s blood through the tissue called the placenta. The placenta is a temporary organ that connects the developing fetus to the uterine cavity of the mother via the umbilical. It facilitates the uptake of nutrients and the exchange of gases and waste products from the fetus to the mother. It also helps in regulating the body temperature of the fetus.
Additional Information:
Humans have a chorioallantoic placenta that forms from the chorion and allantois. In humans, the placenta is approximately 22 cm in length and weighs approximately 500 grams. It has a dark reddish-blue or crimson color. It connects to the fetus by an umbilical cord of approximately 55–60 cm in length, which contains two umbilical arteries and one umbilical vein.

Note: Numerous pathologies can affect the placenta like-
1. Placenta accreta- It is caused by the deep plantation of the placenta into the wall of the uterus.
2. Placenta praevia- It is caused by the placement of the placenta in such a way that either it is too close to the cervix or blocks the cervix.
3. Placental abruption- The premature detachment of the placenta is known as placental abruption.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




