
How does pH affect amino acid structure?
Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint: We need to know the amino acid structure and accordingly understand the effect of pH on its structure. An amino acid is an organic molecule that is made up of a basic amino group $\left( { - N{H_2}} \right)$ , an acidic carboxyl group $\left( { - COOH} \right)$ , and an organic R group (or side chain) which is unique to each of the $20$ amino acids, and a hydrogen atom. In addition to the structure, we must know that the amino acids are amphoteric in nature, that is they can act both as an acid or a base hence they are greatly affected by pH.
Complete step by step answer:
We need to know that since amino acids are amphoteric in nature, they can act both as an acid or a base hence affected by pH. They have the capacity to protonate as well as deprotonate. Here the concept of $p{K_a}$ comes into picture. The $p{K_a}$ value given for the amino group on any amino acid specifically refers to the equilibrium between the protonated positive nitrogen and deprotonated neutral nitrogen. Both the amino as well as the carboxyl groups have the capacity to protonate as well as deprotonate, hence it has two $p{K_a}$ values.
-The $p{K_a}$ of the carboxyl group is always lower than that of the amino group hence when pH increases, the carboxyl group will be deprotonated before the amino group.
-The $p{K_b}$ values for amino groups are lower than that of carboxyl groups, hence the amino groups will be protonated before the carboxyl groups.
The structures of amino acids with respect to pH is given below:
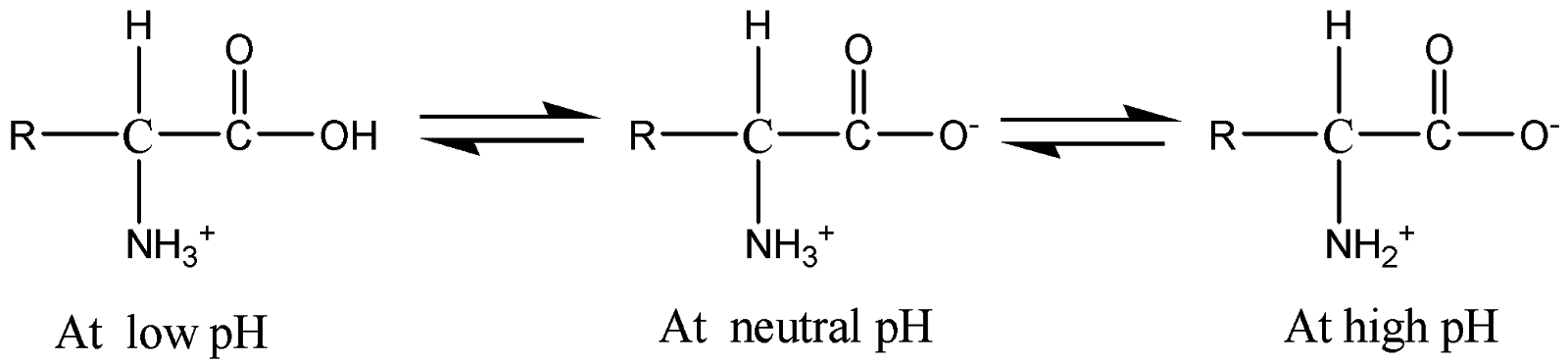
The forward arrow represents deprotonation and the backward arrow represents protonation of amino acids with respect to pH.
Hence pH directly affects the structure of amino acids as a slight increase in pH will protonate and deprotonated the amino acid.
Note:
It must be noted that amino acids are zwitterionic in nature. A zwitterion is a compound that has no overall charge but that has charge separation within it. An amino acid is therefore zwitterionic at neutral pH and this pH is known as the isoelectric point. The zwitterionic nature of amino acids has an effect on their properties.
Complete step by step answer:
We need to know that since amino acids are amphoteric in nature, they can act both as an acid or a base hence affected by pH. They have the capacity to protonate as well as deprotonate. Here the concept of $p{K_a}$ comes into picture. The $p{K_a}$ value given for the amino group on any amino acid specifically refers to the equilibrium between the protonated positive nitrogen and deprotonated neutral nitrogen. Both the amino as well as the carboxyl groups have the capacity to protonate as well as deprotonate, hence it has two $p{K_a}$ values.
-The $p{K_a}$ of the carboxyl group is always lower than that of the amino group hence when pH increases, the carboxyl group will be deprotonated before the amino group.
-The $p{K_b}$ values for amino groups are lower than that of carboxyl groups, hence the amino groups will be protonated before the carboxyl groups.
The structures of amino acids with respect to pH is given below:

The forward arrow represents deprotonation and the backward arrow represents protonation of amino acids with respect to pH.
Hence pH directly affects the structure of amino acids as a slight increase in pH will protonate and deprotonated the amino acid.
Note:
It must be noted that amino acids are zwitterionic in nature. A zwitterion is a compound that has no overall charge but that has charge separation within it. An amino acid is therefore zwitterionic at neutral pH and this pH is known as the isoelectric point. The zwitterionic nature of amino acids has an effect on their properties.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE

Explain sex determination in humans with line diag class 12 biology CBSE

Organisms of a higher trophic level which feed on several class 12 biology CBSE




