
Why does obtaining the image of the sun on a paper with the help of a concave mirror burn the paper?
Answer
561k+ views
Hint: When the light reflects back from a mirror, none of it is absorbed, its energy is completely reflected back. A concave mirror is a type of spherical mirror in which the concave part is the reflecting part.
Complete answer:
Light is a form of energy which enables us to see.
Mirrors are silvered surfaces which have the ability to reflect maximum light energy when it strikes the mirror.
Mirrors can be classified into two types. First, the plane mirror, in which the surface which is silvered is a plane surface. Second, the spherical mirror, in which the surface which is silvered is a spherical surface.
Spherical mirrors can further be classified into concave and convex mirrors. In concave mirrors the concave part is silver whereas in convex mirrors, the convex part is silvered.
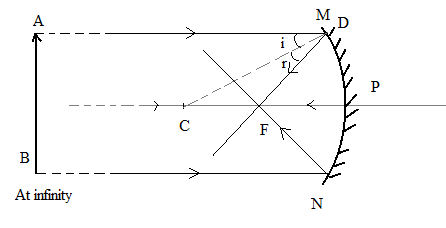
The centre of the sphere from which the concave mirror is made is known as the centre of curvature $\left( C \right)$ and the radius is known as the radius of curvature $R$. The point at which a light ray coming from infinity would cross the axis of mirror after reflection is known as the focus of the mirror $\left( F \right)$.
Since the distance of the sun from the mirror is very large therefore, the light rays coming from the sun can be considered as coming from infinity. All the rays coming from infinity meet at the focus $\left( F \right)$ after getting reflected. That is all the energy of rays that strike the mirror is concentrated at the focus because of the mirror. If a paper is kept at the focus and the alignment of the whole setup is not changed for an adequate amount of time, because of the concentrated energy of the sun, by the virtue of the concave mirror, the paper starts to burn.
Note: The point at which two or more reflected rays meet is known as an image. When the rays actually meet after getting reflected, the image is known as a real image. Whereas when the rays do not actually meet after getting reflected but appear to meet virtually behind the mirror, the image formed is known as a virtual image.
Complete answer:
Light is a form of energy which enables us to see.
Mirrors are silvered surfaces which have the ability to reflect maximum light energy when it strikes the mirror.
Mirrors can be classified into two types. First, the plane mirror, in which the surface which is silvered is a plane surface. Second, the spherical mirror, in which the surface which is silvered is a spherical surface.
Spherical mirrors can further be classified into concave and convex mirrors. In concave mirrors the concave part is silver whereas in convex mirrors, the convex part is silvered.
The centre of the sphere from which the concave mirror is made is known as the centre of curvature $\left( C \right)$ and the radius is known as the radius of curvature $R$. The point at which a light ray coming from infinity would cross the axis of mirror after reflection is known as the focus of the mirror $\left( F \right)$.
Since the distance of the sun from the mirror is very large therefore, the light rays coming from the sun can be considered as coming from infinity. All the rays coming from infinity meet at the focus $\left( F \right)$ after getting reflected. That is all the energy of rays that strike the mirror is concentrated at the focus because of the mirror. If a paper is kept at the focus and the alignment of the whole setup is not changed for an adequate amount of time, because of the concentrated energy of the sun, by the virtue of the concave mirror, the paper starts to burn.

Note: The point at which two or more reflected rays meet is known as an image. When the rays actually meet after getting reflected, the image is known as a real image. Whereas when the rays do not actually meet after getting reflected but appear to meet virtually behind the mirror, the image formed is known as a virtual image.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




