
Why does $N{H_3}$ have a lower boiling point than ${H_2}O$? How would you explain this in terms of H-bonding?
Answer
494.1k+ views
Hint: A special type of dipole-dipole attraction between the highly electronegative atoms and hydrogen atom which is not covalently bonded to that hydrogen atom, is known as hydrogen bonding. The electronegative atoms which show hydrogen bonding with hydrogen atoms are fluorine, oxygen and nitrogen.
Complete answer:
We know that hydrogen bonding is observed in both ammonia $\left( {N{H_3}} \right)$ as well as water $\left( {{H_2}O} \right)$. But the strength of intermolecular hydrogen bonding differs in both the molecules because of the following reason:
In ${H_2}O$, the oxygen atom of a water molecule shows intermolecular hydrogen bonding with the hydrogen atom of another molecule of ${H_2}O$. Due to the presence of two lone pair of electrons on the oxygen atom, the single oxygen atom can form a hydrogen bond with two hydrogen atoms as shown in the figure below:
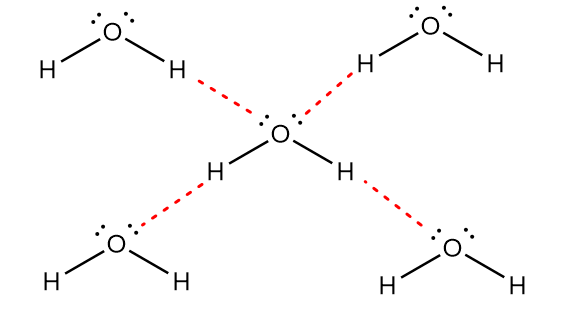
In the diagram, red lines represent the hydrogen bonding. Now, for $N{H_3}$, the nitrogen atom of an ammonia molecule shows intermolecular hydrogen bonding with the hydrogen atom of another molecule of $N{H_3}$. Due to the presence of one lone pair of electrons on a nitrogen atom, the single nitrogen atom can form a hydrogen bond with only one hydrogen atom as shown in the figure below:
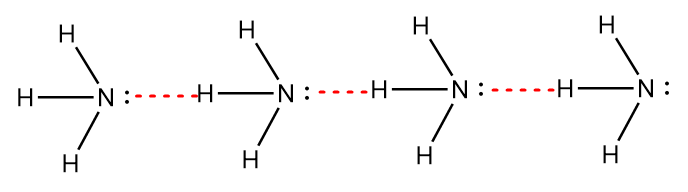
Thus, it is observed that in the water molecule, the hydrogen bonding network is extensive whereas the hydrogen bonding network of the ammonia molecule is simply linear. Hence, the strength of hydrogen bonding in water is greater than ammonia and will require higher temperature to weaken the bonding.
Therefore, From the above discussion it is clear that $N{H_3}$ has a lower boiling point than ${H_2}O$.
Note:
It is important to note that the boiling point of ammonia and water can also be compared by the values of bond enthalpies predicted for the hydrogen bonds. The enthalpies in vapour phase of $O - H - - - O$ and $N - H - - - N$ are $21\;kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$ and $13\;kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$ respectively. Higher the bond enthalpy, the more energy is required to break the bond and the stronger will be the bond due to which higher will be the boiling point. Thus, the ammonia molecule has a lower boiling point than water.
Complete answer:
We know that hydrogen bonding is observed in both ammonia $\left( {N{H_3}} \right)$ as well as water $\left( {{H_2}O} \right)$. But the strength of intermolecular hydrogen bonding differs in both the molecules because of the following reason:
In ${H_2}O$, the oxygen atom of a water molecule shows intermolecular hydrogen bonding with the hydrogen atom of another molecule of ${H_2}O$. Due to the presence of two lone pair of electrons on the oxygen atom, the single oxygen atom can form a hydrogen bond with two hydrogen atoms as shown in the figure below:

In the diagram, red lines represent the hydrogen bonding. Now, for $N{H_3}$, the nitrogen atom of an ammonia molecule shows intermolecular hydrogen bonding with the hydrogen atom of another molecule of $N{H_3}$. Due to the presence of one lone pair of electrons on a nitrogen atom, the single nitrogen atom can form a hydrogen bond with only one hydrogen atom as shown in the figure below:

Thus, it is observed that in the water molecule, the hydrogen bonding network is extensive whereas the hydrogen bonding network of the ammonia molecule is simply linear. Hence, the strength of hydrogen bonding in water is greater than ammonia and will require higher temperature to weaken the bonding.
Therefore, From the above discussion it is clear that $N{H_3}$ has a lower boiling point than ${H_2}O$.
Note:
It is important to note that the boiling point of ammonia and water can also be compared by the values of bond enthalpies predicted for the hydrogen bonds. The enthalpies in vapour phase of $O - H - - - O$ and $N - H - - - N$ are $21\;kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$ and $13\;kJmo{l^{ - 1}}$ respectively. Higher the bond enthalpy, the more energy is required to break the bond and the stronger will be the bond due to which higher will be the boiling point. Thus, the ammonia molecule has a lower boiling point than water.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




