
Why does DNA replication need to occur?
Answer
487.5k+ views
Hint: During cell division, DNA replication is the process by which DNA duplicates itself. A replication 'fork' is formed when two single strands of DNA are separated, forming a 'Y' shape. The two split strands will serve as templates for the creation of new DNA strands.
Complete answer:
DNA serves as a blueprint for constructing and functioning a cell.
Existing cells divide to make new cells, therefore DNA replication is required.
To function effectively, each cell needs a complete instruction manual. So, before cell division, the DNA must be replicated to ensure that each new cell receives a complete set of instructions.
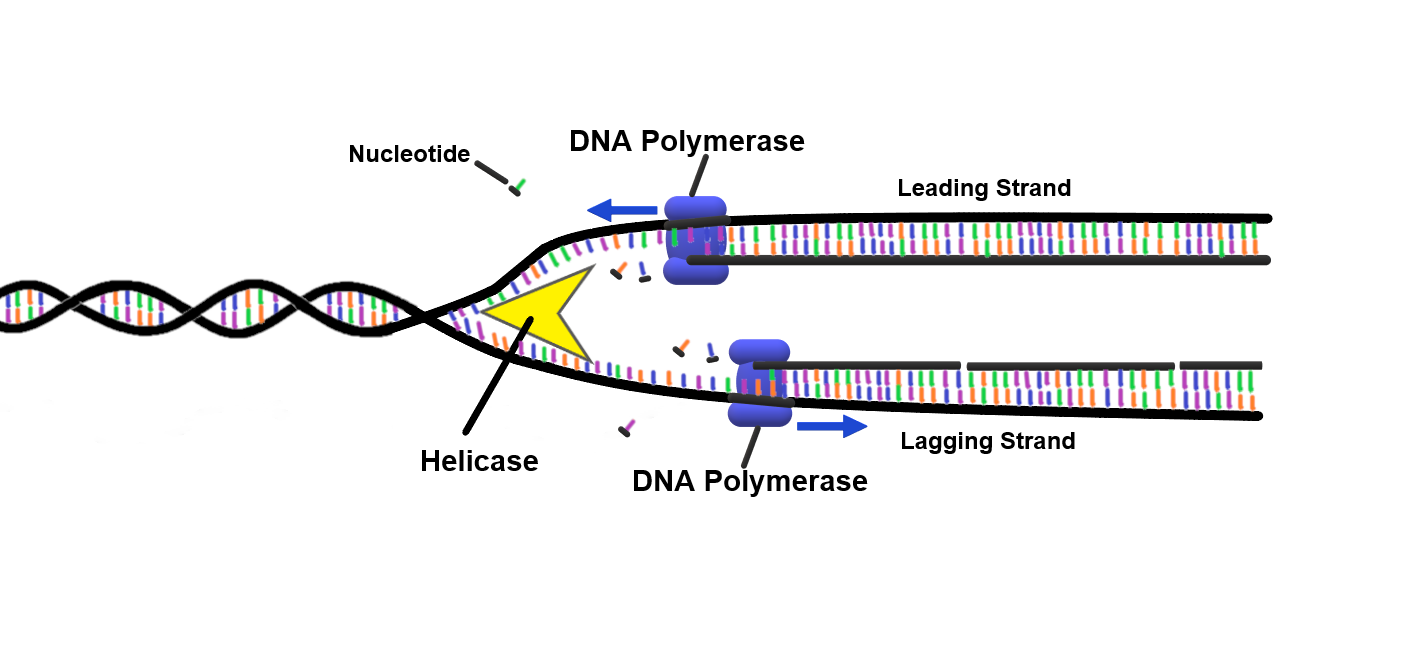
Fig: Replication fork
Basically, as a cell divides, several enzymes work to split each DNA strand in half and then replace the missing half with equivalent nucleotides, resulting in two identical strands. When a cell's genome (together with all of its organelles) is copied in its entirety, the cell can split into two daughter cells.
DNA replicates itself in order to reproduce.
Because every time a cell splits, the two new daughter cells must have the same genetic information, or DNA, as the parent cell, replication is required. Once a cell's DNA has been copied, it can divide into two cells, each with an exact copy of the original DNA.
Note:
The purpose of replication is to create a second double strand that is identical to the first. The initial step in DNA replication is to separate the two strands of the dsDNA molecule, which serves as a template for a new DNA strand. A DNA helicase is responsible for this.
Complete answer:
DNA serves as a blueprint for constructing and functioning a cell.
Existing cells divide to make new cells, therefore DNA replication is required.
To function effectively, each cell needs a complete instruction manual. So, before cell division, the DNA must be replicated to ensure that each new cell receives a complete set of instructions.

Fig: Replication fork
Basically, as a cell divides, several enzymes work to split each DNA strand in half and then replace the missing half with equivalent nucleotides, resulting in two identical strands. When a cell's genome (together with all of its organelles) is copied in its entirety, the cell can split into two daughter cells.
DNA replicates itself in order to reproduce.
Because every time a cell splits, the two new daughter cells must have the same genetic information, or DNA, as the parent cell, replication is required. Once a cell's DNA has been copied, it can divide into two cells, each with an exact copy of the original DNA.
Note:
The purpose of replication is to create a second double strand that is identical to the first. The initial step in DNA replication is to separate the two strands of the dsDNA molecule, which serves as a template for a new DNA strand. A DNA helicase is responsible for this.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




