
How does distance affect magnetic force ?
Answer
525.9k+ views
Hint:Coulomb's Inverse Square Law of Magnetic Force, also known as Coulomb's Law of Magnetic Force, was introduced in \[1785\] by Charles-Augustin de Coulomb, a French physicist and military engineer. For two isolated point poles, he interpreted the quantitative expression of power.
Complete answer:
The force of attraction or repulsion between two magnetic poles of strengths \[{m_1}\] and \[{m_2}\] held at a distance r apart is directly proportional to the product of their pole strengths and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
$F \propto \dfrac{{{m_1}{m_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$ or $F = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{{4\pi }}\dfrac{{{m_1}{m_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$
Any scientific law stating that a given physical quantity is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source of that physical quantity is known as an inverse-square law.With respect to distance, magnetic force follows an inverse square law. The magnetic force equation is identical to Coulomb's law (if you are familiar with it). The important thing to remember is that force is inversely proportional to distance squared (i.e. it obeys an inverse square law with distance).
$F \propto \dfrac{1}{{{r^2}}}$
Where $r$ is the distance between the magnets.
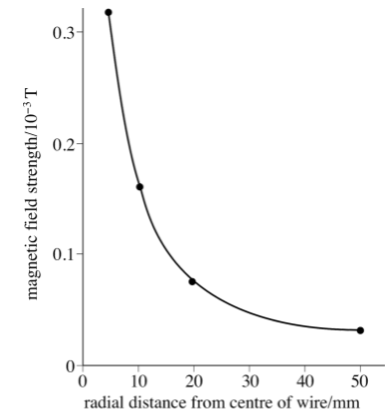
Note:A unit magnetic pole is known as a magnetic pole that experiences a force of \[1/2r\] newtons when placed one metre away from a very long straight conductor carrying a current of one ampere.
Complete answer:
The force of attraction or repulsion between two magnetic poles of strengths \[{m_1}\] and \[{m_2}\] held at a distance r apart is directly proportional to the product of their pole strengths and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
$F \propto \dfrac{{{m_1}{m_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$ or $F = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{{4\pi }}\dfrac{{{m_1}{m_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$
Any scientific law stating that a given physical quantity is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source of that physical quantity is known as an inverse-square law.With respect to distance, magnetic force follows an inverse square law. The magnetic force equation is identical to Coulomb's law (if you are familiar with it). The important thing to remember is that force is inversely proportional to distance squared (i.e. it obeys an inverse square law with distance).
$F \propto \dfrac{1}{{{r^2}}}$
Where $r$ is the distance between the magnets.

Note:A unit magnetic pole is known as a magnetic pole that experiences a force of \[1/2r\] newtons when placed one metre away from a very long straight conductor carrying a current of one ampere.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




