
Does diffused reflection mean failure of the laws of reflection?
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint:Reflection of light from a reflecting surface can be of two types – regular reflection or irregular reflection. Diffused reflection refers to irregular reflection which is caused due to the irregularities of the reflecting surface. The laws of reflection will be obeyed in all kinds of reflection.
Complete step by step answer.
Step 1: Try to explain the process of reflection in diffused reflection with suitable diagrams.
Diffused reflection of light, also known as irregular reflection, occurs when the reflecting surface is not smooth but rough and has irregularities.
Because of the uneven nature of the reflecting surface, the light rays will be incident at different angles and hence, the reflected rays will not be parallel to each other. This type of reflection where the light rays upon reflection are not parallel to one another is referred to as diffused reflection.
The figure given below shows the reflection of parallel rays of light from a rough surface.
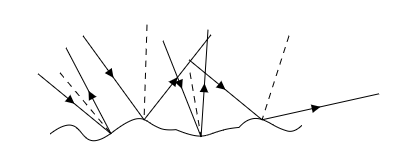
The dotted line represents the normal at the point of incidence. As seen from the above figure, light is incident at different angles at different points on the surface.
However, the laws of reflection will be obeyed in this type of reflection. The laws of reflection require the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection to be the same and for the incident ray, the normal at the point of incidence and the reflected ray to all lie in the same plane. These two laws of reflection will be obeyed in a diffused reflection.
So to conclude, diffused reflection does not mean the failure of the laws of reflection.
Additional information: In regular reflection, the incident light rays will be parallel to one another and upon reflection at the smooth reflecting surface, they will remain to be parallel to one another. The figure given below depicts the reflection of parallel rays of light from a regular surface.
Complete step by step answer.
Step 1: Try to explain the process of reflection in diffused reflection with suitable diagrams.
Diffused reflection of light, also known as irregular reflection, occurs when the reflecting surface is not smooth but rough and has irregularities.
Because of the uneven nature of the reflecting surface, the light rays will be incident at different angles and hence, the reflected rays will not be parallel to each other. This type of reflection where the light rays upon reflection are not parallel to one another is referred to as diffused reflection.
The figure given below shows the reflection of parallel rays of light from a rough surface.

The dotted line represents the normal at the point of incidence. As seen from the above figure, light is incident at different angles at different points on the surface.
However, the laws of reflection will be obeyed in this type of reflection. The laws of reflection require the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection to be the same and for the incident ray, the normal at the point of incidence and the reflected ray to all lie in the same plane. These two laws of reflection will be obeyed in a diffused reflection.
So to conclude, diffused reflection does not mean the failure of the laws of reflection.
Additional information: In regular reflection, the incident light rays will be parallel to one another and upon reflection at the smooth reflecting surface, they will remain to be parallel to one another. The figure given below depicts the reflection of parallel rays of light from a regular surface.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




