
How does a test cross help in identifying the genotype of the organism? Explain.
Answer
591k+ views
Hint: The test cross is a very useful way to explore the genotype of an unknown organism. The early use of the test cross was a new type of experimental mating test that was used to determine the genotype of an unprofiled organism. That means that the genotype of an organism with a phenotype that is dominant and maybe either heterozygous and homozygous for that dominant allele.
Complete answer:
Identify the genotype: -
The genotype is the complete heritable set of genes present in the organism. Specifically, for one trait to which we want to identify the genotype, we use the convention where we represent the alleles with the help of two-letter, for example for trait Height, we use two letters i.e. Homozygous Tall as “TT”, Heterozygous “Tt” and Dwarf as “tt”. Here the capital letter represents the dominant one and the small letter represents the abbreviation which is the recessive and dominant allele of the genes.
The phenotype is defined as the physical appearance of a trait in an organism.
Test cross: -
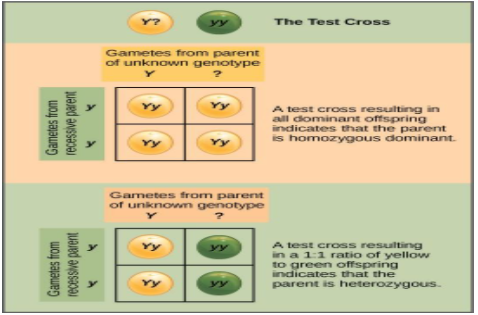
There is an organism which is showing dominance in phenotype, then it means that it has the homozygous alleles. Due to this the resulting F1 generation progeny have the dominant phenotype.
If the organism has a heterozygous genotype for a trait and then the F1 progeny will have the dominant phenotype, but they bear half dominant allele and half recessive allele.
A test cross is also used for the test of an individual’s genotype with the help of crossing it with the known genotype of a parent.
The test cross is involved with the breeding of an individual with the help of another individual which expresses itself a recessive version of the same trait.
Note:
In genetics, there is also a three-point cross that is used to determine the Loci of the organism’s genome of three genes. Most importantly the recombinant frequency is the ratio of the total individuals which are non-parental phenotypes.
Complete answer:
Identify the genotype: -
The genotype is the complete heritable set of genes present in the organism. Specifically, for one trait to which we want to identify the genotype, we use the convention where we represent the alleles with the help of two-letter, for example for trait Height, we use two letters i.e. Homozygous Tall as “TT”, Heterozygous “Tt” and Dwarf as “tt”. Here the capital letter represents the dominant one and the small letter represents the abbreviation which is the recessive and dominant allele of the genes.
The phenotype is defined as the physical appearance of a trait in an organism.
Test cross: -
There is an organism which is showing dominance in phenotype, then it means that it has the homozygous alleles. Due to this the resulting F1 generation progeny have the dominant phenotype.
If the organism has a heterozygous genotype for a trait and then the F1 progeny will have the dominant phenotype, but they bear half dominant allele and half recessive allele.
A test cross is also used for the test of an individual’s genotype with the help of crossing it with the known genotype of a parent.
The test cross is involved with the breeding of an individual with the help of another individual which expresses itself a recessive version of the same trait.

Note:
In genetics, there is also a three-point cross that is used to determine the Loci of the organism’s genome of three genes. Most importantly the recombinant frequency is the ratio of the total individuals which are non-parental phenotypes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




