
How does a solenoid behave like a magnet? Can you determine the north and the south poles of a current-carrying solenoid with help of a bar magnet? Explain.
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: We need to understand the methods and techniques in which the magnetic materials can be made to be magnetic using electromagnetic induction. The concept of magnetism and electrodynamics needs to be discussed to get a clear idea.
Complete answer:
We know from Ampere’s circuital law that the loops of current flowing can act as magnetic dipoles. We know that the strength of this magnetic field created by the loop is proportional to the number of turns, direction, and magnitude of current and the radius of the loop.
We know that the solenoid is a tightly wound piece of wire around a core, which can be air or any other material with higher magnetic permeability. So, the solenoid is a continuous loop with ‘n’ turns with a current flowing through it.
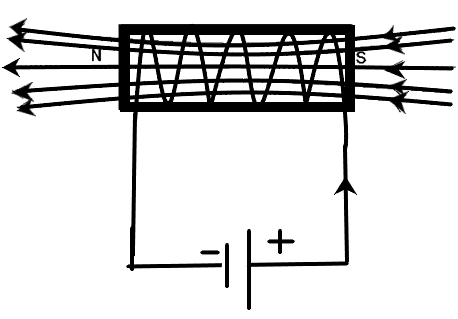
The magnetic field due to this setup can be given as –
\[B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}nI}{L}\]
Where L is the length of the solenoid and I is the current through the coil.
The magnetic field due to each of the coils adds up to form a large single field that resembles that of a bar magnet as shown below.
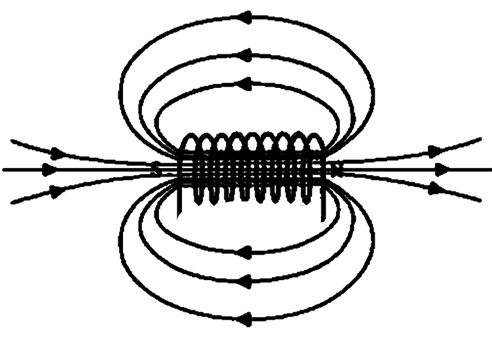
We can see that it acts exactly like a bar magnet.
Now, if we bring a bar magnet close to this, the like poles will repel and the unlike poles will attract as expected. This way we can easily distinguish the poles of a solenoid acting as a bar magnet.
Note: The magnetic property induced in the solenoid due to the current flow may persist for a long time after the current supply is cut. This is due to the ferromagnetic cores used inside the coil which turns to be a permanent magnet eventually.
Complete answer:
We know from Ampere’s circuital law that the loops of current flowing can act as magnetic dipoles. We know that the strength of this magnetic field created by the loop is proportional to the number of turns, direction, and magnitude of current and the radius of the loop.
We know that the solenoid is a tightly wound piece of wire around a core, which can be air or any other material with higher magnetic permeability. So, the solenoid is a continuous loop with ‘n’ turns with a current flowing through it.

The magnetic field due to this setup can be given as –
\[B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}nI}{L}\]
Where L is the length of the solenoid and I is the current through the coil.
The magnetic field due to each of the coils adds up to form a large single field that resembles that of a bar magnet as shown below.

We can see that it acts exactly like a bar magnet.
Now, if we bring a bar magnet close to this, the like poles will repel and the unlike poles will attract as expected. This way we can easily distinguish the poles of a solenoid acting as a bar magnet.
Note: The magnetic property induced in the solenoid due to the current flow may persist for a long time after the current supply is cut. This is due to the ferromagnetic cores used inside the coil which turns to be a permanent magnet eventually.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




