
Why Does a Ray of Light Actually Bend While Going From One Medium To Another?
Answer
508.5k+ views
Hint: Refraction means the change in the direction of an incident ray of light when it is passing from one medium to another. It is clearly explained by snell's law and it is also known as Law of refraction. We need to discuss the topics of Law of refraction and refractive index to find why a ray of light bends when traveling from one medium to another.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Snell's law describes the relations between the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction of an incident ray of light. Snell's law states that the ratio between the sine of the angles between the angle of incidence and refraction is equal to the ratio of refractive indices of two mediums and also equal to the ratio of velocities of an incident ray of light in two mediums.
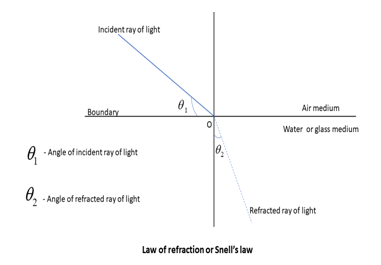
$\dfrac{{\sin {\theta _2}}}{{\sin {\theta _1}}} = \dfrac{{{v_2}}}{{{v_1}}} = \dfrac{{{n_1}}}{{{n_2}}}$
Where, ${\theta _2}$- the angle of refraction
${\theta _1}$-angle of incidence
${n_1},{n_2}$- the indices of refraction
${v_1},{v_2}$- velocities of an incident ray of light in two media.
During refraction, the light ray bends due to the nature of the light and its properties. The main cause for the bending is due to a change in the velocity of a light ray in different mediums and also the angle of incidence and angle of refraction.
This is the reason for a ray of light bend while traveling from one medium to another medium.
Note:The bending of light can also be explained by Fermat’s principle. It defines that the light will always choose the direction when it reaches a distance with less amount of time. It occurs due to photon behavior in a wave, it takes all possible directions of light in refraction. The Fermat principle is applicable for any waves traveling and not only for light.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Snell's law describes the relations between the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction of an incident ray of light. Snell's law states that the ratio between the sine of the angles between the angle of incidence and refraction is equal to the ratio of refractive indices of two mediums and also equal to the ratio of velocities of an incident ray of light in two mediums.

$\dfrac{{\sin {\theta _2}}}{{\sin {\theta _1}}} = \dfrac{{{v_2}}}{{{v_1}}} = \dfrac{{{n_1}}}{{{n_2}}}$
Where, ${\theta _2}$- the angle of refraction
${\theta _1}$-angle of incidence
${n_1},{n_2}$- the indices of refraction
${v_1},{v_2}$- velocities of an incident ray of light in two media.
During refraction, the light ray bends due to the nature of the light and its properties. The main cause for the bending is due to a change in the velocity of a light ray in different mediums and also the angle of incidence and angle of refraction.
This is the reason for a ray of light bend while traveling from one medium to another medium.
Note:The bending of light can also be explained by Fermat’s principle. It defines that the light will always choose the direction when it reaches a distance with less amount of time. It occurs due to photon behavior in a wave, it takes all possible directions of light in refraction. The Fermat principle is applicable for any waves traveling and not only for light.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




