
What does $ 6,6 $ indicate in $ Nylon - 6,6 $ ? In what way is it different from $ Nylon - 6 $.
Answer
502.8k+ views
Hint: Both $ Nylon - 6,6 $ and $ Nylon - 6 $ are types of condensation polymers and mainly differ in terms of the monomers used in their synthesis. The numbers written along with polymer names indicated the number of atoms involved.
Complete answer:
Condensation polymerization is a method of combining small units or small organic molecules through covalent linkages that involve removal of small molecules like water or ammonia in the process. Polymers consist of long chains made up of small repeating units (organic molecules) that are known as the monomers.
The $ Nylon - 6,6 $ is known as a copolymer and is synthesized with the help of two monomeric units that are lined to each other through an amide linkage. The monomers involved in the preparation of $ Nylon - 6,6 $ are hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid. The process of condensation results in the loss of a water molecule to form an amide bond between the amino terminal of hexamethylenediamine and the carboxylic acid terminal of adipic acid.
The numbers $ 6,6 $ indicate that both the monomers i.e. hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid consist of six carbon atoms each. Thus, $ Nylon - 6,6 $ is a copolymer formed from two different monomers.
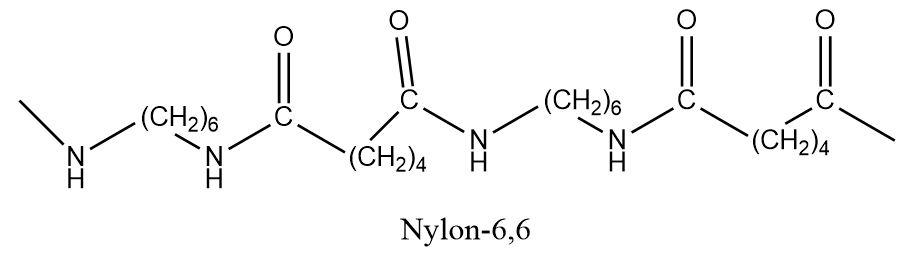
But $ Nylon - 6 $ is a condensation polymer that is formed from a single monomer known as caprolactam that also contains six carbons atoms in it.
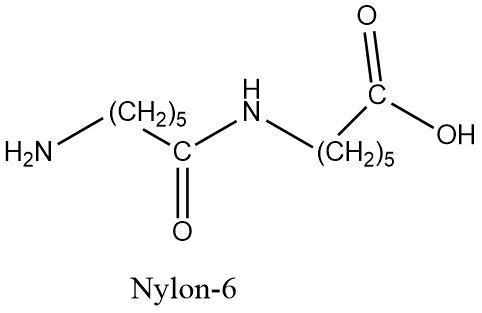
Hence, the $ 6,6 $ is used to describe the two six-membered monomers used in the formation of $ Nylon - 6,6 $ and $ Nylon - 6 $ consists of a single monomer which is structurally different from both the monomers of $ Nylon - 6,6 $ .
Note:
The starting material used in preparing the monomers of both $ Nylon - 6,6 $ and $ Nylon - 6 $ can be the same, which is cyclohexanone. Cyclohexanone can be used for the preparation of adipic acid as well as Caprolactam.
Complete answer:
Condensation polymerization is a method of combining small units or small organic molecules through covalent linkages that involve removal of small molecules like water or ammonia in the process. Polymers consist of long chains made up of small repeating units (organic molecules) that are known as the monomers.
The $ Nylon - 6,6 $ is known as a copolymer and is synthesized with the help of two monomeric units that are lined to each other through an amide linkage. The monomers involved in the preparation of $ Nylon - 6,6 $ are hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid. The process of condensation results in the loss of a water molecule to form an amide bond between the amino terminal of hexamethylenediamine and the carboxylic acid terminal of adipic acid.
The numbers $ 6,6 $ indicate that both the monomers i.e. hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid consist of six carbon atoms each. Thus, $ Nylon - 6,6 $ is a copolymer formed from two different monomers.

But $ Nylon - 6 $ is a condensation polymer that is formed from a single monomer known as caprolactam that also contains six carbons atoms in it.

Hence, the $ 6,6 $ is used to describe the two six-membered monomers used in the formation of $ Nylon - 6,6 $ and $ Nylon - 6 $ consists of a single monomer which is structurally different from both the monomers of $ Nylon - 6,6 $ .
Note:
The starting material used in preparing the monomers of both $ Nylon - 6,6 $ and $ Nylon - 6 $ can be the same, which is cyclohexanone. Cyclohexanone can be used for the preparation of adipic acid as well as Caprolactam.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




