
Do electric flux passing through a 3d object is always 0?
Answer
522.9k+ views
Hint: We can find the electric field orientation using Gauss's law. Electric flux is the number of field lines passing through a given surface. Gauss’s law deals with the electric flux through a closed surface.
Complete step by step solution:
Gauss’s law states that,
“The net electric flux through any hypothetical closed surface is equal to \[\dfrac{1}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}\] times the net charge within that closed surface.”
Hence, Gauss’s law can be expressed as:
\[{\phi _E} = \dfrac{Q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}\]
Where,
\[{\phi _E}\]is the electric flux through a closed surface
Q is the total charge enclosed by the surface
\[{\varepsilon _0}\]is di-electric constant of that medium
So, the net charge in the above question is zero
Electron dipole is a positive and negative charge of equal magnitude at a specific distance.
Hence, the total charge inside the cube is zero.
So, if we apply Gauss’s law, then the net electric field through the cube is zero.
Let’s look at the reason behind this zero-electric flux.
We can take any of the 6 sides of the box (3D surface) to explain this.
Let’s look at the following diagram:
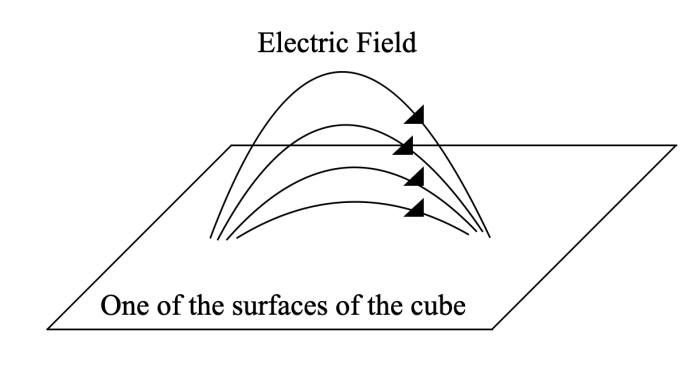
In an electric dipole the electric field lines start at the positive charge and end at the negative charge. So, if we check the electric field lines originating from the positive charge, they will contribute a positive flux at the surface of the cube.
However, the same field lines will have to cross the side again to end at the negative pole. Hence, it will contribute to the same magnitude of negative electrical flux.
Hence, positive and electric flux cancel each other to have a net electric flux of zero.
Note: Gauss’s law is one of the fundamental laws of electrodynamics. This law can be applied to gravitational force of attraction or magnetic force as well. Coulomb's law in electrostatics and Newton’s law in gravity can be derived from Gauss’s law. However, the constant is different in those two cases.
Complete step by step solution:
Gauss’s law states that,
“The net electric flux through any hypothetical closed surface is equal to \[\dfrac{1}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}\] times the net charge within that closed surface.”
Hence, Gauss’s law can be expressed as:
\[{\phi _E} = \dfrac{Q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}\]
Where,
\[{\phi _E}\]is the electric flux through a closed surface
Q is the total charge enclosed by the surface
\[{\varepsilon _0}\]is di-electric constant of that medium
So, the net charge in the above question is zero
Electron dipole is a positive and negative charge of equal magnitude at a specific distance.
Hence, the total charge inside the cube is zero.
So, if we apply Gauss’s law, then the net electric field through the cube is zero.
Let’s look at the reason behind this zero-electric flux.
We can take any of the 6 sides of the box (3D surface) to explain this.
Let’s look at the following diagram:

In an electric dipole the electric field lines start at the positive charge and end at the negative charge. So, if we check the electric field lines originating from the positive charge, they will contribute a positive flux at the surface of the cube.
However, the same field lines will have to cross the side again to end at the negative pole. Hence, it will contribute to the same magnitude of negative electrical flux.
Hence, positive and electric flux cancel each other to have a net electric flux of zero.
Note: Gauss’s law is one of the fundamental laws of electrodynamics. This law can be applied to gravitational force of attraction or magnetic force as well. Coulomb's law in electrostatics and Newton’s law in gravity can be derived from Gauss’s law. However, the constant is different in those two cases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




