
DNA is a polymer of
(a) Proteins
(b) Carbohydrates
(c) RNA
(d) Nucleotides
Answer
583.5k+ views
Hint: These are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) , both of which are essential biomolecules within all life- forms on Earth.
Correct step by step answer:
DNA is a polymer of nucleotides. The nucleotides are the elementary unit that forms DNA. Nucleotides are composed of three subunit molecules: a nitrogenous base, a five- carbon sugar (a pentose sugar: ribose or deoxyribose) , and a phosphate group consisting of one to three phosphates DNA is formed through phosphorylation of nucleoside. The chain of nucleotides or the polymer of nucleotides is the DNA. It is acidic in nature. There are four different types of nucleotides found in DNA, the only difference among them is of the nitrogenous base. The four nitrogenous bases in DNA are guanine, adenine, cytosine, and thymine; in RNA, uracil is used in place of thymine.
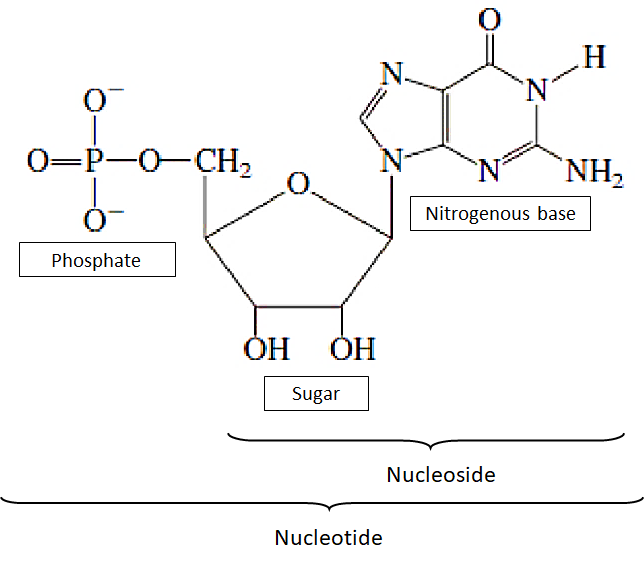
The abbreviation for these nucleotide bases are as follows:
A is for adenine
G is for guanine
C is for cytosine
T is for thymine
U is for uracil
So, the correct answer is, ’Nucleotides’.
Note:
- Adenine and guanine are purines. Purines are the larger of the 2 sorts of bases found in DNA.
- The deoxyribose sugar of the DNA backbone has 5 carbons and three oxygens. The carbon atoms are numbered 1', 2', 3', 4', and 5' to distinguish from the numbering of the atoms of the purine and pyrimidine rings.
- The hydroxyl groups on the 5'- and 3'- carbons link to the phosphate groups to make the DNA backbone. Deoxyribose lacks a hydroxyl at the 2'-position in comparison to ribose, the sugar component of RNA.
- DNA is a normal double- stranded macromolecule. Two polynucleotide chains form a DNA molecule, being held together by weak thermodynamic forces.
Correct step by step answer:
DNA is a polymer of nucleotides. The nucleotides are the elementary unit that forms DNA. Nucleotides are composed of three subunit molecules: a nitrogenous base, a five- carbon sugar (a pentose sugar: ribose or deoxyribose) , and a phosphate group consisting of one to three phosphates DNA is formed through phosphorylation of nucleoside. The chain of nucleotides or the polymer of nucleotides is the DNA. It is acidic in nature. There are four different types of nucleotides found in DNA, the only difference among them is of the nitrogenous base. The four nitrogenous bases in DNA are guanine, adenine, cytosine, and thymine; in RNA, uracil is used in place of thymine.

The abbreviation for these nucleotide bases are as follows:
A is for adenine
G is for guanine
C is for cytosine
T is for thymine
U is for uracil
So, the correct answer is, ’Nucleotides’.
Note:
- Adenine and guanine are purines. Purines are the larger of the 2 sorts of bases found in DNA.
- The deoxyribose sugar of the DNA backbone has 5 carbons and three oxygens. The carbon atoms are numbered 1', 2', 3', 4', and 5' to distinguish from the numbering of the atoms of the purine and pyrimidine rings.
- The hydroxyl groups on the 5'- and 3'- carbons link to the phosphate groups to make the DNA backbone. Deoxyribose lacks a hydroxyl at the 2'-position in comparison to ribose, the sugar component of RNA.
- DNA is a normal double- stranded macromolecule. Two polynucleotide chains form a DNA molecule, being held together by weak thermodynamic forces.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




