
How will you distinguish between primary, secondary and tertiary amines by Hinsberg’s Test?
Answer
521.7k+ views
Hint: In this test the amines are treated with benzene sulfonyl chloride. Here amines act as nucleophiles which attack the electrophilic sulfonyl chloride. Now try and put together the reaction yourself.
Complete-step- by- step answer:
Hinsberg’s test is done to distinguish between primary, secondary and tertiary amines.
A German chemist named Oscar Heinrich Daniel Hinsberg gave this reaction in 1890.
The reagent used: known as Hinsberg’s reagent is benzene sulfonyl chloride (${C_6}{H_5}Cl{O_2}S$) which is an organosulfur compound. In this test the given amine is shaken with Hinsberg’s reagent in the presence of aqueous alkali which is either KOH or NaOH.
Now you might be thinking how to distinguish the amines using this reagent. So, to distinguish let us see the reactions of various amides with benzene sulfonyl chloride:
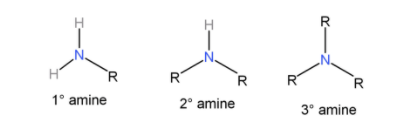
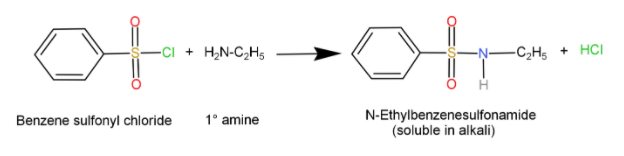
Primary amines ($R - N{H_2}$): When they react with Sulfonyl chloride it forms a sulfonamide salt which is soluble in alkali.
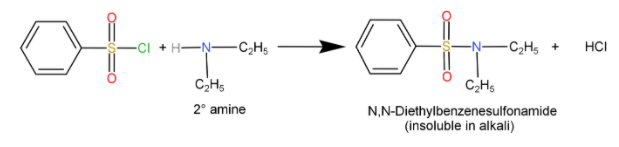
Secondary amines (${R_2} - NH$): When they react with sulfonyl chloride, it forms a sulfonamide salt which is insoluble in alkali.
Tertiary amines (${R_3}N$): They do not form any sulfonamide salt with sulfonyl chloride. Instead they cause the sulfonyl chloride to hydrolyse and form salts that are insoluble in water.
This is how Hinsberg’s test helps to differentiate between primary, secondary and tertiary amines by observing the difference in the solubility of the sulfonamide product in alkali.
Note: First draw the structures of primary, secondary and tertiary amines and also of benzene sulfonyl chloride properly. You should also keep in mind that in this test amine is acting as the nucleophile and sulfonyl chloride is acting as the electrophile. Do not get confused here.
Complete-step- by- step answer:
Hinsberg’s test is done to distinguish between primary, secondary and tertiary amines.

A German chemist named Oscar Heinrich Daniel Hinsberg gave this reaction in 1890.
The reagent used: known as Hinsberg’s reagent is benzene sulfonyl chloride (${C_6}{H_5}Cl{O_2}S$) which is an organosulfur compound. In this test the given amine is shaken with Hinsberg’s reagent in the presence of aqueous alkali which is either KOH or NaOH.
Now you might be thinking how to distinguish the amines using this reagent. So, to distinguish let us see the reactions of various amides with benzene sulfonyl chloride:
Primary amines ($R - N{H_2}$): When they react with Sulfonyl chloride it forms a sulfonamide salt which is soluble in alkali.

Secondary amines (${R_2} - NH$): When they react with sulfonyl chloride, it forms a sulfonamide salt which is insoluble in alkali.

Tertiary amines (${R_3}N$): They do not form any sulfonamide salt with sulfonyl chloride. Instead they cause the sulfonyl chloride to hydrolyse and form salts that are insoluble in water.
This is how Hinsberg’s test helps to differentiate between primary, secondary and tertiary amines by observing the difference in the solubility of the sulfonamide product in alkali.
Note: First draw the structures of primary, secondary and tertiary amines and also of benzene sulfonyl chloride properly. You should also keep in mind that in this test amine is acting as the nucleophile and sulfonyl chloride is acting as the electrophile. Do not get confused here.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




