
Differentiate between monozygotic twins and dizygotic twins.
Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint: There are different types of twins seen in the case of humans. Some develop from a single fertilization event and show natural similarities whereas some develop from two different fertilization events.
Complete answer:
The differences between monozygotic twins and dizygotic twins are listed below:
Additional Information: Monozygotic twins, also known as identical twins or fraternal twins, are developed by the splitting of a fertilized embryo and therefore, share the same chromosome. The genetic codes are also considered the same for the same reason. The separation occurs with the separation of both chorion and amniotic sac.
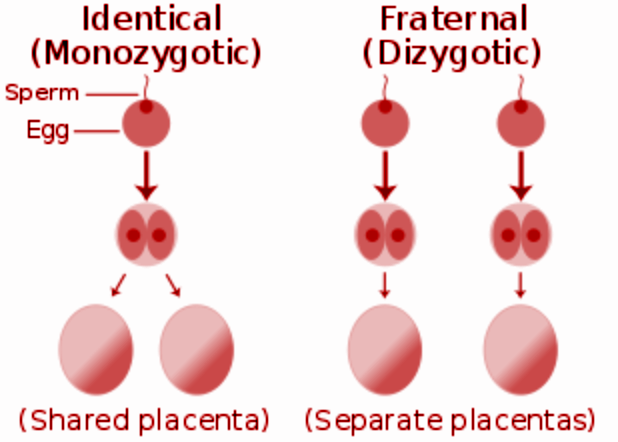
Dizygotic twins, also known as non-identical twins or fraternal twins, are formed by separate fertilization of two eggs by two sperms. These are genetically varied and gender-wise different from each other.
Note: Some of the monozygotic twins consist of a separate placenta and the amniotic sac, and this situation is known as Di-Di twins which occurred by the splitting of the embryo within 2-3 days after fertilization. The twins that share the same placenta and two separate amniotic sacs are known as Mono-Di twins and are formed by the splitting of the embryo within 3-8 days after fertilization. Mono-Mono twins are formed by the splitting of the embryo within 8-13 days after fertilization and share the amniotic sac as well as the placenta. Another type of embryo known as conjoint embryo forms by the splitting of the embryo after 13 days of fertilization and creates twins with jointed body parts.
Complete answer:
The differences between monozygotic twins and dizygotic twins are listed below:
| Monozygotic twins | Dizygotic twins |
| 1.Monozygotic twins develop from one embryo which splits into two embryos. | 1. Dizygotic twins develop from two distinct eggs by two separate simultaneous fertilization events. |
| 2. Geneders of the individuals are the same. | 2. Genders are different. |
| 3. The cause of monozygotic twins is not known till now. | 3. Cause of dizygotic twins is either by IVF, certain fertility drugs, or hereditary predispositions. |
| 4. The genetic codes in the case of monozygotic twins are nearly identical. | 4. In the case of dizygotic twins, the genetic codes are the same as any other siblings. |
| 5. Blood types are similar. | 5. Blood types are different in each twin. |
| 6. The twins can be Di-Di, Mono-Di, or Mono-Mono. | 6. Only Di-Di twins are seen in the case of dizygotic. |
| 7. The twins have a high risk of TTTS. | 7. The twins have a lower risk for TTTS. |
| 8. The appearance of the twins is extremely similar but Environmental factors may affect it. | 8. The appearance is similar to any other siblings. |
Additional Information: Monozygotic twins, also known as identical twins or fraternal twins, are developed by the splitting of a fertilized embryo and therefore, share the same chromosome. The genetic codes are also considered the same for the same reason. The separation occurs with the separation of both chorion and amniotic sac.

Dizygotic twins, also known as non-identical twins or fraternal twins, are formed by separate fertilization of two eggs by two sperms. These are genetically varied and gender-wise different from each other.
Note: Some of the monozygotic twins consist of a separate placenta and the amniotic sac, and this situation is known as Di-Di twins which occurred by the splitting of the embryo within 2-3 days after fertilization. The twins that share the same placenta and two separate amniotic sacs are known as Mono-Di twins and are formed by the splitting of the embryo within 3-8 days after fertilization. Mono-Mono twins are formed by the splitting of the embryo within 8-13 days after fertilization and share the amniotic sac as well as the placenta. Another type of embryo known as conjoint embryo forms by the splitting of the embryo after 13 days of fertilization and creates twins with jointed body parts.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




