
Difference between $S{N^{_1}}\& S{N^{_2}}$ reactions
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: We know that, $S{N^{_1}}\& S{N^{_2}}$ are two types of nucleophilic substitution reactions. A reaction in which an atom or a functional group is replaced by a negatively charged species is known as nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Complete step by step answer:First, we see the $S{N^1}$ reaction mechanism.
The $S{N^1}$ reaction:
It is two step reactions, at first step the bond between the carbon and hydrogen breaks hydrolytically and in the second step nucleophile reacts with the carbocation formed in the first step.
The general mechanism of $S{N^1}$ reaction is,
Step 1: $R - X\xrightarrow{{Polar\,solvent}}{R^ + } + {X^ - }$
Step 2: \[{R^ + } + {X^ - }\xrightarrow{{{{\left[ {OH} \right]}^ - }}}R - OH\]
The $S{N^2}$ reaction:
It is a single step reaction in which the formation of carbocation and leaving of halogen take place simultaneously.
The mechanism of $S{N^2}$ reaction is,
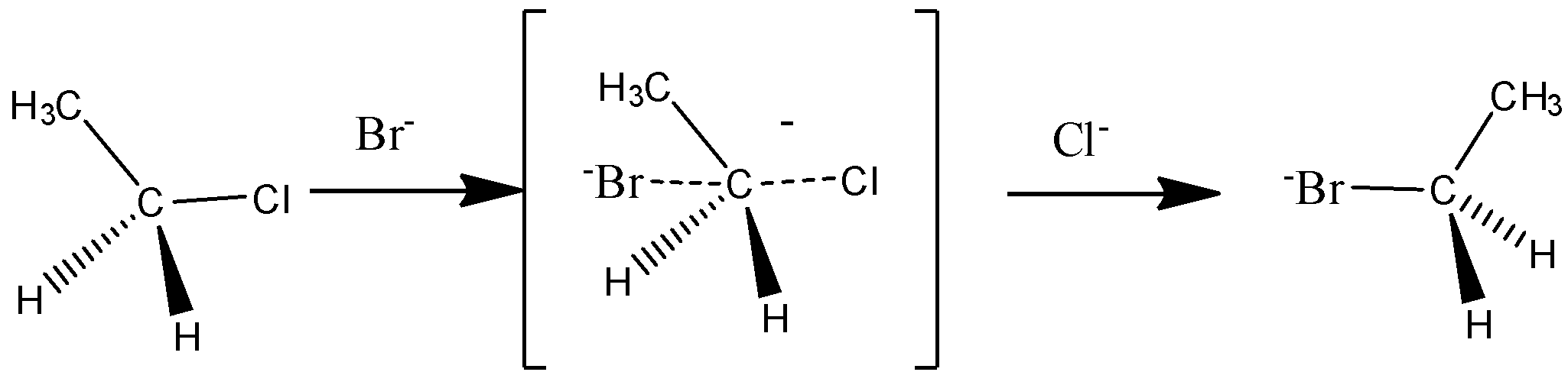
Let us discuss the difference between $S{N^{_1}}\& S{N^{_2}}$ reactions.
Note:
We can call electron rich species as nucleophiles; it may be anion, or compound, or atom with at least one lone pair of electrons and the opposite of nucleophile is an electrophile. Electrophile may be a positively charged species.
Complete step by step answer:First, we see the $S{N^1}$ reaction mechanism.
The $S{N^1}$ reaction:
It is two step reactions, at first step the bond between the carbon and hydrogen breaks hydrolytically and in the second step nucleophile reacts with the carbocation formed in the first step.
The general mechanism of $S{N^1}$ reaction is,
Step 1: $R - X\xrightarrow{{Polar\,solvent}}{R^ + } + {X^ - }$
Step 2: \[{R^ + } + {X^ - }\xrightarrow{{{{\left[ {OH} \right]}^ - }}}R - OH\]
The $S{N^2}$ reaction:
It is a single step reaction in which the formation of carbocation and leaving of halogen take place simultaneously.
The mechanism of $S{N^2}$ reaction is,

Let us discuss the difference between $S{N^{_1}}\& S{N^{_2}}$ reactions.
| $S{N^1}$ reactions | $S{N^2}$ reactions |
| The rate of $S{N^1}$ reaction is unimolecular. | The rate of $S{N^2}$ reaction is bimolecular. |
| The rate of the reaction depends on the concentration of the substance, thus it follows first order kinetics. | The rate of reaction depends on the concentration of both nucleophile and substrate. Thus, it follows second order kinetics |
| It is a two step process. | It is a one step process. |
| The intermediate formed is carbocation. | No intermediate is formed during the reaction. |
| No partial bond is formed | Carbon forms a partial bond with the nucleophile and the leaving group. |
| Optically inactive substance becomes optically active. | In $S{N^2}$ inversion of reaction takes place. |
Note:
We can call electron rich species as nucleophiles; it may be anion, or compound, or atom with at least one lone pair of electrons and the opposite of nucleophile is an electrophile. Electrophile may be a positively charged species.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




