
What is the difference between primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols?
Answer
526.8k+ views
Hint :Look for primary, secondary and tertiary carbon in the Hydrocarbon chain. The number of alkyl groups attached tells us whether the carbon of the hydrocarbon chain is primary, tertiary or secondary. Alcohols are associated with the -OH group.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
A primary carbon is the one which is attached to an alkyl chain by a one single bond only.
A secondary carbon is the one bonded by an alkyl chain on two sides.
A tertiary carbon is the one bonded by an alkyl chain on three sides.
In the figure given below, we can identify all three types of C atoms in the same diagram
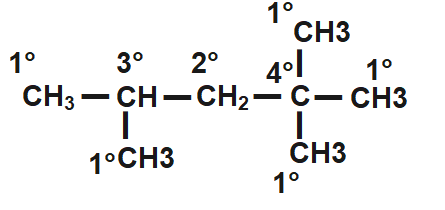
Hence, a primary alcohol is the one where the -OH group is attached to primary carbon.
A secondary alcohol is the one where -OH group is bonded to a secondary carbon
A tertiary carbon is the one where -OH group is bonded to a tertiary carbon in the carbon chain
For example, $ $ $ C{{H}_{3}}-CHOH-C{{H}_{3}} $ , is a secondary alcohol, because the carbon with the -OH group has two $ C{{H}_{3}} $ attached to it.
$ C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}OH $ is a primary alcohol as the carbon attached to the -OH group has only one alkyl group attached to it.
Lucas test is also used to differentiate between primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols
Lucas reagent( $ HCl/ZnC{{l}_{2}} $ ) when reacted with alcohols gives differentiable results.
When a primary alcohol reacts with Lucas reagent, turbidity appears in the test tube only on heating.
When a secondary alcohol reacts with Lucas reagent, turbidity appears within five minutes.
When a tertiary alcohol reacts with Lucas reagent, turbidity appears immediately.
Note :
-OH group is also known as hydroxyl group.
In a primary alcohol the carbon with the hydroxyl group should be bonded to not more than one carbon directly.
In a secondary alcohol the carbon with the hydroxyl group is bonded to two carbons directly.
In a tertiary alcohol the carbon with the hydroxyl group is bonded to two three carbons directly.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
A primary carbon is the one which is attached to an alkyl chain by a one single bond only.
A secondary carbon is the one bonded by an alkyl chain on two sides.
A tertiary carbon is the one bonded by an alkyl chain on three sides.
In the figure given below, we can identify all three types of C atoms in the same diagram

Hence, a primary alcohol is the one where the -OH group is attached to primary carbon.
A secondary alcohol is the one where -OH group is bonded to a secondary carbon
A tertiary carbon is the one where -OH group is bonded to a tertiary carbon in the carbon chain
For example, $ $ $ C{{H}_{3}}-CHOH-C{{H}_{3}} $ , is a secondary alcohol, because the carbon with the -OH group has two $ C{{H}_{3}} $ attached to it.
$ C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}OH $ is a primary alcohol as the carbon attached to the -OH group has only one alkyl group attached to it.
Lucas test is also used to differentiate between primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols
Lucas reagent( $ HCl/ZnC{{l}_{2}} $ ) when reacted with alcohols gives differentiable results.
When a primary alcohol reacts with Lucas reagent, turbidity appears in the test tube only on heating.
When a secondary alcohol reacts with Lucas reagent, turbidity appears within five minutes.
When a tertiary alcohol reacts with Lucas reagent, turbidity appears immediately.
Note :
-OH group is also known as hydroxyl group.
In a primary alcohol the carbon with the hydroxyl group should be bonded to not more than one carbon directly.
In a secondary alcohol the carbon with the hydroxyl group is bonded to two carbons directly.
In a tertiary alcohol the carbon with the hydroxyl group is bonded to two three carbons directly.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




