
Difference between homopolymer and copolymer.
Answer
548.4k+ views
Hint: To get an idea about these, separate their names into two words. Here we can write a homopolymer as homo + polymer, “homo” means the same unit and copolymer as co+polymer, where “co” means different. Now try to answer this question accordingly.
Complete step by step answer:
We should know that the main difference between copolymer and homopolymer is that copolymers are formed by using two different types of monomers, whereas homopolymers are produced by using a single type of monomer. This difference is responsible for the unique set of properties of homopolymers and copolymers.

- Polythene
- Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE or Teflon)
Examples of copolymers:
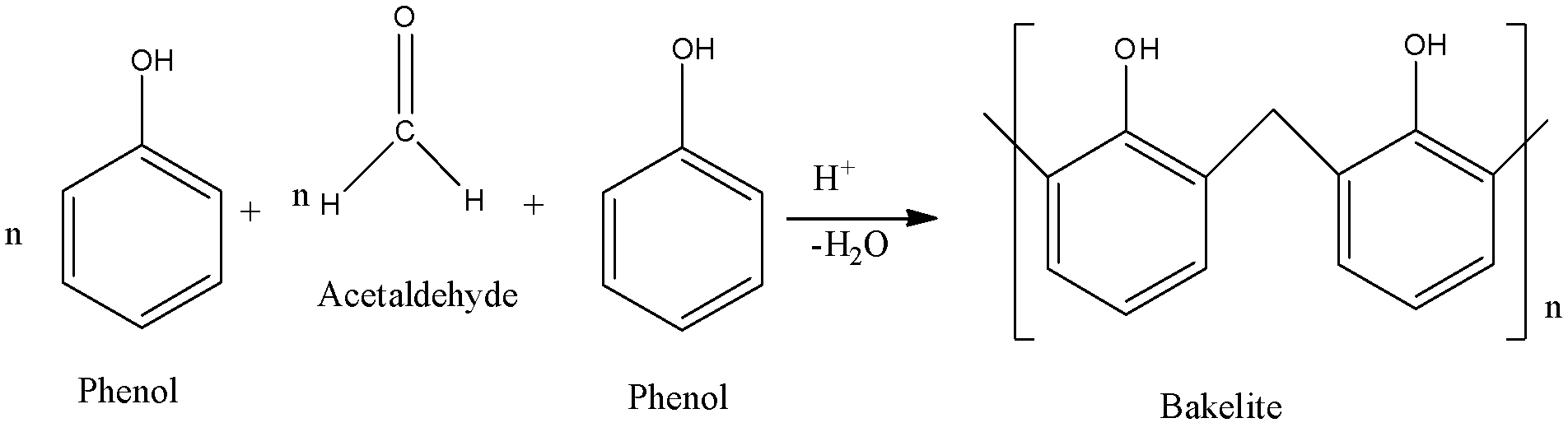
- Bakelite (copolymer of phenol and formaldehyde)
- Buna-N (copolymer of 1,3-butadiene and acrylonitrile )
- Buna-S (copolymer of 1,3-butadiene and styrene )
Therefore, we differentiated between homopolymers and copolymers.
Note: We should also know that there are also some subcategories of copolymers -
- If the two monomers are arranged in an alternative way, it is known as an alternating copolymer.
for example, if the two monomers are P and Q, they will arrange like PQPQPQPQPQPQ
- If the monomers are arranged in a random order like AABAAABBBBAB, it is known as a random copolymer.
- If each monomer joins with the same type of monomers, and then the two blocks of homopolymers join each other. This type is known as block copolymers.
For example, if the two monomers are A and B, they will arrange like AAAAAAABBBBBBB
Complete step by step answer:
We should know that the main difference between copolymer and homopolymer is that copolymers are formed by using two different types of monomers, whereas homopolymers are produced by using a single type of monomer. This difference is responsible for the unique set of properties of homopolymers and copolymers.

- Polythene
- Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE or Teflon)
Examples of copolymers:

- Bakelite (copolymer of phenol and formaldehyde)
- Buna-N (copolymer of 1,3-butadiene and acrylonitrile )
- Buna-S (copolymer of 1,3-butadiene and styrene )
Therefore, we differentiated between homopolymers and copolymers.
Note: We should also know that there are also some subcategories of copolymers -
- If the two monomers are arranged in an alternative way, it is known as an alternating copolymer.
for example, if the two monomers are P and Q, they will arrange like PQPQPQPQPQPQ
- If the monomers are arranged in a random order like AABAAABBBBAB, it is known as a random copolymer.
- If each monomer joins with the same type of monomers, and then the two blocks of homopolymers join each other. This type is known as block copolymers.
For example, if the two monomers are A and B, they will arrange like AAAAAAABBBBBBB
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




