
What is the difference between exons and introns?
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: mRNA produced from transcription doesn’t consist of all coding sequences. Therefore, the presence of non-coding sequences make mRNA compulsory to undergo spliceosome in order to form a protein.
Complete step by step answer:
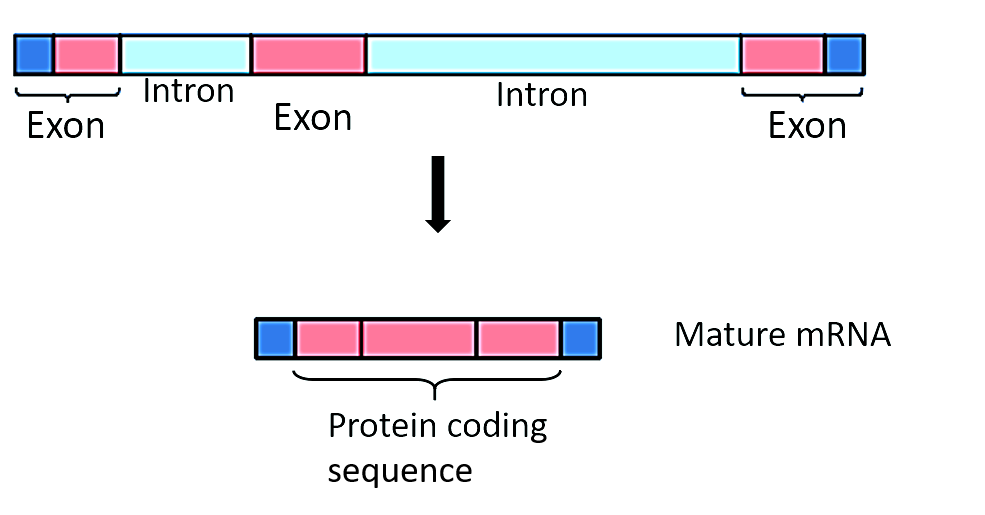
Additional Information:
- Introns sequences in nuclear protein- coding genes that are removed by spliceosomes.
- Introns are a comparatively recent arrival within the eukaryotic lineage that to assist generate the range of regulatory mechanisms that are required to regulate organic phenomenon in multicellular highly differentiated organisms.
- The term "intervening sequence" can ask any of several families of internal macromolecule sequences that aren't present within the final gene product, including inteins, untranslated sequences (UTR), and nucleotides removed by RNA editing, additionally to introns.
Significance of introns
- Introns don't specify the synthesis of proteins but produce other important cellular activities.
- Many introns encode RNA that are major regulators of the organic phenomenon.
- This contains regulatory sequences that control transcription and mRNA processing.
- Introns allow exons to be joined in several combinations(alternative splicing), leading to the synthesis of various proteins from an equivalent gene.
- An important role in evolution by facilitating recombination between exons of various genes(exon shuffling).
Note:
Promotor
- A promoter may be a regulatory region of DNA located upstream controlling organic phenomenon .
- Core promoter – transcription start site(- 34) Binding site for RNA polymerase.
- Proximal promoter- contains the first regulatory element and approximately 250, specific transcription factor binding sites.
- Proximal promoter- contains primary regulatory element approximately - 250, specific transcription factor binding sites.
Complete step by step answer:
| Introns | Exons |
| An intron is any nucleotide sequence within a gene that's removed by RNA splicing to get the ultimate mature RNA product of a gene. | Unlike introns, exons are coding sections that remain within the mRNA sequence. |
| The term intron corresponds to both the DNA sequence within a gene and the corresponding sequence in RNA transcripts. | In the Eukaryotic gene, the coding sequence exon is separated by non- coding sequence introns. |
| The word intron springs from the term intragenic region, i.e. a neighbourhood inside a gene. Although introns are sometimes called intervening sequences. | In complex eukaryotes, introns account for quite 10 times the maximum amount of DNA as exons. |
| The intron distributions in 5’UTR, CDS and 3’UTR are different for the same organism. | Exon varies in number, sequence and length. A gene starts and ends with exons (5’ to 3’). Some exons include the untranslated (UTR) region. |

Additional Information:
- Introns sequences in nuclear protein- coding genes that are removed by spliceosomes.
- Introns are a comparatively recent arrival within the eukaryotic lineage that to assist generate the range of regulatory mechanisms that are required to regulate organic phenomenon in multicellular highly differentiated organisms.
- The term "intervening sequence" can ask any of several families of internal macromolecule sequences that aren't present within the final gene product, including inteins, untranslated sequences (UTR), and nucleotides removed by RNA editing, additionally to introns.
Significance of introns
- Introns don't specify the synthesis of proteins but produce other important cellular activities.
- Many introns encode RNA that are major regulators of the organic phenomenon.
- This contains regulatory sequences that control transcription and mRNA processing.
- Introns allow exons to be joined in several combinations(alternative splicing), leading to the synthesis of various proteins from an equivalent gene.
- An important role in evolution by facilitating recombination between exons of various genes(exon shuffling).
Note:
Promotor
- A promoter may be a regulatory region of DNA located upstream controlling organic phenomenon .
- Core promoter – transcription start site(- 34) Binding site for RNA polymerase.
- Proximal promoter- contains the first regulatory element and approximately 250, specific transcription factor binding sites.
- Proximal promoter- contains primary regulatory element approximately - 250, specific transcription factor binding sites.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

How is the angle of emergence e related to the angle class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between lanthanoids and actinoids class 12 chemistry CBSE

Derive Lens Makers formula for a convex lens class 12 physics CBSE

a Draw Labelled diagram of Standard Hydrogen Electrode class 12 chemistry CBSE




