
Develop reactions route to convert:
a. Propyne to Propanone
b. Methane to Ethane
Answer
522.5k+ views
Hint:The above reaction includes chlorination, dimerization of free radical and synthesization of ketones from alkynes. Ketones can be synthesized from alkenes, arenes and secondary alcohol.
Complete step by step solution:
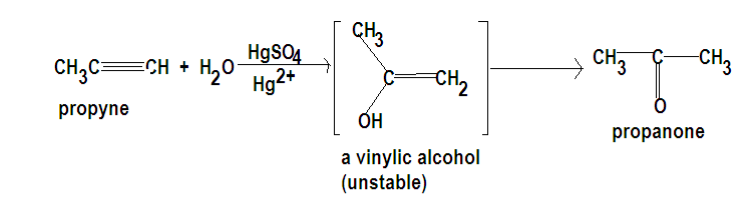
a. Let us therefore understand the reaction route for the conversion of the first reaction which includes conversion of an alkyne into a ketone .
Alkynes add water readily when the reaction is catalyzed by strong acids and mercuric ions. Aqueous solution of sulphuric acids and mercuric sulfate are often used for this purpose. The vinylic alcohol that is initially produced is usually unstable, and it rearranges rapidly to ketone (or in this case of Propyne, to Propanol). The rearrangement involves the loss of proton from the hydroxyl group, the addition of proton to the vicinal carbon atom, and the relocation of the double bond.
b. In the second reaction methane undergoes chlorination and we know that chlorination of methane can easily be controlled by judicious control of heat and light. It takes place by the attack of the chlorine free radical on methane and abstraction of its hydrogen to from HCl and methyl free radical which further reacts with di-chloride to form methyl chloride.
$
C{l_2} \to 2Cl ^{\cdot} \\
Cl ^{\cdot} + C{H_4} \to HCl + C{H_3} ^{\cdot} \\
C{H_3} + C{l_2} \to C{H_3}Cl + Cl ^{\cdot}
$
Now, we observe the formation of higher alkane i.e ethane as an end product, Therefore the formation of higher alkanes from alkyl halides in the presence of dry ether is named Wurtz reaction it goes on like:
$C{H_3}Cl\xrightarrow[{dryether(E{t_2}O)}]{{2Na}}C{H_3} - C{H_3} + 2NaCl$
In higher alkanes traces of alkenes and alkanes are forms due to dimerization and disproportionation. The whole reaction proceeds like:
$C{H_4} + C{l_2}\xrightarrow{{hv}}C{H_3}Cl + HCl\xrightarrow[{dryether(E{t_2}O)}]{{2Na}}C{H_3} - C{H_3} + 2NaCl$
Note:
Bromine is much less reactive towards methane than chlorine and iodine is so unreactive that for all practical purposes we can say that no reaction can take place. Wurtz reaction cannot prepare methane and gives best yield in case of symmetrical alkanes.
Complete step by step solution:
a. Let us therefore understand the reaction route for the conversion of the first reaction which includes conversion of an alkyne into a ketone .
Alkynes add water readily when the reaction is catalyzed by strong acids and mercuric ions. Aqueous solution of sulphuric acids and mercuric sulfate are often used for this purpose. The vinylic alcohol that is initially produced is usually unstable, and it rearranges rapidly to ketone (or in this case of Propyne, to Propanol). The rearrangement involves the loss of proton from the hydroxyl group, the addition of proton to the vicinal carbon atom, and the relocation of the double bond.

b. In the second reaction methane undergoes chlorination and we know that chlorination of methane can easily be controlled by judicious control of heat and light. It takes place by the attack of the chlorine free radical on methane and abstraction of its hydrogen to from HCl and methyl free radical which further reacts with di-chloride to form methyl chloride.
$
C{l_2} \to 2Cl ^{\cdot} \\
Cl ^{\cdot} + C{H_4} \to HCl + C{H_3} ^{\cdot} \\
C{H_3} + C{l_2} \to C{H_3}Cl + Cl ^{\cdot}
$
Now, we observe the formation of higher alkane i.e ethane as an end product, Therefore the formation of higher alkanes from alkyl halides in the presence of dry ether is named Wurtz reaction it goes on like:
$C{H_3}Cl\xrightarrow[{dryether(E{t_2}O)}]{{2Na}}C{H_3} - C{H_3} + 2NaCl$
In higher alkanes traces of alkenes and alkanes are forms due to dimerization and disproportionation. The whole reaction proceeds like:
$C{H_4} + C{l_2}\xrightarrow{{hv}}C{H_3}Cl + HCl\xrightarrow[{dryether(E{t_2}O)}]{{2Na}}C{H_3} - C{H_3} + 2NaCl$
Note:
Bromine is much less reactive towards methane than chlorine and iodine is so unreactive that for all practical purposes we can say that no reaction can take place. Wurtz reaction cannot prepare methane and gives best yield in case of symmetrical alkanes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




