
Determine the potential difference ${{V}_{A}}-{{V}_{B}}$ between points $A$ and $B$ of circuit shown in the figure. Under what condition is it equal to zero ?
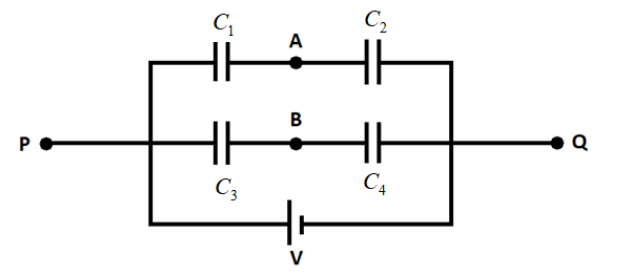

Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint: In order to find the solution of the above question, we will be using Kirchhoff’s Law. We will apply the Kirchhoff’s Law of loop and will derive the potential difference between the required points.
Complete step by step answer:
First of all, we will redraw the diagram which is given in the above question
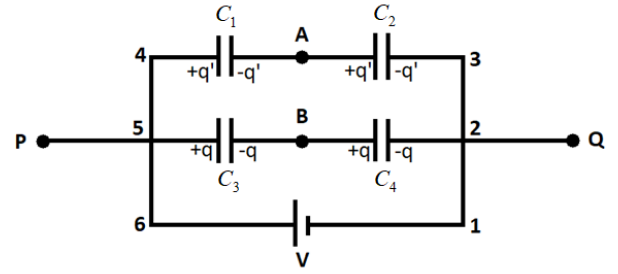
As we can see in the above drawn figure, we have mentioned the charge distribution across the capacitors. We also have labelled the loop with numbering. Now, as we know that the voltage across the capacitor is given by
$V=\dfrac{q}{C}$
Now, we use the Kirchhoff’s loop law for the loop \[12561\]
$V-{{V}_{{{C}_{4}}}}-{{V}_{{{C}_{3}}}}=0 \\
\Rightarrow V-\dfrac{q}{{{C}_{4}}}-\dfrac{q}{{{C}_{3}}}=0 \\
\Rightarrow V=q\left( \dfrac{1}{{{C}_{4}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{3}}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow q=\dfrac{V{{C}_{3}}{{C}_{4}}}{{{C}_{3}}+{{C}_{4}}} \\ $
Similarly, for the loop $13461$, we get
$V-{{V}_{{{C}_{2}}}}-{{V}_{{{C}_{1}}}}=0 \\
\Rightarrow V-\dfrac{q'}{{{C}_{2}}}-\dfrac{q'}{{{C}_{1}}}=0 \\
\Rightarrow V=q'\left( \dfrac{1}{{{C}_{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{1}}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow q'=\dfrac{V{{C}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}}{{{C}_{1}}+{{C}_{2}}} \\ $
Now, we want to find the voltage across point $A$ and $B$. Therefore, we will apply Kirchhoff's Law across these two points.
${{V}_{A}}-{{V}_{B}}=\dfrac{q'}{{{C}_{1}}}-\dfrac{q}{{{C}_{3}}} \\
\Rightarrow {{V}_{AB}}=V\left[ \dfrac{{{C}_{2}}}{{{C}_{1}}+{{C}_{2}}}-\dfrac{{{C}_{4}}}{{{C}_{3}}+{{C}_{4}}} \right] \\
\therefore {{V}_{AB}}=V\left[ \dfrac{{{C}_{2}}{{C}_{3}}-{{C}_{1}}{{C}_{4}}}{({{C}_{1}}+{{C}_{2}})({{C}_{3}}+{{C}_{4}})} \right] \\$
The above equation gives us the voltage difference between the required points.
Now, it is also asked in what condition does this value of potential difference shown in the above equation become zero. As we all know, for the value of the above equation to be zero, the value of the numerator must be equal to zero. Hence,
${{C}_{2}}{{C}_{3}}-{{C}_{1}}{{C}_{4}}=0 \\
\Rightarrow {{C}_{2}}{{C}_{3}}={{C}_{1}}{{C}_{4}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{C}_{1}}}{{{C}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{C}_{3}}}{{{C}_{4}}} \\ $
The above equation implies that the capacitors in the circuit should be balanced in order to make the value of the potential difference to be zero . Hence, the above circuit represents a similar construction to the Wheatstone bridge. The only change is that this circuit consists of capacitors in place of resistors.
Note: It is important to note that the potential difference can also be calculated using the capacitors ${{C}_{2}}$and ${{C}_{4}}$ instead of using the capacitors ${{C}_{1}}$ and ${{C}_{3}}$ as both of these combinations forms a circuit on either side of the points $A$ and $B$. It is also possible to make the value of this potential to be zero by taking out the battery from the circuit and draining the charge from the capacitors.
Complete step by step answer:
First of all, we will redraw the diagram which is given in the above question

As we can see in the above drawn figure, we have mentioned the charge distribution across the capacitors. We also have labelled the loop with numbering. Now, as we know that the voltage across the capacitor is given by
$V=\dfrac{q}{C}$
Now, we use the Kirchhoff’s loop law for the loop \[12561\]
$V-{{V}_{{{C}_{4}}}}-{{V}_{{{C}_{3}}}}=0 \\
\Rightarrow V-\dfrac{q}{{{C}_{4}}}-\dfrac{q}{{{C}_{3}}}=0 \\
\Rightarrow V=q\left( \dfrac{1}{{{C}_{4}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{3}}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow q=\dfrac{V{{C}_{3}}{{C}_{4}}}{{{C}_{3}}+{{C}_{4}}} \\ $
Similarly, for the loop $13461$, we get
$V-{{V}_{{{C}_{2}}}}-{{V}_{{{C}_{1}}}}=0 \\
\Rightarrow V-\dfrac{q'}{{{C}_{2}}}-\dfrac{q'}{{{C}_{1}}}=0 \\
\Rightarrow V=q'\left( \dfrac{1}{{{C}_{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{1}}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow q'=\dfrac{V{{C}_{1}}{{C}_{2}}}{{{C}_{1}}+{{C}_{2}}} \\ $
Now, we want to find the voltage across point $A$ and $B$. Therefore, we will apply Kirchhoff's Law across these two points.
${{V}_{A}}-{{V}_{B}}=\dfrac{q'}{{{C}_{1}}}-\dfrac{q}{{{C}_{3}}} \\
\Rightarrow {{V}_{AB}}=V\left[ \dfrac{{{C}_{2}}}{{{C}_{1}}+{{C}_{2}}}-\dfrac{{{C}_{4}}}{{{C}_{3}}+{{C}_{4}}} \right] \\
\therefore {{V}_{AB}}=V\left[ \dfrac{{{C}_{2}}{{C}_{3}}-{{C}_{1}}{{C}_{4}}}{({{C}_{1}}+{{C}_{2}})({{C}_{3}}+{{C}_{4}})} \right] \\$
The above equation gives us the voltage difference between the required points.
Now, it is also asked in what condition does this value of potential difference shown in the above equation become zero. As we all know, for the value of the above equation to be zero, the value of the numerator must be equal to zero. Hence,
${{C}_{2}}{{C}_{3}}-{{C}_{1}}{{C}_{4}}=0 \\
\Rightarrow {{C}_{2}}{{C}_{3}}={{C}_{1}}{{C}_{4}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{C}_{1}}}{{{C}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{C}_{3}}}{{{C}_{4}}} \\ $
The above equation implies that the capacitors in the circuit should be balanced in order to make the value of the potential difference to be zero . Hence, the above circuit represents a similar construction to the Wheatstone bridge. The only change is that this circuit consists of capacitors in place of resistors.
Note: It is important to note that the potential difference can also be calculated using the capacitors ${{C}_{2}}$and ${{C}_{4}}$ instead of using the capacitors ${{C}_{1}}$ and ${{C}_{3}}$ as both of these combinations forms a circuit on either side of the points $A$ and $B$. It is also possible to make the value of this potential to be zero by taking out the battery from the circuit and draining the charge from the capacitors.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




