
How do you determine the number of possible triangles and find the measure of the three angles given \[a=8,b=10,m\angle A=20\]?
Answer
555.9k+ views
Hint: From the question given, we have been asked to determine the number of possible triangles, and asked to find the measure of the three angles given \[a=8,b=10,m\angle A=20\]. Since the given information is for a SSA triangle. It is an ambiguous case. In the ambiguous case we first find the height by using the formula given as \[h=b\sin A\].
Complete step by step answer:
Now considering from the question we have been given the information stated as “ \[a=8,b=10,m\angle A=20\]” we need to find the number of possible triangles and the measure of the three triangles.
Since the given information is for a SSA triangle. It is an ambiguous case. In the ambiguous case we first find the height by using the formula given as \[h=b\sin A\].
By applying it here we will have \[h=10\sin {{20}^{0}}\approx 3.42\]
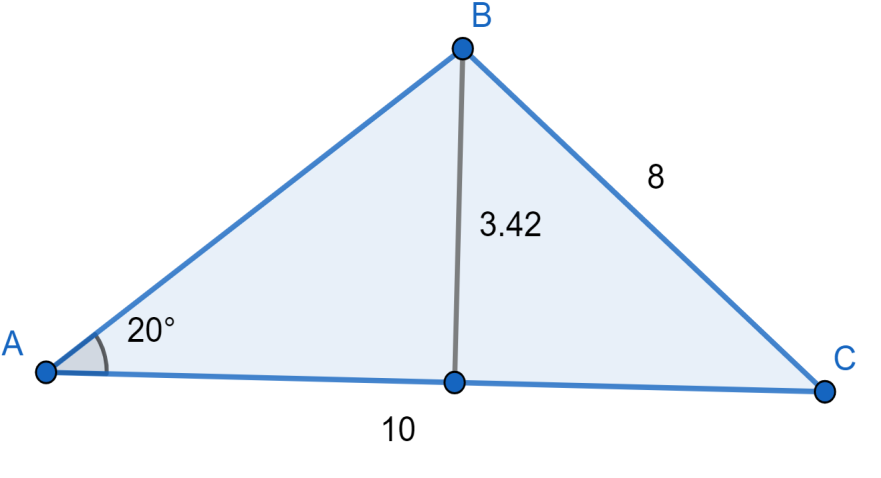
From the basic concept we know that \[A\]is the given angle and its side is always \[a\] so the other side will be \[b\].
So if \[A<{{90}^{0}}\] and if
Case 1:\[\text{ }hCase 2: \[hCase 3: \[\text{a}If \[A\ge {{90}^{0}}\] and if
Case 1: \[\text{ab}\] then there is one solution or one triangle.
Case 2: \[\text{a}\le \text{b}\] there is no solution.
Since \[3.42<8<10\] we have \[hNow, let us use the law of cosine given as \[{{a}^{2}}={{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}-2bc\cos A\] and the formulae for finding the solutions of any quadratic formula in the form of $a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0$ is given as \[x=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}\].
Hence we will have
\[{{a}^{2}}={{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}-2bc\cos A\]
\[\Rightarrow {{8}^{2}}={{10}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}-2\left( 10 \right)c\cos {{20}^{0}}\]
\[\Rightarrow 64=100+{{c}^{2}}-20c\cos {{20}^{0}}\]
\[\Rightarrow 0={{c}^{2}}-\left( 20\cos {{20}^{0}} \right)c+36\]
\[\Rightarrow c=\dfrac{\left( 20\cos {{20}^{0}} \right)\pm \sqrt{{{\left( -20\cos {{20}^{0}} \right)}^{2}}-4\left( 1 \right)\left( 36 \right)}}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow c=\dfrac{\left( 20\cos {{20}^{0}} \right)+\sqrt{{{\left( -20\cos {{20}^{0}} \right)}^{2}}-144}}{2}\] OR
\[\Rightarrow c=\dfrac{\left( 20\cos {{20}^{0}} \right)-\sqrt{{{\left( -20\cos {{20}^{0}} \right)}^{2}}-144}}{2}\]
By simplifying the above equation, we get \[{{c}_{1}}\approx 16.63\text{ or }{{\text{c}}_{2}}\approx 2.16\]
To find the measures of angle \[B\] we use the law of cosine and solve for \[B\]. That is \[\Rightarrow {{B}_{1}}={{\cos }^{-1}}\left[ \dfrac{{{8}^{2}}+c_{1}^{2}-{{10}^{2}}}{2.{{c}_{1}}.8} \right]={{25}^{0}}{{19}^{1}}\]
And therefore,
\[\Rightarrow {{C}_{1}}={{180}^{0}}-{{20}^{0}}-{{25}^{0}}{{19}^{1}}={{134}^{0}}{{41}^{1}}\]
and
\[\Rightarrow {{B}_{2}}={{\cos }^{-1}}\left[ \dfrac{{{8}^{2}}+c_{2}^{2}-{{10}^{2}}}{2.{{c}_{2}}.8} \right]={{154}^{0}}{{41}^{1}}\]
and
\[\Rightarrow {{C}_{2}}={{180}^{0}}-{{20}^{0}}-{{154}^{0}}{{41}^{1}}={{5}^{0}}{{19}^{1}}\]
Hence, the given angles are determined.
Note:
We should be very careful while applying the formula, we should be very careful while doing the calculation part. We should be well aware of the conditions of triangles and formulas for the law of cosine and quadratic formulas. We must know the importance and its application part very well. The cosine law states that the following three equations are valid they are : \[{{a}^{2}}={{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}-2bc\cos A\] , \[{{b}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}-2ac\cos B\] and \[{{c}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-2ab\cos C\] .
Complete step by step answer:
Now considering from the question we have been given the information stated as “ \[a=8,b=10,m\angle A=20\]” we need to find the number of possible triangles and the measure of the three triangles.
Since the given information is for a SSA triangle. It is an ambiguous case. In the ambiguous case we first find the height by using the formula given as \[h=b\sin A\].
By applying it here we will have \[h=10\sin {{20}^{0}}\approx 3.42\]

From the basic concept we know that \[A\]is the given angle and its side is always \[a\] so the other side will be \[b\].
So if \[A<{{90}^{0}}\] and if
Case 1:\[\text{ }h
Case 1: \[\text{ab}\] then there is one solution or one triangle.
Case 2: \[\text{a}\le \text{b}\] there is no solution.
Since \[3.42<8<10\] we have \[h
Hence we will have
\[{{a}^{2}}={{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}-2bc\cos A\]
\[\Rightarrow {{8}^{2}}={{10}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}-2\left( 10 \right)c\cos {{20}^{0}}\]
\[\Rightarrow 64=100+{{c}^{2}}-20c\cos {{20}^{0}}\]
\[\Rightarrow 0={{c}^{2}}-\left( 20\cos {{20}^{0}} \right)c+36\]
\[\Rightarrow c=\dfrac{\left( 20\cos {{20}^{0}} \right)\pm \sqrt{{{\left( -20\cos {{20}^{0}} \right)}^{2}}-4\left( 1 \right)\left( 36 \right)}}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow c=\dfrac{\left( 20\cos {{20}^{0}} \right)+\sqrt{{{\left( -20\cos {{20}^{0}} \right)}^{2}}-144}}{2}\] OR
\[\Rightarrow c=\dfrac{\left( 20\cos {{20}^{0}} \right)-\sqrt{{{\left( -20\cos {{20}^{0}} \right)}^{2}}-144}}{2}\]
By simplifying the above equation, we get \[{{c}_{1}}\approx 16.63\text{ or }{{\text{c}}_{2}}\approx 2.16\]
To find the measures of angle \[B\] we use the law of cosine and solve for \[B\]. That is \[\Rightarrow {{B}_{1}}={{\cos }^{-1}}\left[ \dfrac{{{8}^{2}}+c_{1}^{2}-{{10}^{2}}}{2.{{c}_{1}}.8} \right]={{25}^{0}}{{19}^{1}}\]
And therefore,
\[\Rightarrow {{C}_{1}}={{180}^{0}}-{{20}^{0}}-{{25}^{0}}{{19}^{1}}={{134}^{0}}{{41}^{1}}\]
and
\[\Rightarrow {{B}_{2}}={{\cos }^{-1}}\left[ \dfrac{{{8}^{2}}+c_{2}^{2}-{{10}^{2}}}{2.{{c}_{2}}.8} \right]={{154}^{0}}{{41}^{1}}\]
and
\[\Rightarrow {{C}_{2}}={{180}^{0}}-{{20}^{0}}-{{154}^{0}}{{41}^{1}}={{5}^{0}}{{19}^{1}}\]
Hence, the given angles are determined.
Note:
We should be very careful while applying the formula, we should be very careful while doing the calculation part. We should be well aware of the conditions of triangles and formulas for the law of cosine and quadratic formulas. We must know the importance and its application part very well. The cosine law states that the following three equations are valid they are : \[{{a}^{2}}={{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}-2bc\cos A\] , \[{{b}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}-2ac\cos B\] and \[{{c}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-2ab\cos C\] .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a labelled diagram of the human heart and label class 11 biology CBSE

What is 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p class 11 chemistry CBSE




