
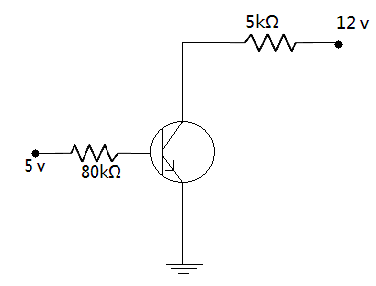
Determine the minimum value of current gain $\beta $ (up to nearest integer) required to put the transistor in saturation when ${V_{BB}} = + 5\,V$ . Assume that in saturation state, ${V_{BE}} = 0.8\,V$ and ${V_{CE}} = 0.12\,V$.

Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: In this problem we need to find the value of current gain. Current gain is the ratio of the collector current to the base current. In order to find the collector current and the base current, apply Kirchhoff’s voltage law in the base-emitter loop and in the collector loop.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us understand current gain and voltage gain first. The current gain in the common-base configuration is defined as the change in collector current divided by the change in emitter current, when base-to-collector voltage is constant. Similarly, the voltage gain for the common base amplifier is the ratio of output voltage to the input voltage.
Let ${I_B}$ and ${I_C}$ be base current and collector current respectively, taking $ + 5V$ as input voltage ${V_{in}}$ , the summation of voltages in the base-emitter loop gives
$8 \times {10^3} \times {I_B} + {V_{BE}} - 5V = 0$
We assume that the transistor is in saturation, this implies
${V_{BE}} = {V_{BE(sat)}} = 0.8V$
$ \Rightarrow 8 \times {10^3} \times {I_B} + 0.8V - 5V = 0$
$$ \Rightarrow {I_B} = \dfrac{{4.2V}}{{80 \times {{10}^3}}} = 0.0525mA$$ --equation $$1$$
The base current is $$0.0525mA$$
Applying Kirchhoff’s voltage law in the collector loop, we have
$$ \Rightarrow 5 \times {10^3} \times {I_C} + {V_{CE}} - 12\,V = 0$$
We assume that the transistor is in saturation, this implies
${V_{CE}} = {V_{CE(sat)}} = 0.12V$
Substituting this value in the above equation, we get
$$ \Rightarrow 5 \times {10^3} \times {I_C} + 0.12V - 12\,V = 0$$
$$ \Rightarrow {I_C} = \dfrac{{12 - 0.12}}{{5 \times {{10}^3}}} = 2.376mA$$
The emitter current is $$2.376mA$$
The current gain is given as
$\beta = \dfrac{{{I_c}}}{{{I_B}}}$
Substituting the values, we get
$$\beta = \dfrac{{2.376}}{{0.0525}} \approx 45.25$$
The minimum value of current gain $\beta $ (up to nearest integer) is $$45$$.
Note: In saturation mode, the transistor acts like a short circuit between the collector and the emitter. In saturation mode both the diodes in the transistor are forward biased. Be careful of the sign conventions when applying Kirchhoff’s voltage law. Remember that the current gain is the ratio of the collector current to the base current.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us understand current gain and voltage gain first. The current gain in the common-base configuration is defined as the change in collector current divided by the change in emitter current, when base-to-collector voltage is constant. Similarly, the voltage gain for the common base amplifier is the ratio of output voltage to the input voltage.
Let ${I_B}$ and ${I_C}$ be base current and collector current respectively, taking $ + 5V$ as input voltage ${V_{in}}$ , the summation of voltages in the base-emitter loop gives
$8 \times {10^3} \times {I_B} + {V_{BE}} - 5V = 0$
We assume that the transistor is in saturation, this implies
${V_{BE}} = {V_{BE(sat)}} = 0.8V$
$ \Rightarrow 8 \times {10^3} \times {I_B} + 0.8V - 5V = 0$
$$ \Rightarrow {I_B} = \dfrac{{4.2V}}{{80 \times {{10}^3}}} = 0.0525mA$$ --equation $$1$$
The base current is $$0.0525mA$$
Applying Kirchhoff’s voltage law in the collector loop, we have
$$ \Rightarrow 5 \times {10^3} \times {I_C} + {V_{CE}} - 12\,V = 0$$
We assume that the transistor is in saturation, this implies
${V_{CE}} = {V_{CE(sat)}} = 0.12V$
Substituting this value in the above equation, we get
$$ \Rightarrow 5 \times {10^3} \times {I_C} + 0.12V - 12\,V = 0$$
$$ \Rightarrow {I_C} = \dfrac{{12 - 0.12}}{{5 \times {{10}^3}}} = 2.376mA$$
The emitter current is $$2.376mA$$
The current gain is given as
$\beta = \dfrac{{{I_c}}}{{{I_B}}}$
Substituting the values, we get
$$\beta = \dfrac{{2.376}}{{0.0525}} \approx 45.25$$
The minimum value of current gain $\beta $ (up to nearest integer) is $$45$$.
Note: In saturation mode, the transistor acts like a short circuit between the collector and the emitter. In saturation mode both the diodes in the transistor are forward biased. Be careful of the sign conventions when applying Kirchhoff’s voltage law. Remember that the current gain is the ratio of the collector current to the base current.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




