
Determine the focal length of convex lens on the following points by describing the displacement method:
i) Derivation of Formula
ii)Draw a ray diagram
iii)Observation table
iv) Precautions (any 2)
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: Let there be two pins placed. Then, find out the distance of the object and then find the distance of the image. Now, use the lens equation,$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u}$
Now, put the values of distance of image and object respectively in the above lens equation. From this, find out the focal length of the lens.
Complete step by step Solution:
(i) Formula Derivation: Let there be two pins $AB$ and $CD$respectively placed such that the distance between both of them is more than $uf$.
When the lens is at $L$then, let the image formed be $A'B'$on pin $CD$
$
\therefore OA = u \\
OA' = v \\
d = v + u \cdots (1) \\
$
The image is again formed on $CD$ because $A$ and $A'$ are conjugate foci. This happens in the second position of ${L_2}$
$
O'A' = u \\
O'A = v \\
$
Let the displacement of the lens be $x$. Therefore,
$x = v - u \cdots (2)$
Using the value of $v$ from equation $(1)$in equation $(2)$we get,
$u = \dfrac{{d - x}}{2}$
Similarly, using the value of $u$ from equation $(1)$in equation $(2)$we get,
$v = \dfrac{{d + x}}{2}$
We know that, the lens formula is
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u}$
Where, $f = $focal length, $u = $object distance and $v = $image distance
Putting the values of $v$and $u$in lens formula
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{{\dfrac{{d + x}}{2}}} - \dfrac{1}{{\dfrac{{d - x}}{2}}}$
According to the sign convention, $u$will be positive and $v$is negative.
$
\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{{\dfrac{{\left( {d + x} \right)}}{2}}} - \dfrac{1}{{ - \dfrac{{\left( {d - x} \right)}}{2}}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{\dfrac{{d + x}}{2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{\dfrac{{d - x}}{2}}} \\
\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{2}{{d + x}} + \dfrac{2}{{d - x}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{2d - 2x + 2d + 2x}}{{(d + x)(d - x)}} \\
\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{{4d}}{{{d^2} - {x^2}}} \\
f = \dfrac{{{d^2} - {x^2}}}{{4d}} \\
$
This is the required formula.
(ii) Ray diagram: The ray diagram can be made as
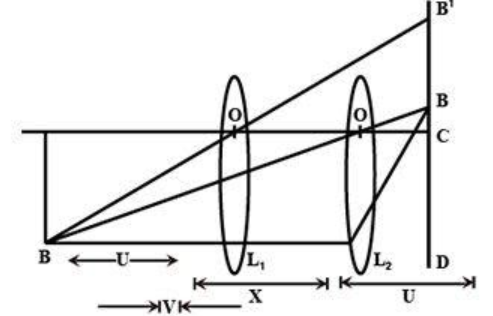
(iii) Observation Table
(iv)Precautions: The line which joins the tip of pins and optical centre should lie on a horizontal line.
The distance between pins should be greater than 4 times of focal length.
Note: The focal length of lens should be four times less than the distance between two pins.
When using the lens formula, keep in mind the sign convention of distance of object, distance of image and focal length.
Now, put the values of distance of image and object respectively in the above lens equation. From this, find out the focal length of the lens.
Complete step by step Solution:
(i) Formula Derivation: Let there be two pins $AB$ and $CD$respectively placed such that the distance between both of them is more than $uf$.
When the lens is at $L$then, let the image formed be $A'B'$on pin $CD$
$
\therefore OA = u \\
OA' = v \\
d = v + u \cdots (1) \\
$
The image is again formed on $CD$ because $A$ and $A'$ are conjugate foci. This happens in the second position of ${L_2}$
$
O'A' = u \\
O'A = v \\
$
Let the displacement of the lens be $x$. Therefore,
$x = v - u \cdots (2)$
Using the value of $v$ from equation $(1)$in equation $(2)$we get,
$u = \dfrac{{d - x}}{2}$
Similarly, using the value of $u$ from equation $(1)$in equation $(2)$we get,
$v = \dfrac{{d + x}}{2}$
We know that, the lens formula is
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u}$
Where, $f = $focal length, $u = $object distance and $v = $image distance
Putting the values of $v$and $u$in lens formula
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{{\dfrac{{d + x}}{2}}} - \dfrac{1}{{\dfrac{{d - x}}{2}}}$
According to the sign convention, $u$will be positive and $v$is negative.
$
\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{{\dfrac{{\left( {d + x} \right)}}{2}}} - \dfrac{1}{{ - \dfrac{{\left( {d - x} \right)}}{2}}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{\dfrac{{d + x}}{2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{\dfrac{{d - x}}{2}}} \\
\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{2}{{d + x}} + \dfrac{2}{{d - x}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{2d - 2x + 2d + 2x}}{{(d + x)(d - x)}} \\
\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{{4d}}{{{d^2} - {x^2}}} \\
f = \dfrac{{{d^2} - {x^2}}}{{4d}} \\
$
This is the required formula.
(ii) Ray diagram: The ray diagram can be made as

(iii) Observation Table
| Position of object pin | Position of image pin | 1st position of lens | 2nd position of lens | Distance between pins | Displacement of lens | $f $ |
| $a cm$ | $b cm$ | $m cm$ | $n cm$ | $d = b - a$ | $x = n - m$ | $\dfrac{{{d^2} - {x^2}}}{{ud}}cm$ |
(iv)Precautions: The line which joins the tip of pins and optical centre should lie on a horizontal line.
The distance between pins should be greater than 4 times of focal length.
Note: The focal length of lens should be four times less than the distance between two pins.
When using the lens formula, keep in mind the sign convention of distance of object, distance of image and focal length.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




